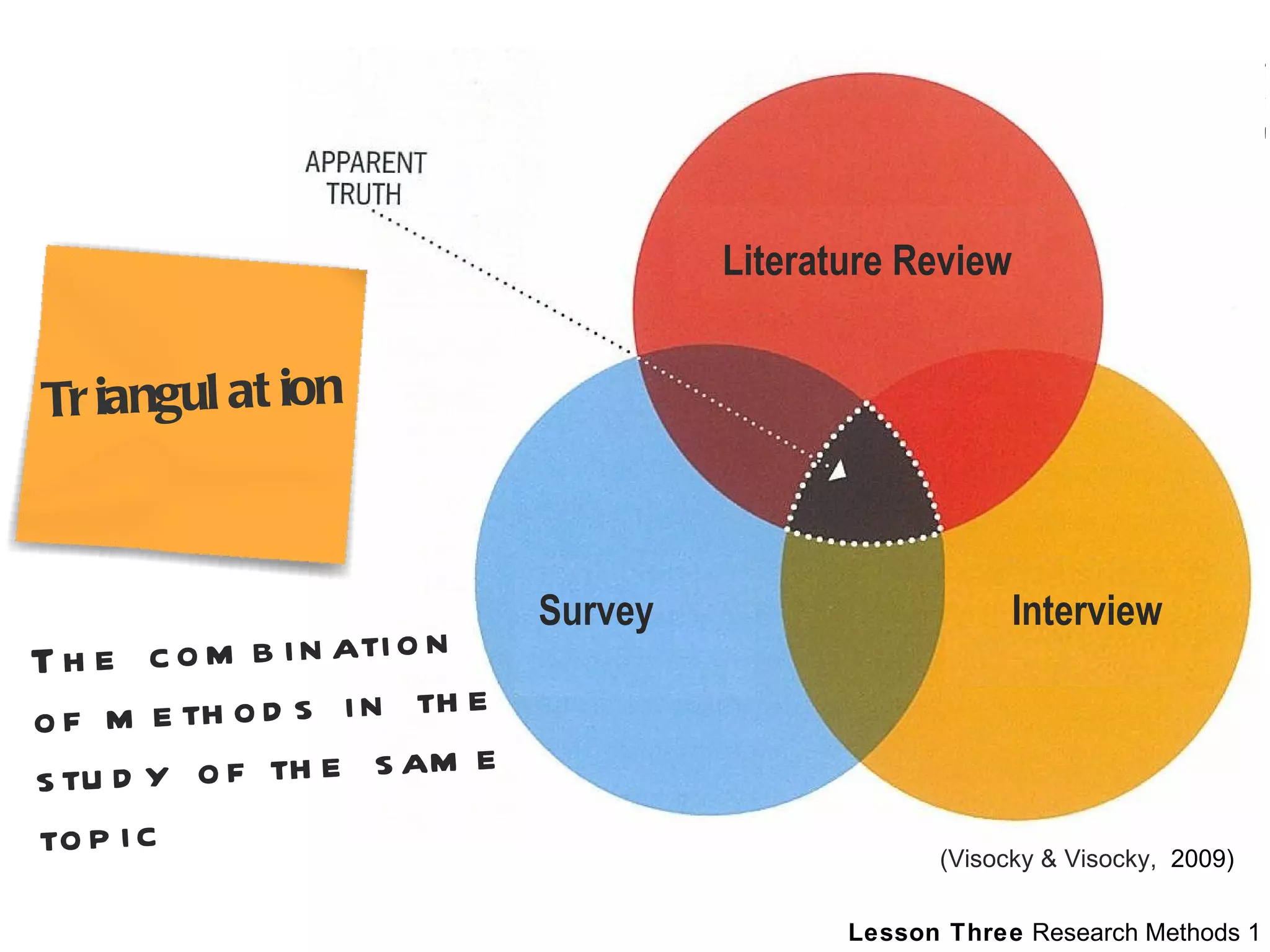
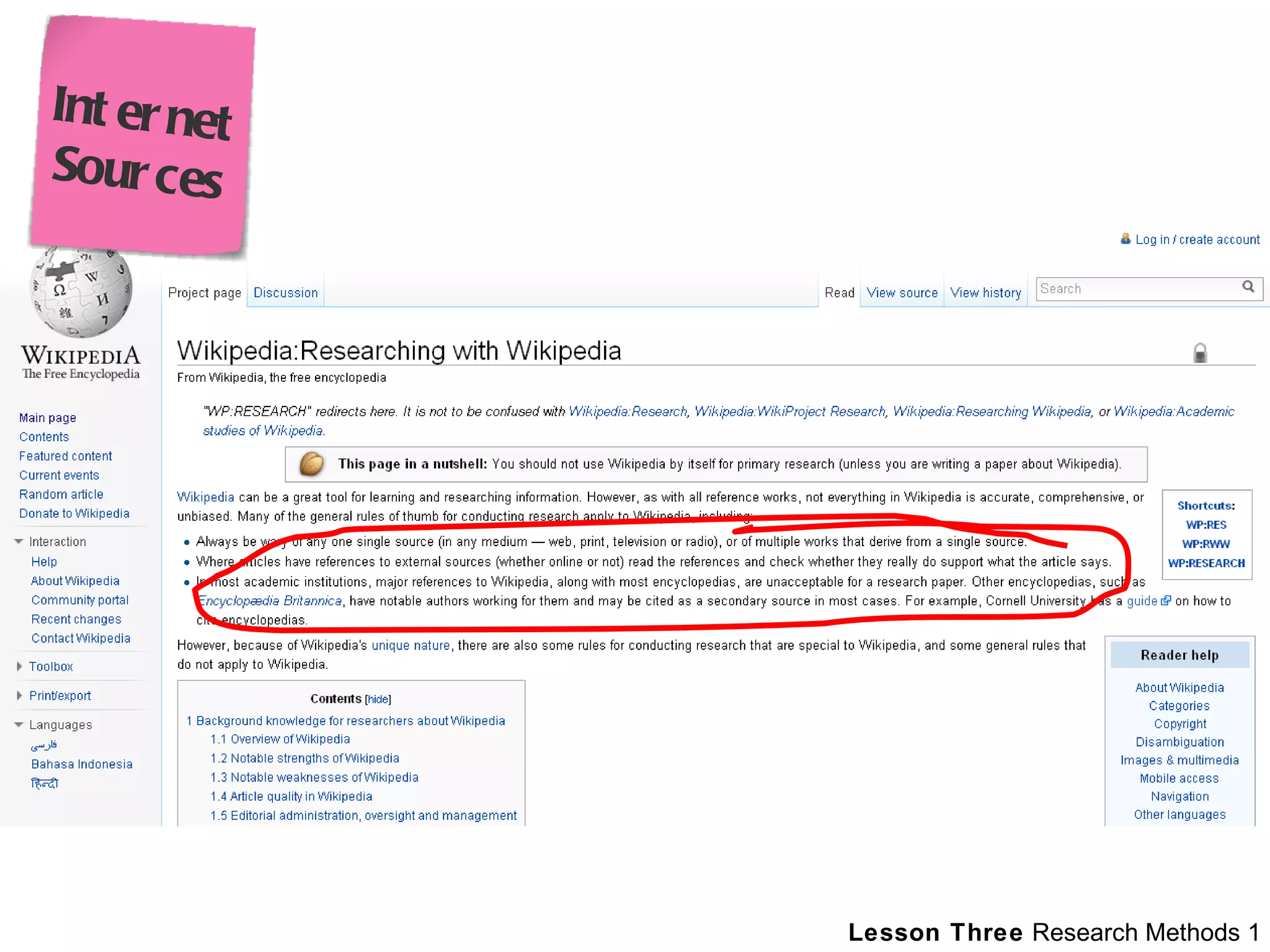
This document outlines a lesson plan on research methods. It discusses the key differences between primary and secondary research approaches and sources. It also distinguishes between quantitative and qualitative research methods. The document provides guidance on evaluating secondary sources and discusses appropriate uses of internet sources for research. It provides examples of exercises for students to apply their learning, involving conducting research to address topics related to fashion, marketing, design, and architecture.