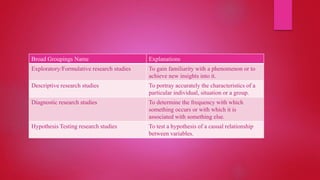
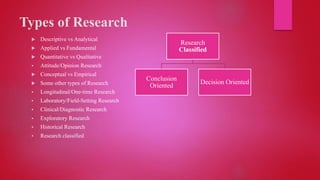
This document defines research and outlines different types of research methodologies. It discusses research as a systematic process of inquiry aimed at discovering and interpreting facts. The document then describes various research objectives, including defining problems, formulating hypotheses, collecting and analyzing data, and testing conclusions. It also outlines different categories of research such as descriptive vs analytical, applied vs fundamental, quantitative vs qualitative, conceptual vs empirical, and longitudinal vs one-time research. Finally, the document discusses factors that motivate research and different orientations of research like conclusion-oriented vs decision-oriented.