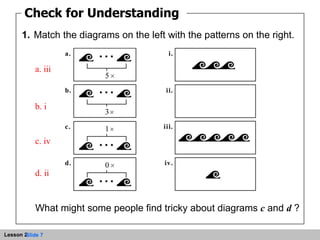
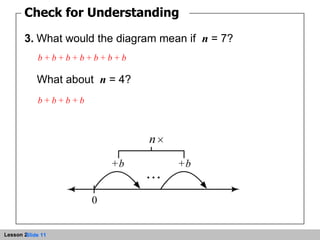
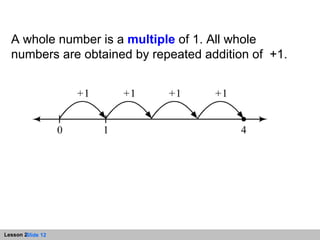
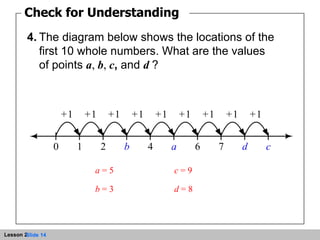
This document discusses representing whole numbers and addition on a number line. It provides examples of using number lines to show repeated addition and multiples. Students are asked to write expressions for repeated addition diagrams, identify values on sample number lines, and write equations corresponding to diagrams. The objectives are to represent repeated addition on the number line, represent whole numbers on the number line, and add whole numbers on the number line.