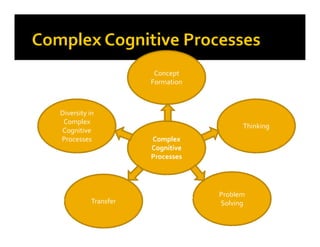
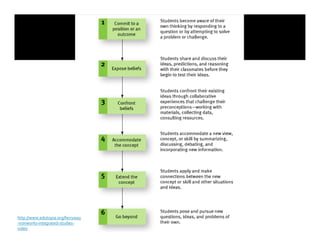
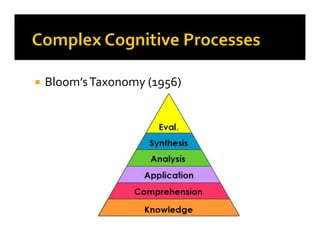
1. The document discusses strategies for addressing diversity in the classroom and facilitating complex cognitive processes in students. It outlines techniques for helping students overcome misconceptions like cognitive conflict, ensuring new concepts make sense and are useful, and using models like hypothesis-experiment-instruction.
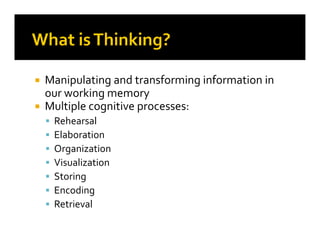
2. The document also discusses multiple cognitive processes involved in learning like encoding, retrieval, and different types of thinking. It analyzes techniques for creativity, critical thinking, and problem solving.
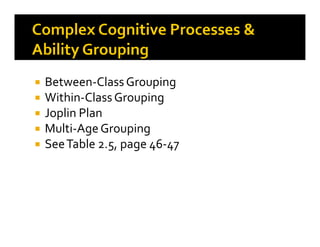
3. Best practices for grouping students discussed include pre-assessing, differentiating instruction, and holding high expectations while avoiding negative labels.