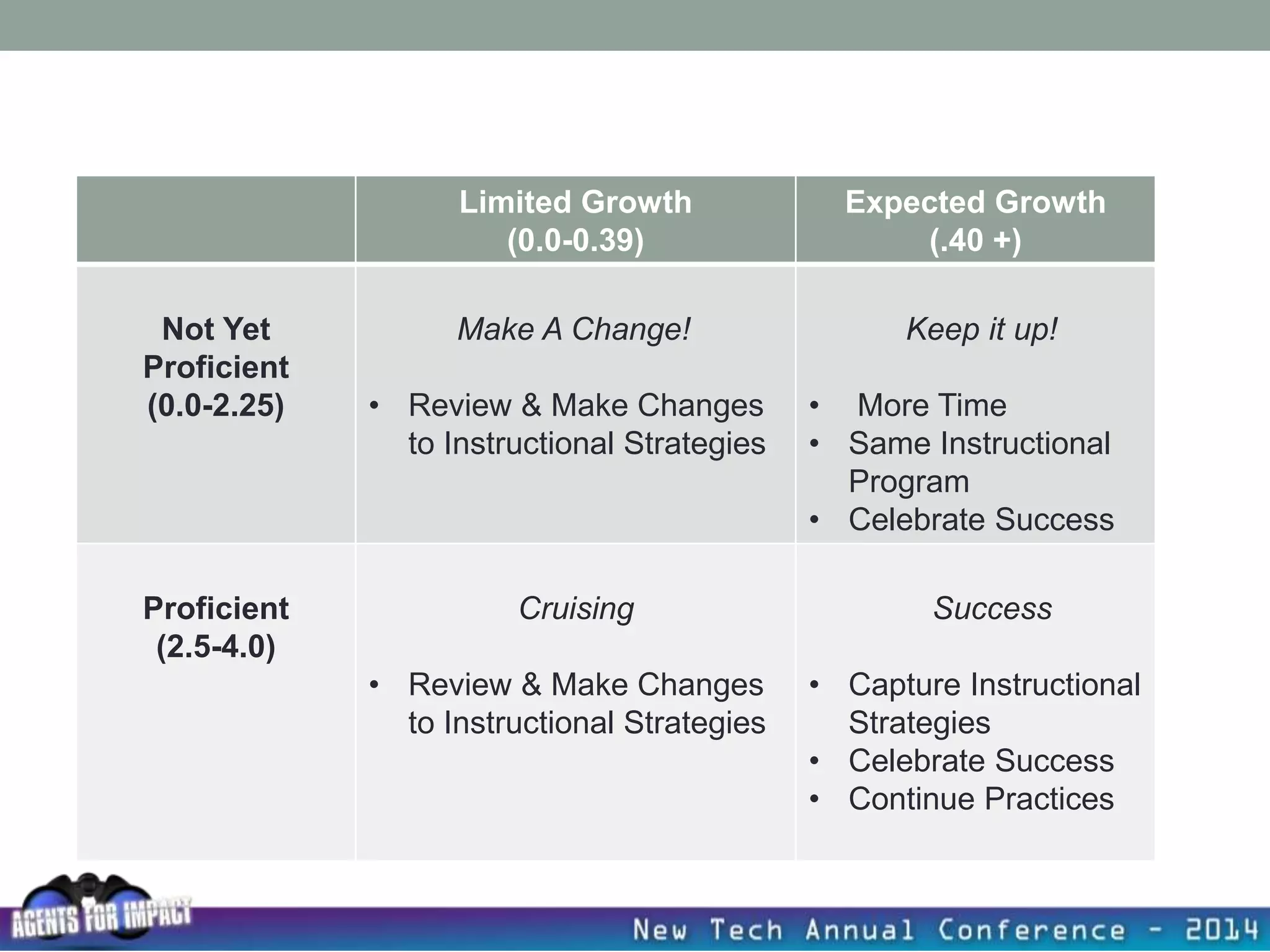
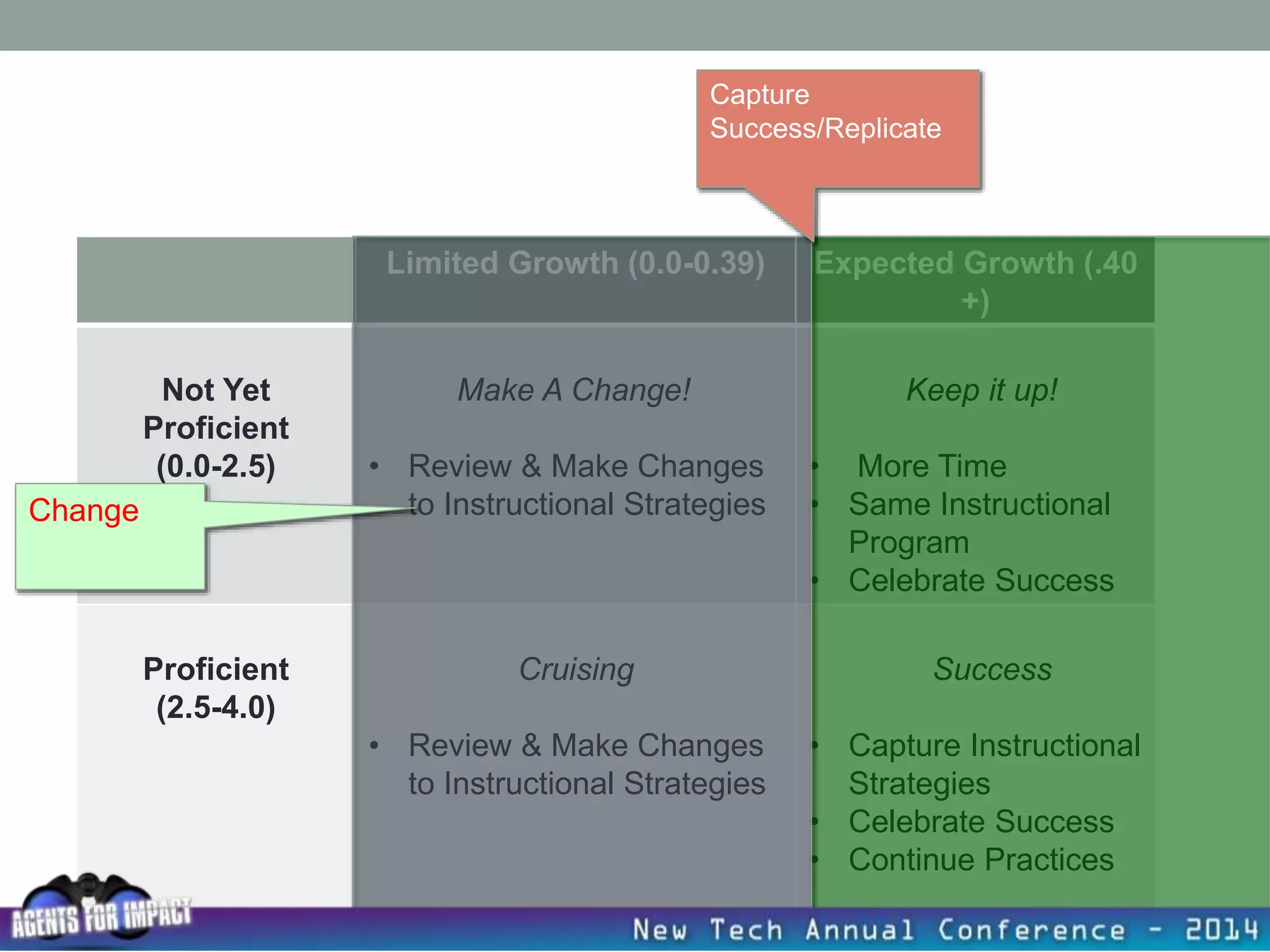
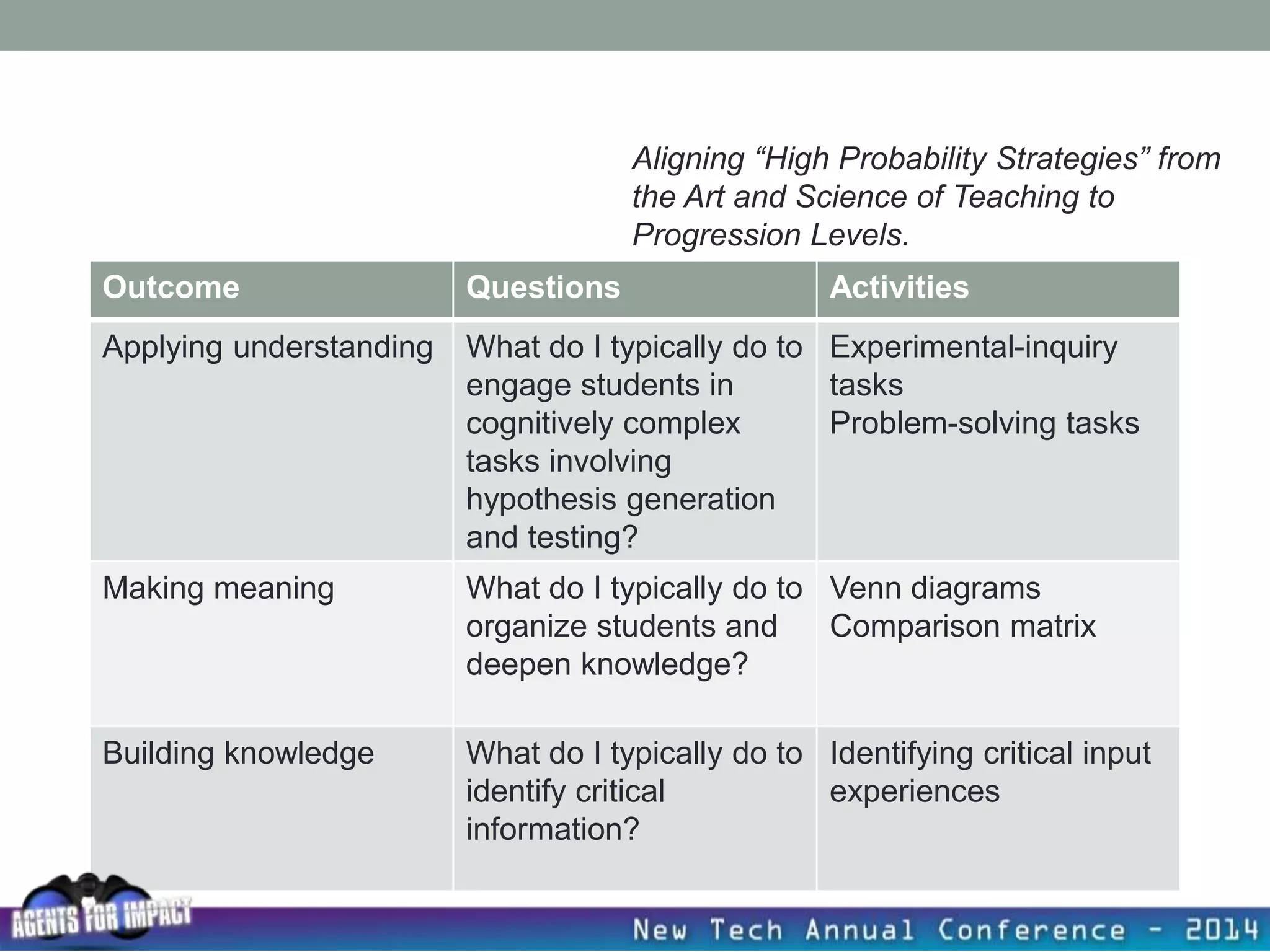
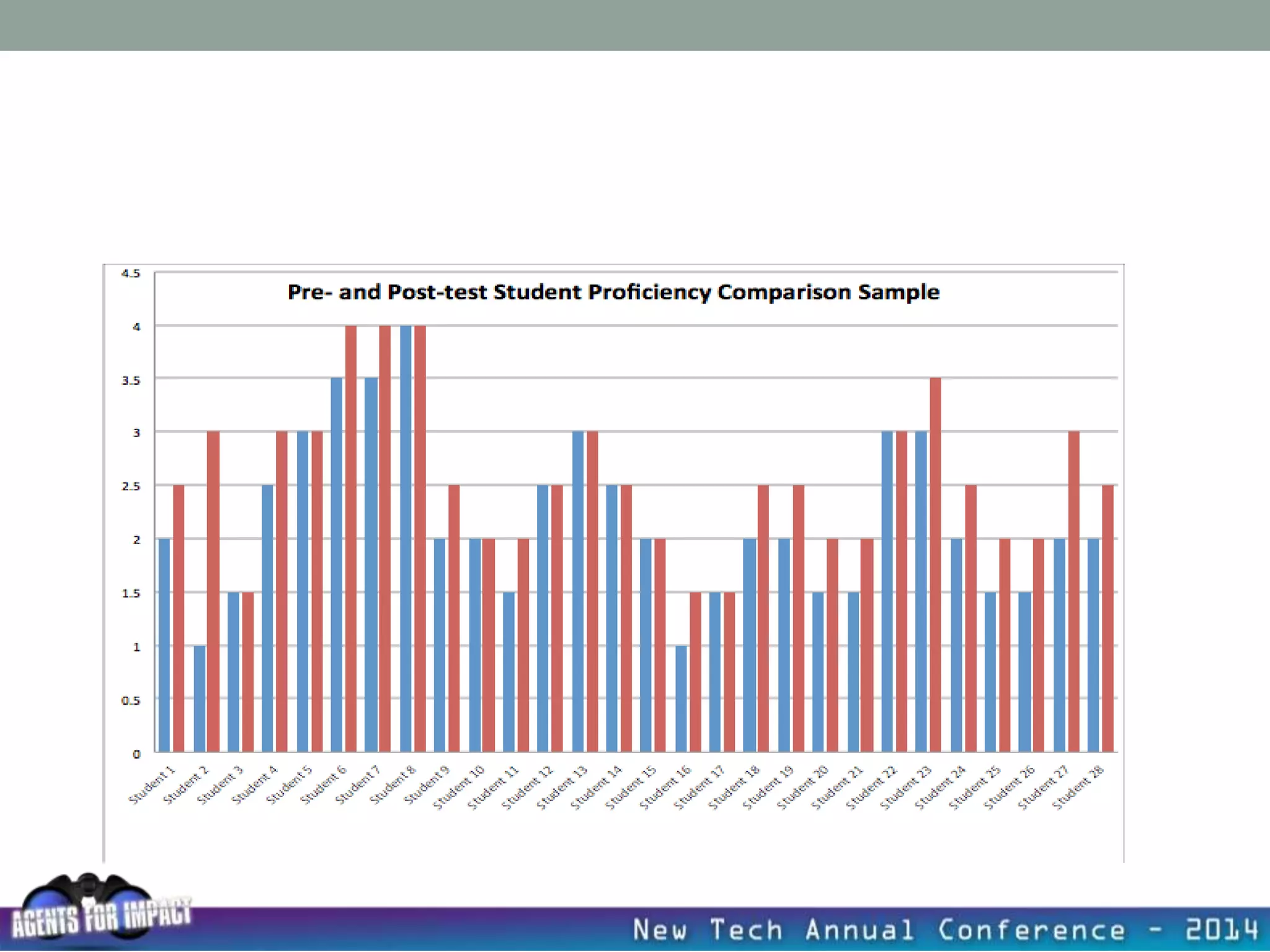
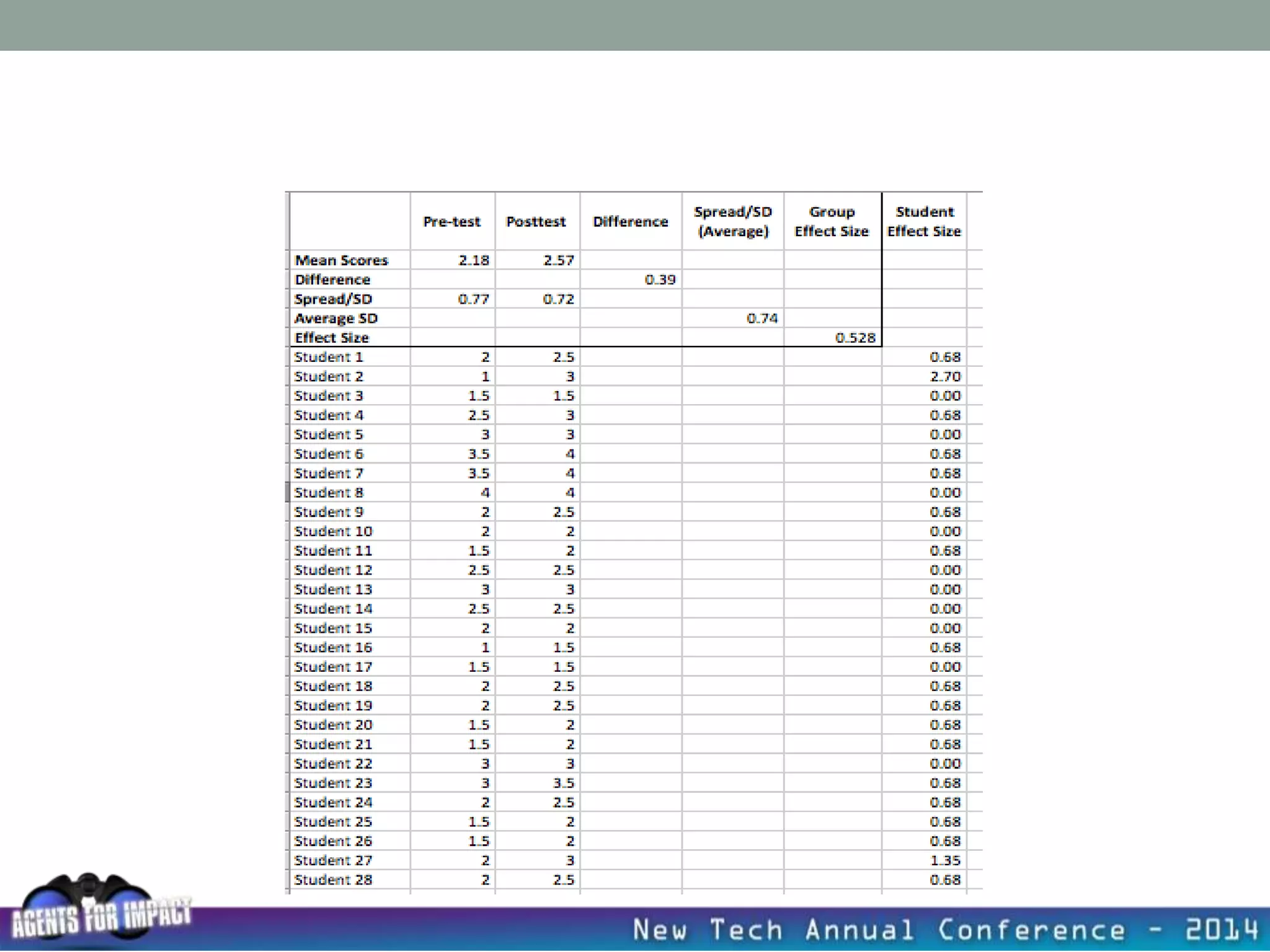
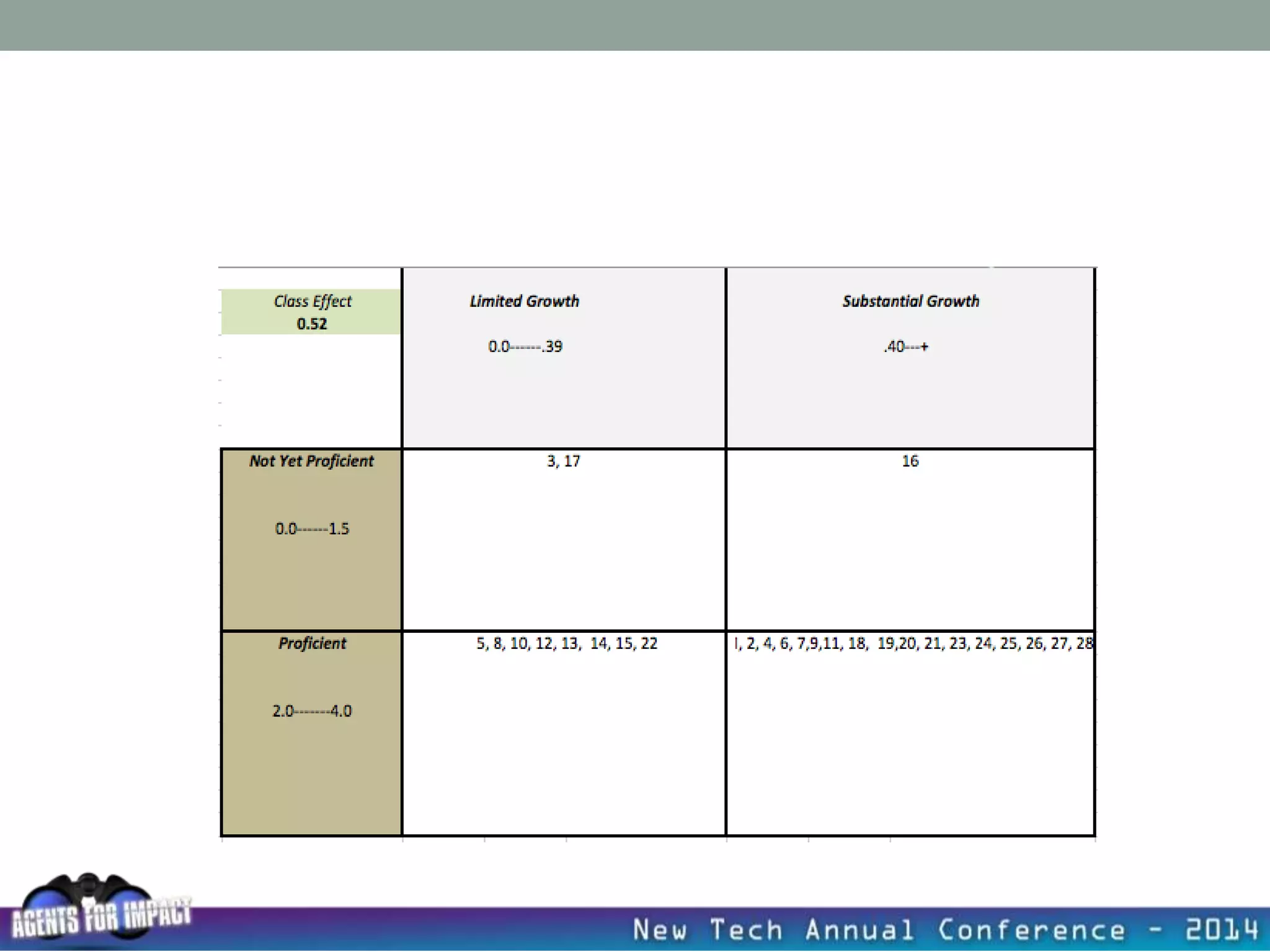
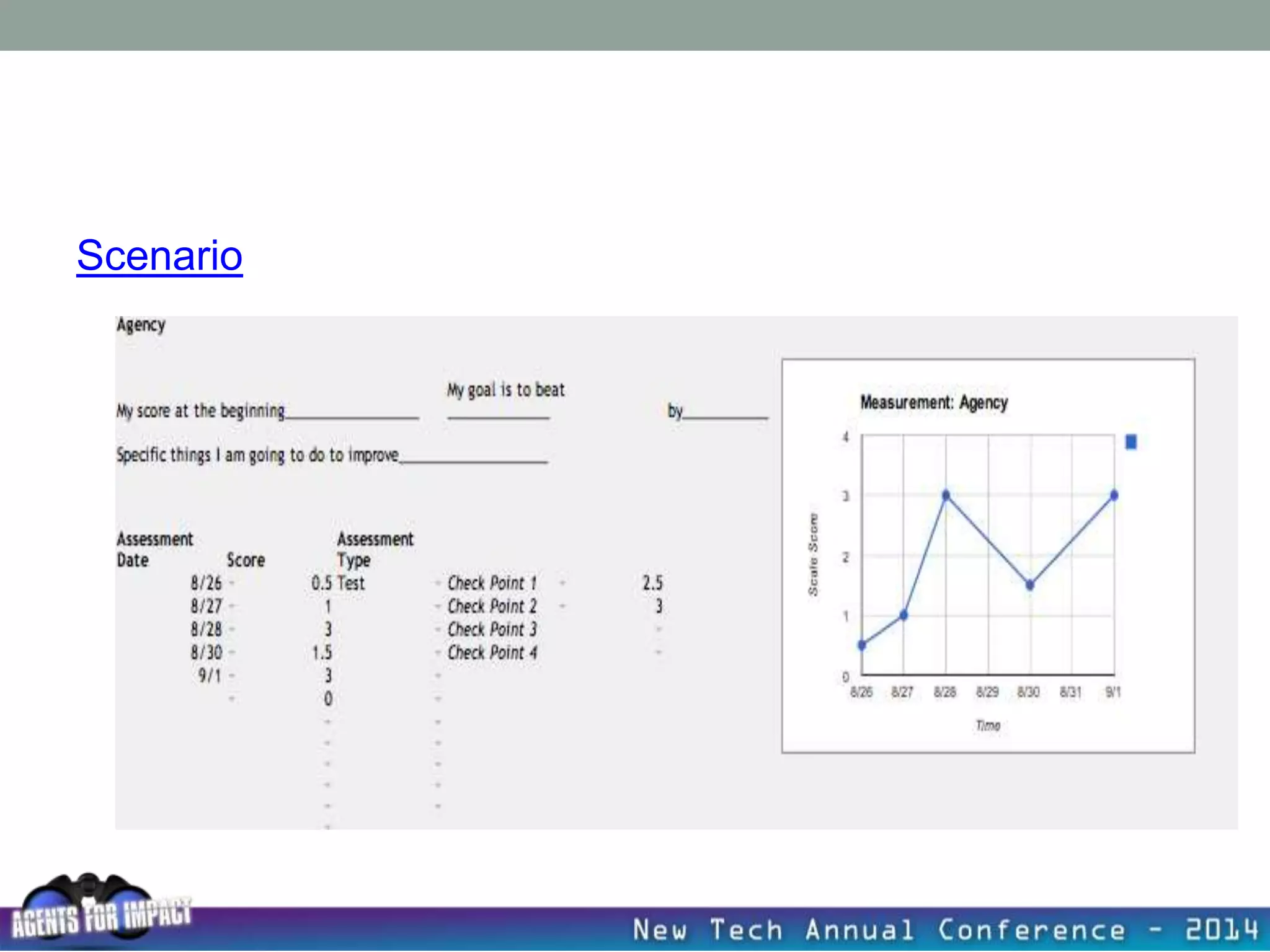
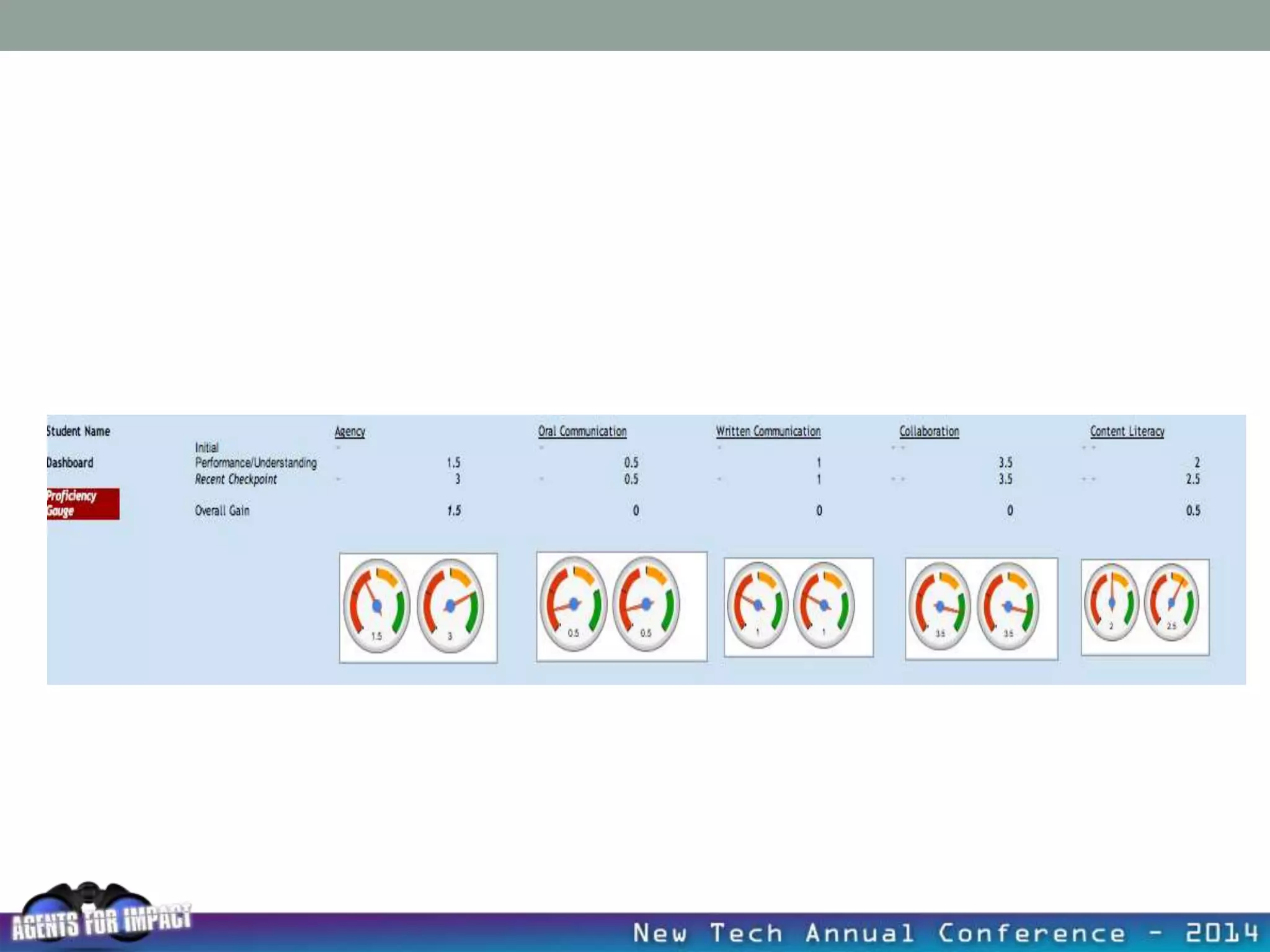
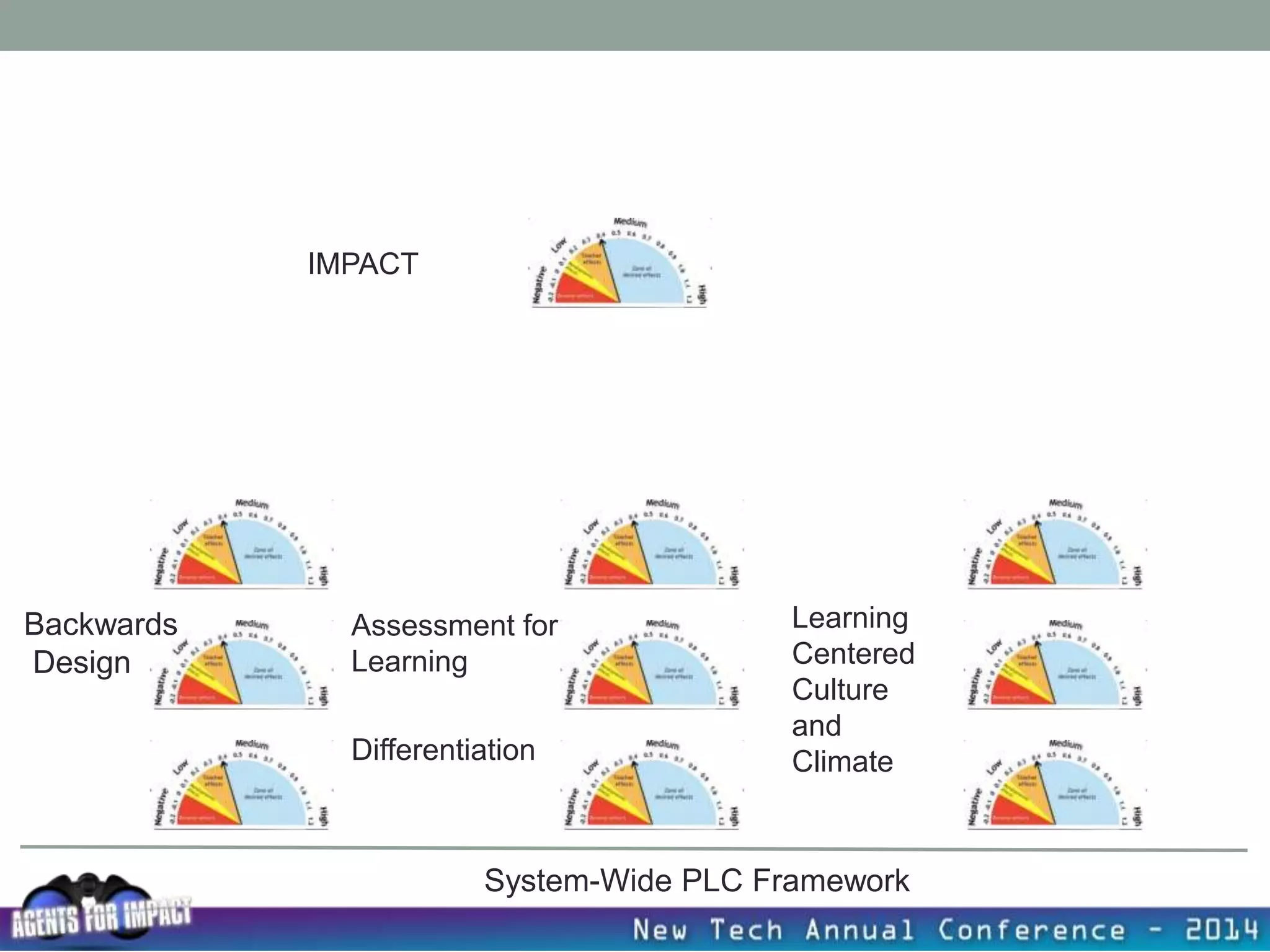
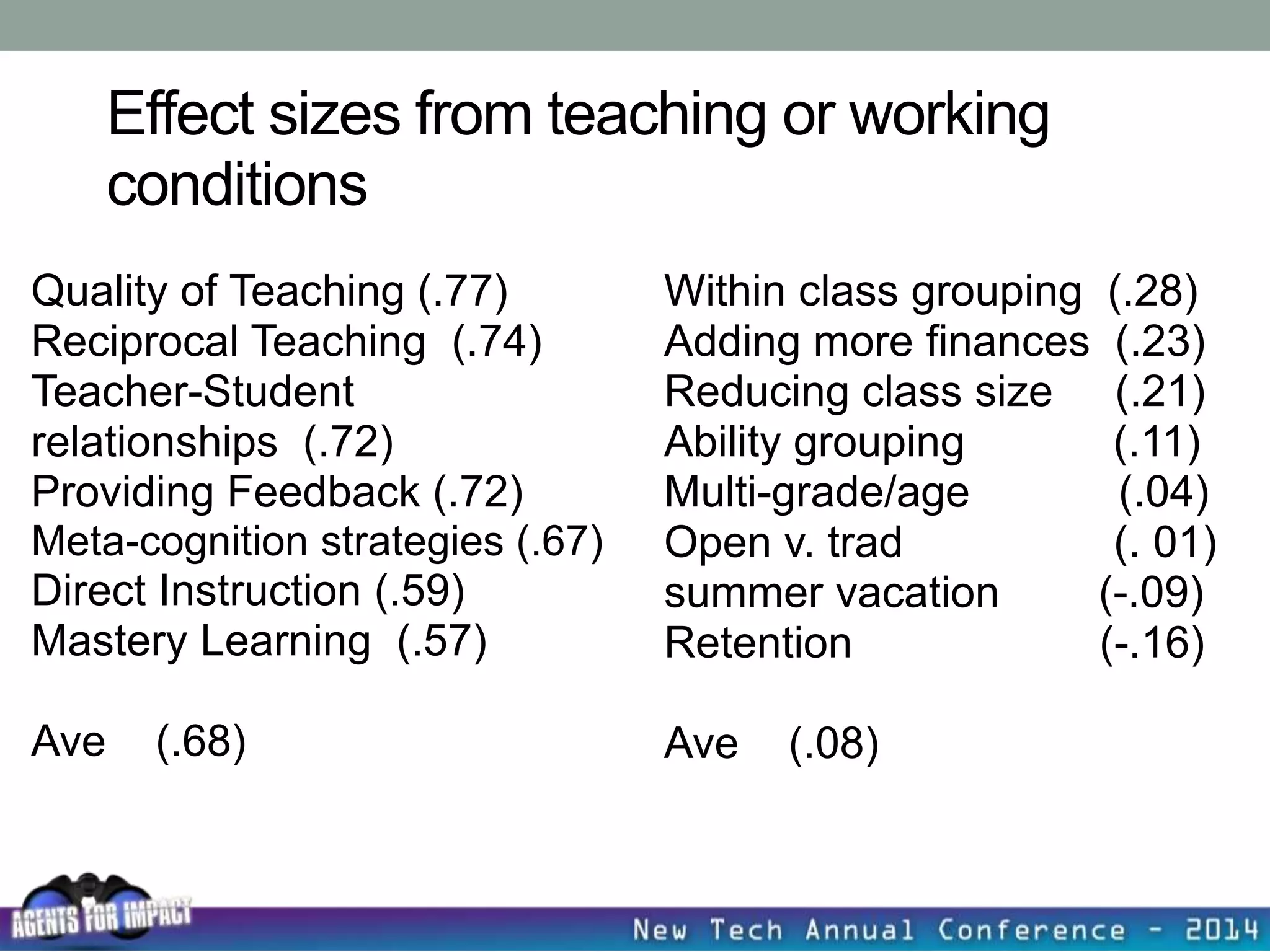
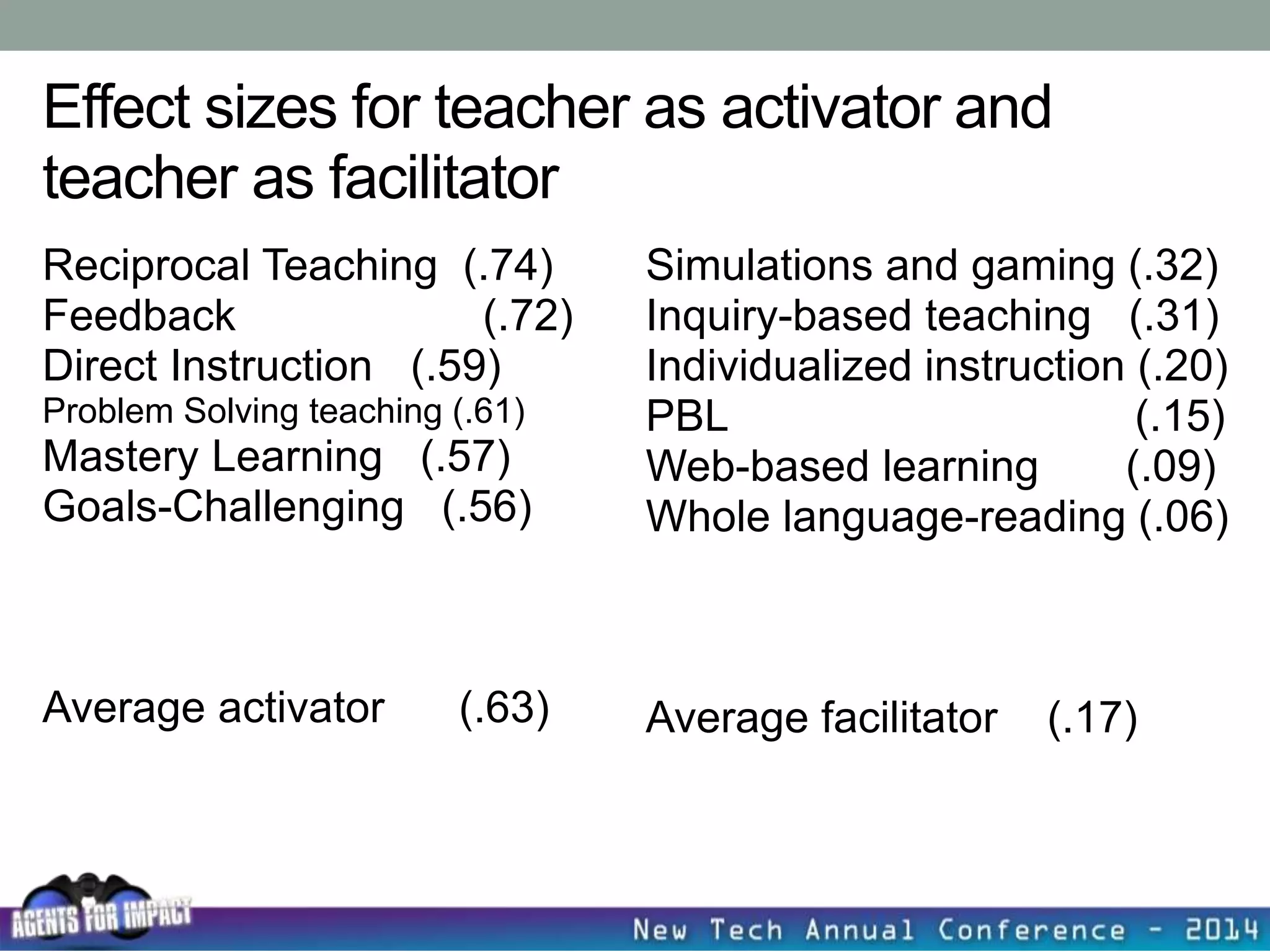
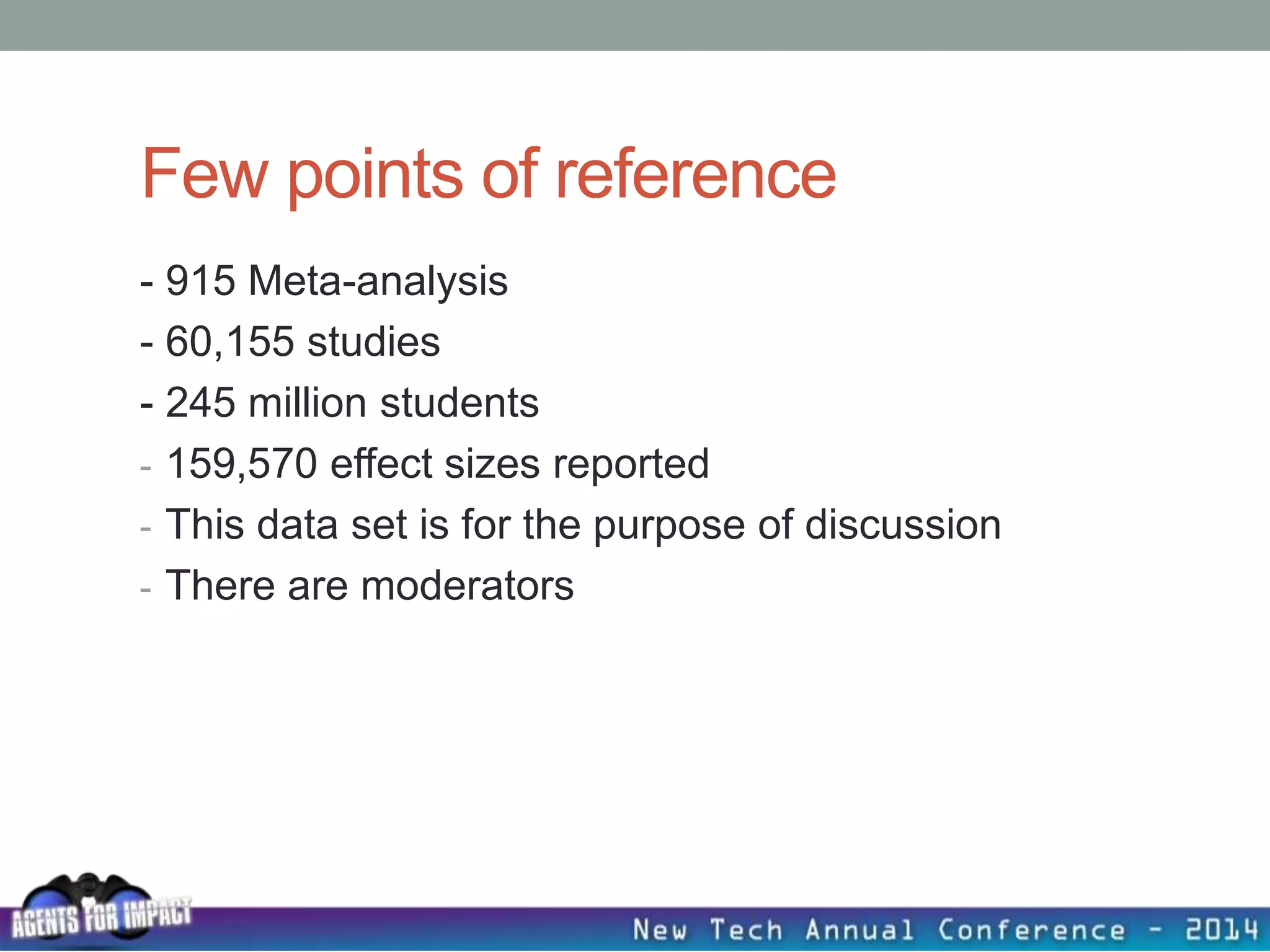
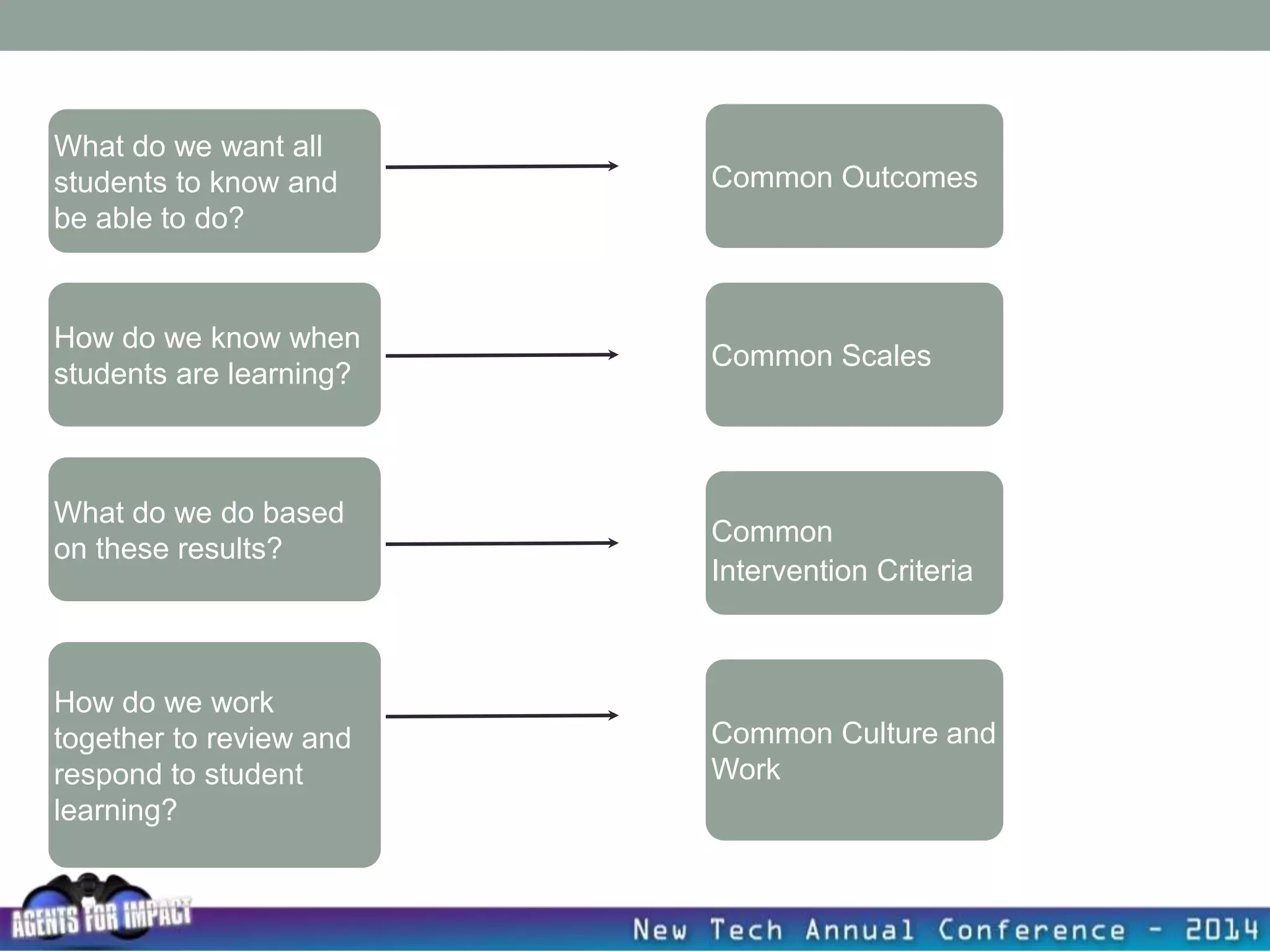
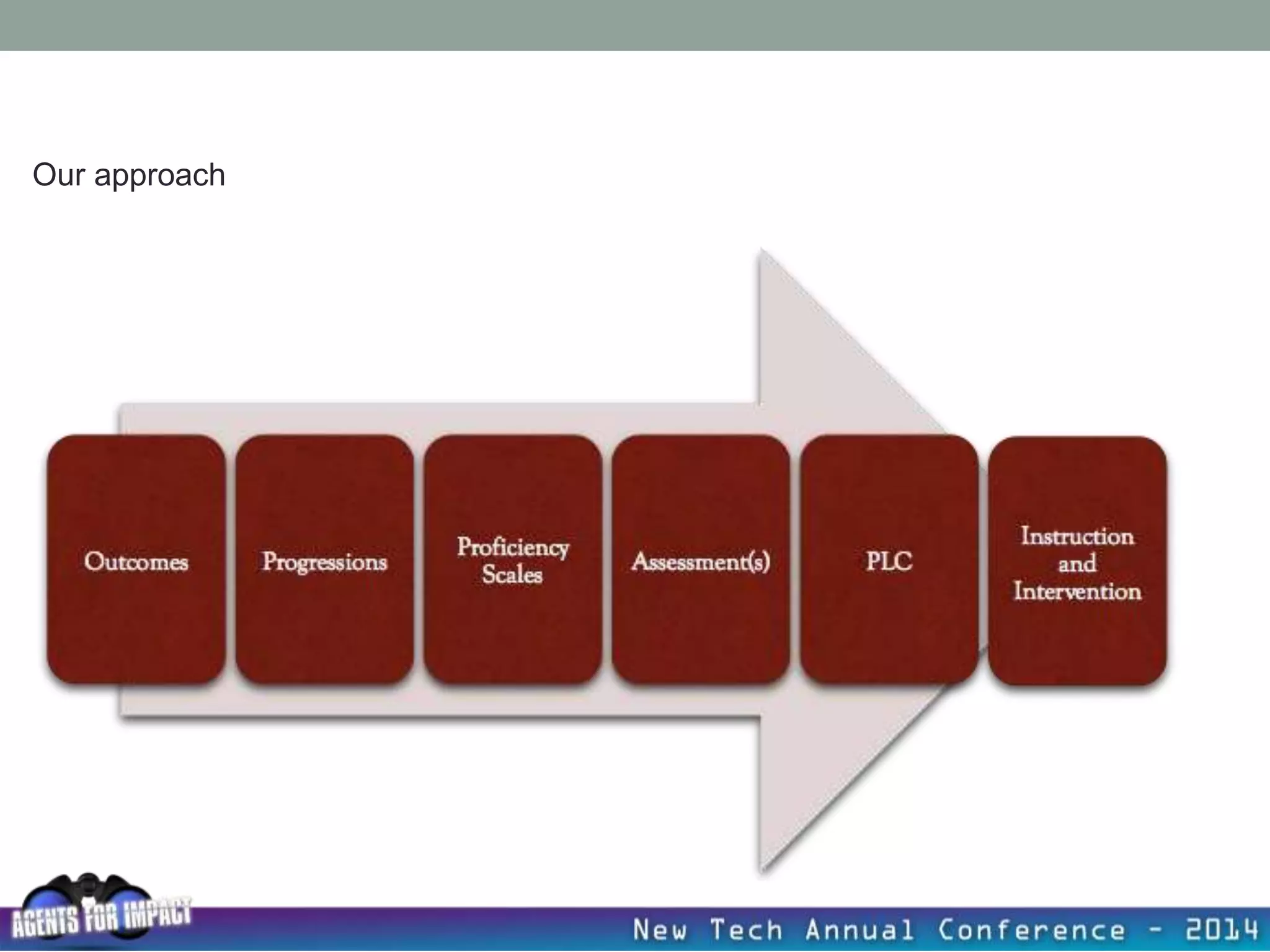
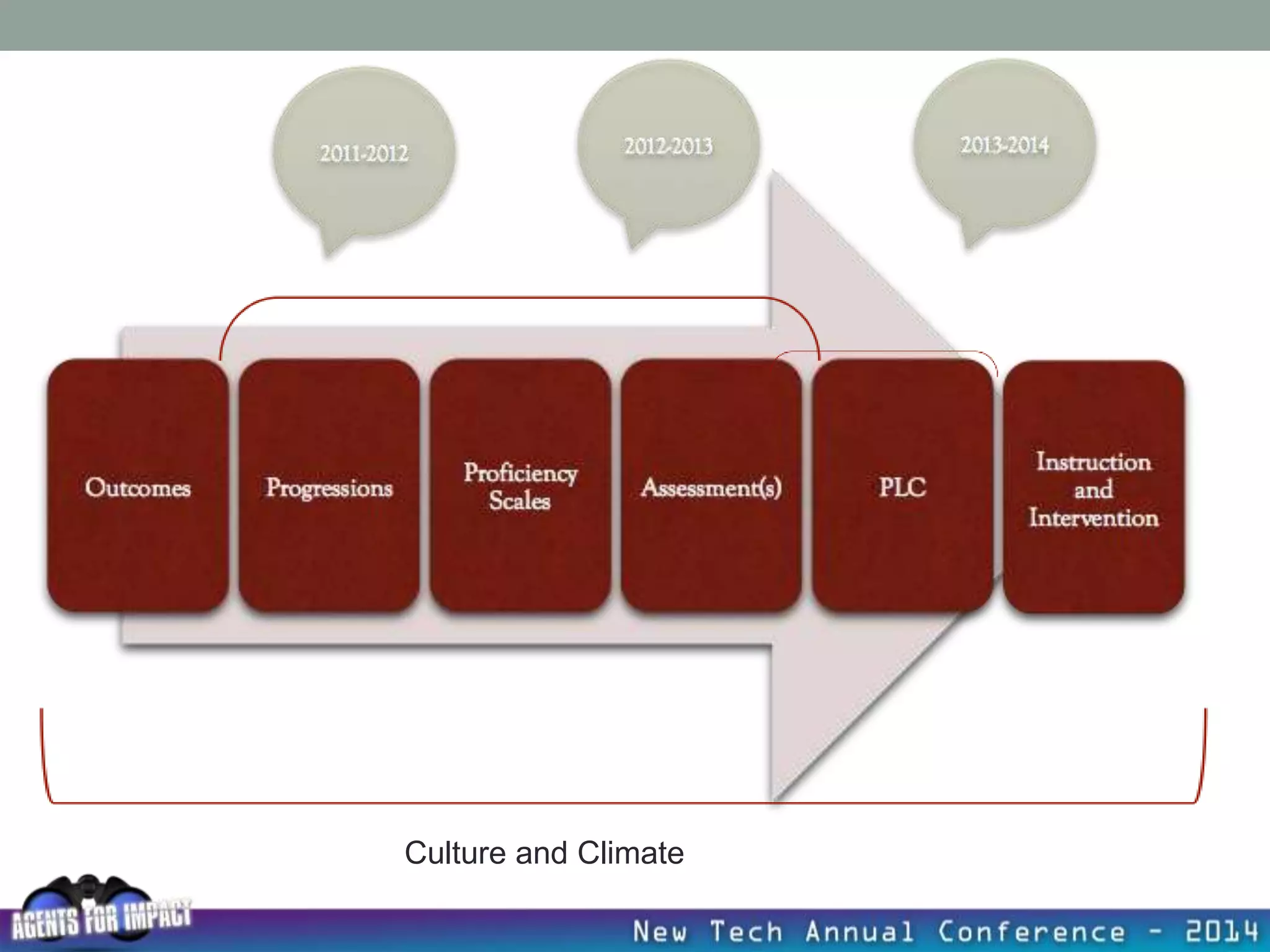
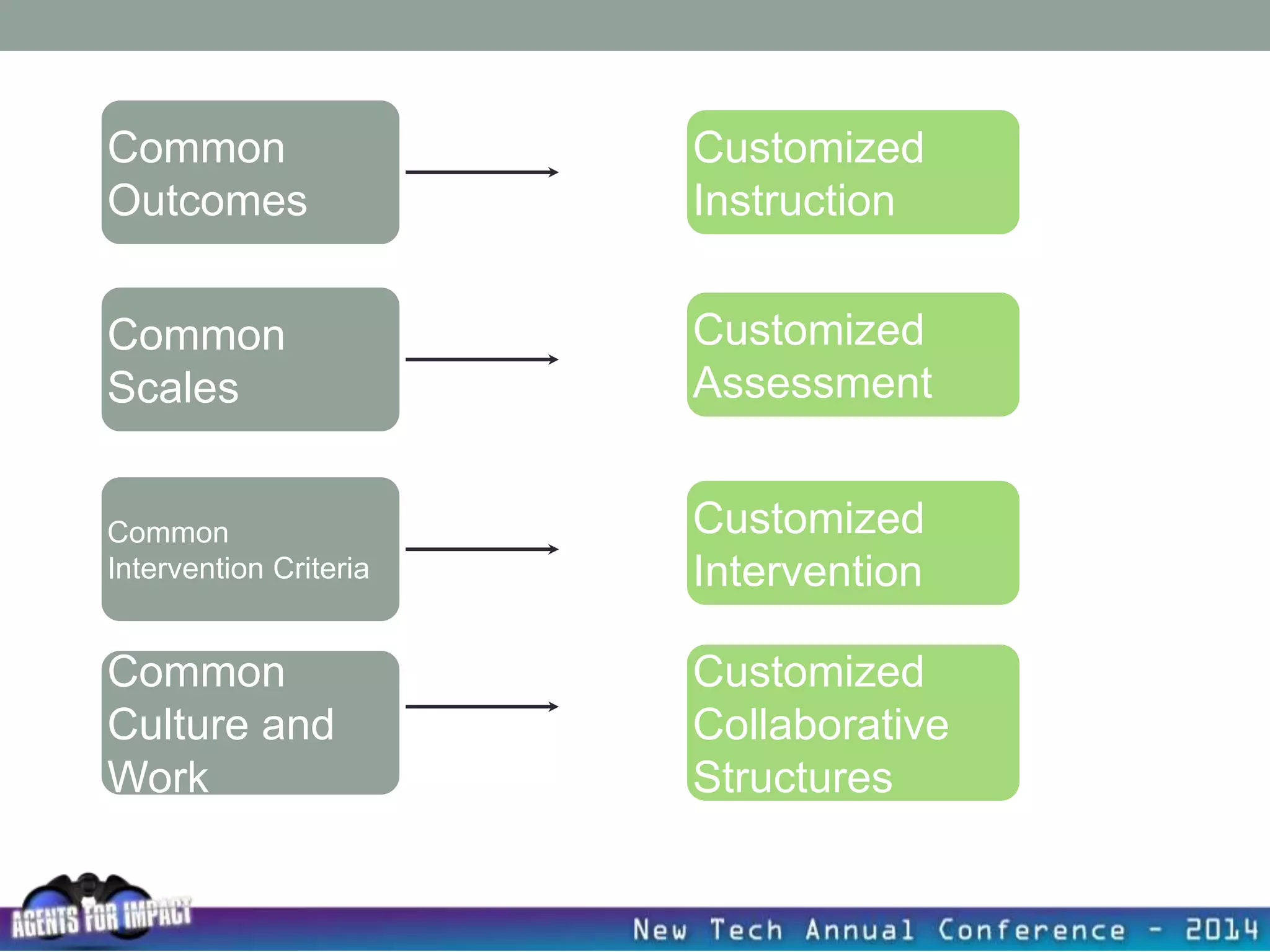
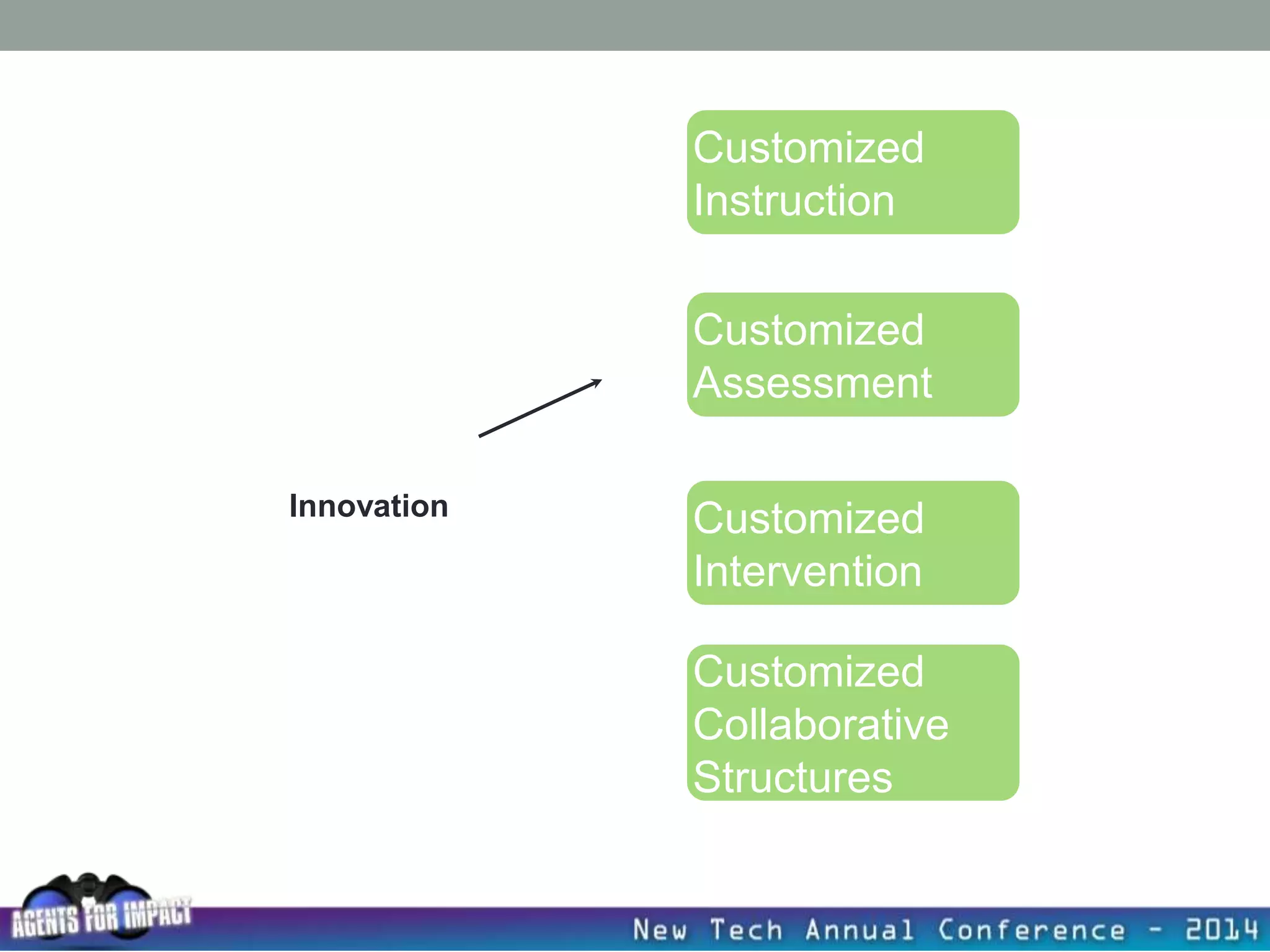
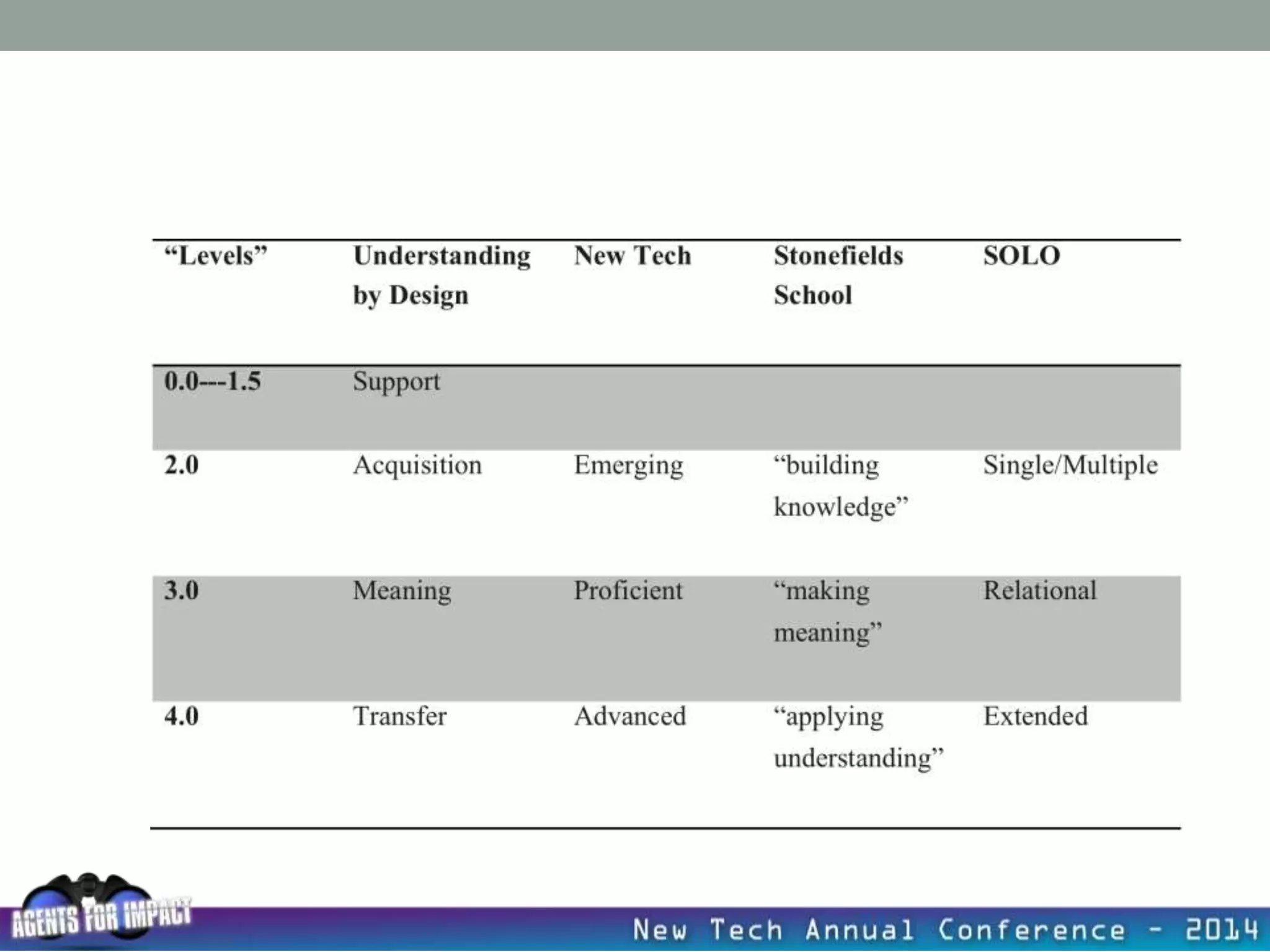
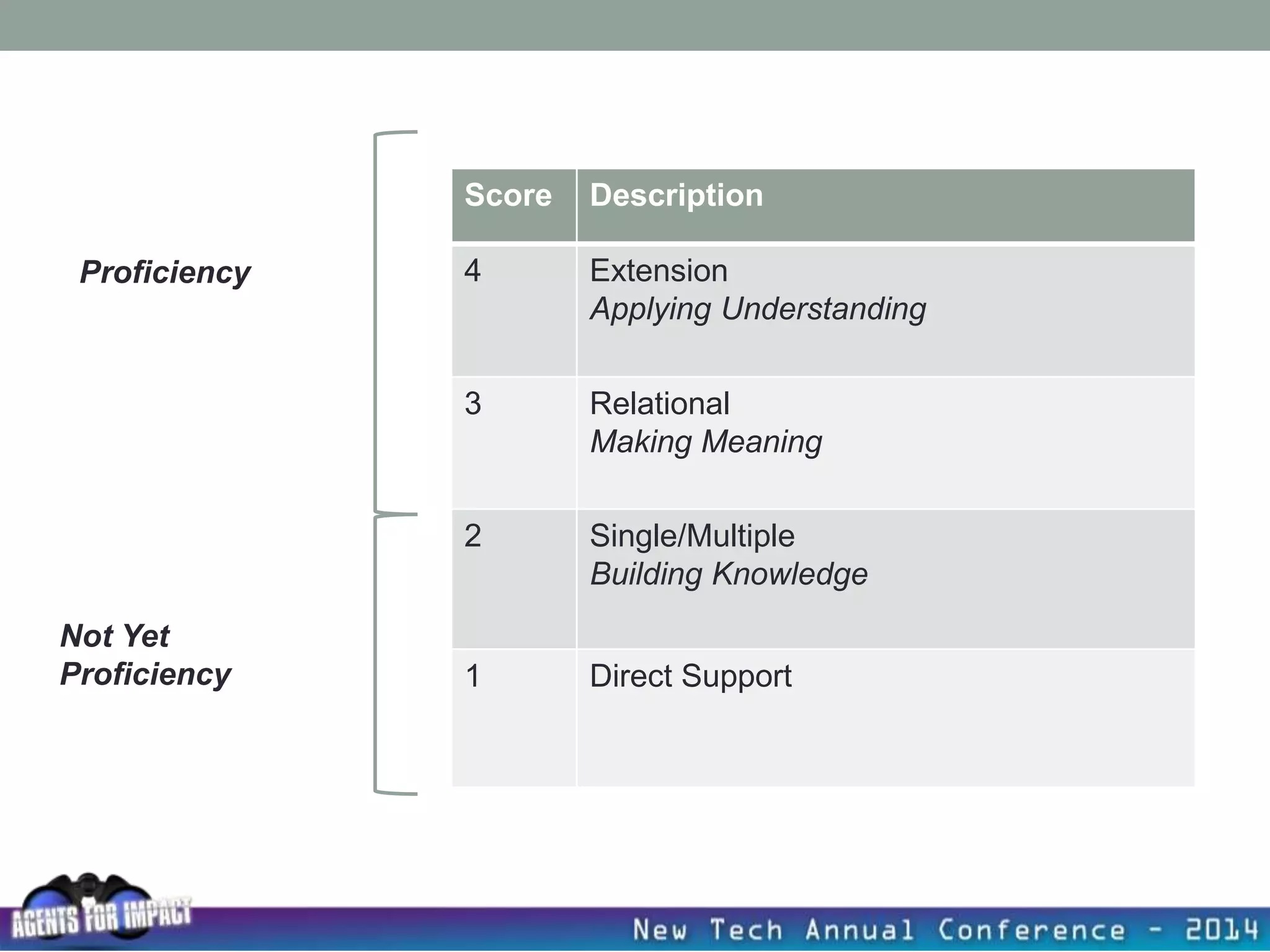
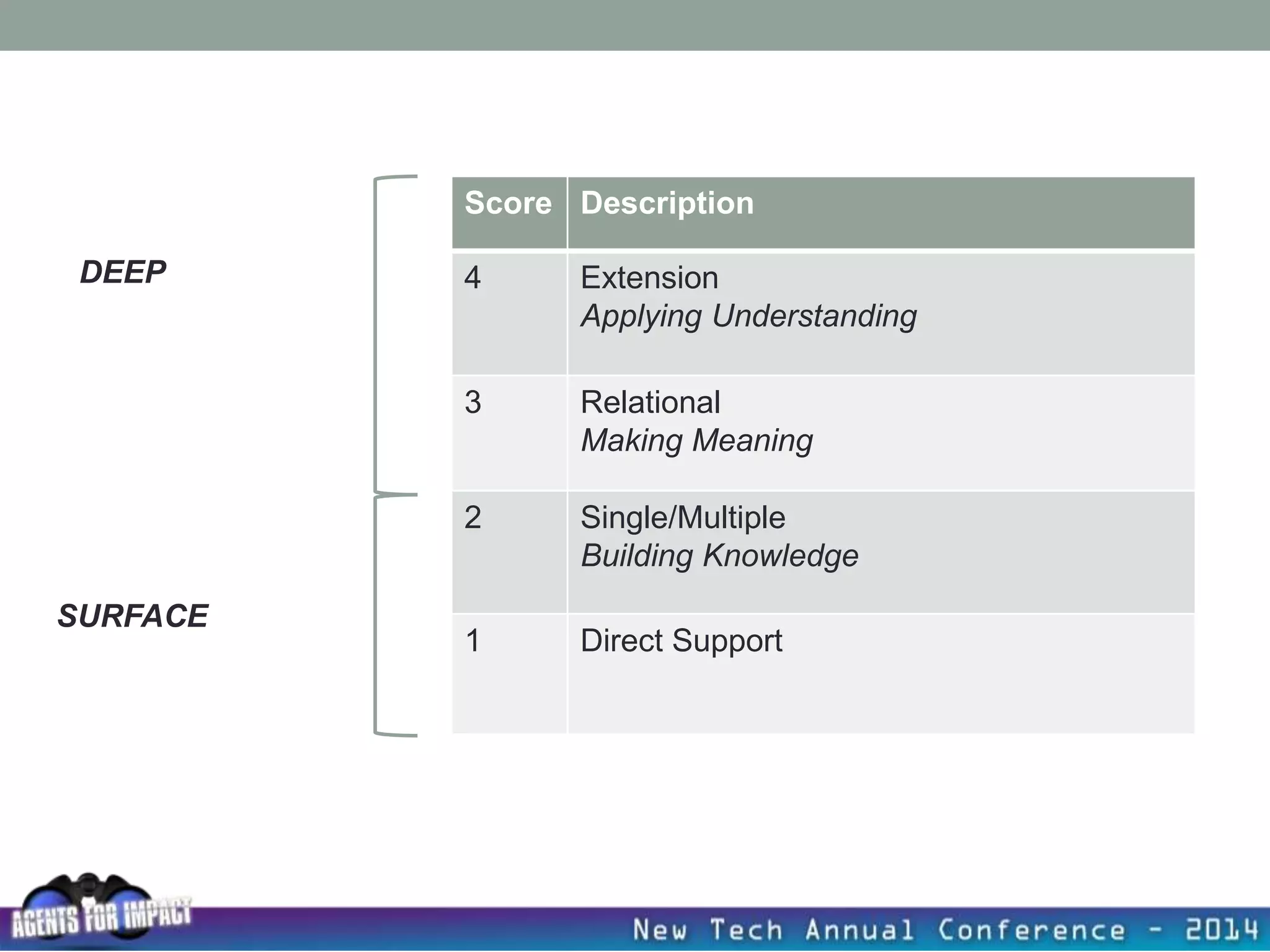
This document discusses creating a system that enhances student learning. It explores how teachers can maximize their impact through practices like collaborating to evaluate impact, using pre-assessments to inform instruction, providing clear learning targets, and valuing student errors. Research shows the most effective strategies include teachers working together in PLCs and providing students with ongoing feedback. The document advocates for a system with common student outcomes, assessment scales, intervention criteria, and a culture where all stakeholders work to understand and improve their impact on learning.

























![Teaching [and learning] in the dark is a questionable
practice” (Taba, 1966)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/system-wideimpactonstudentlearningcopy-140728091107-phpapp01/75/System-Wide-Impact-on-Student-Learning-41-2048.jpg)






![Teaching [and learning] in the dark is a questionable
practice” (Taba, 1966)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/system-wideimpactonstudentlearningcopy-140728091107-phpapp01/75/System-Wide-Impact-on-Student-Learning-60-2048.jpg)