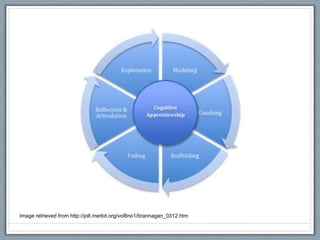
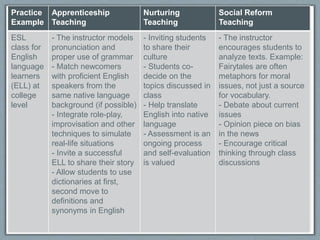
The document discusses different teaching perspectives - cognitive apprenticeship, nurturing teaching, and social reform teaching. Cognitive apprenticeship focuses on applying skills through modeling, coaching, fading, self-directed learning, and generalizing. Nurturing teaching emphasizes caring, empathy, self-efficacy, and connecting learning to students' experiences. Social reform teaching aims to challenge status quo, encourage critical thinking, and empower social action. The document provides characteristics and instructional strategies for each perspective, and an example of integrating them in an ESL class.