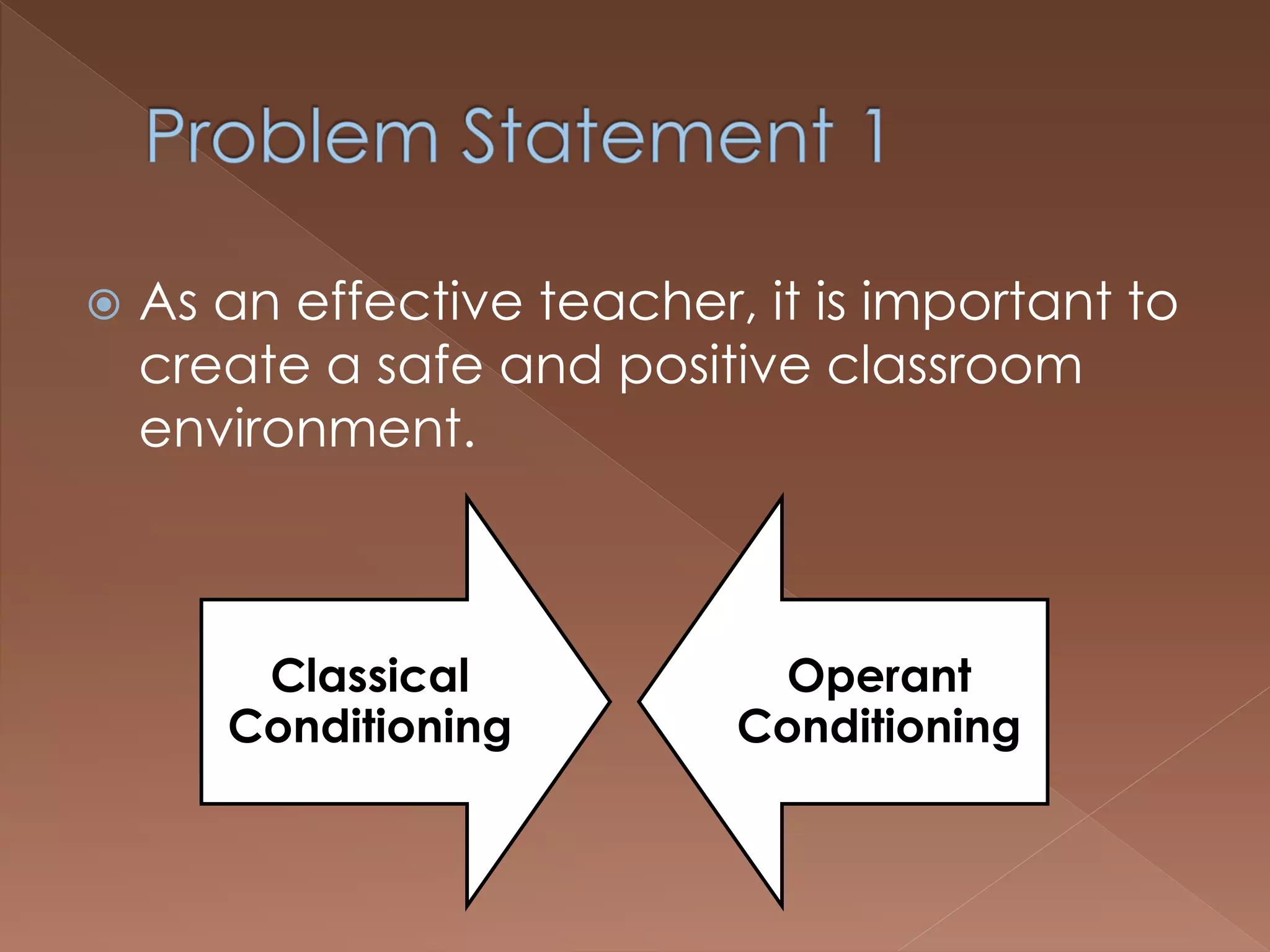
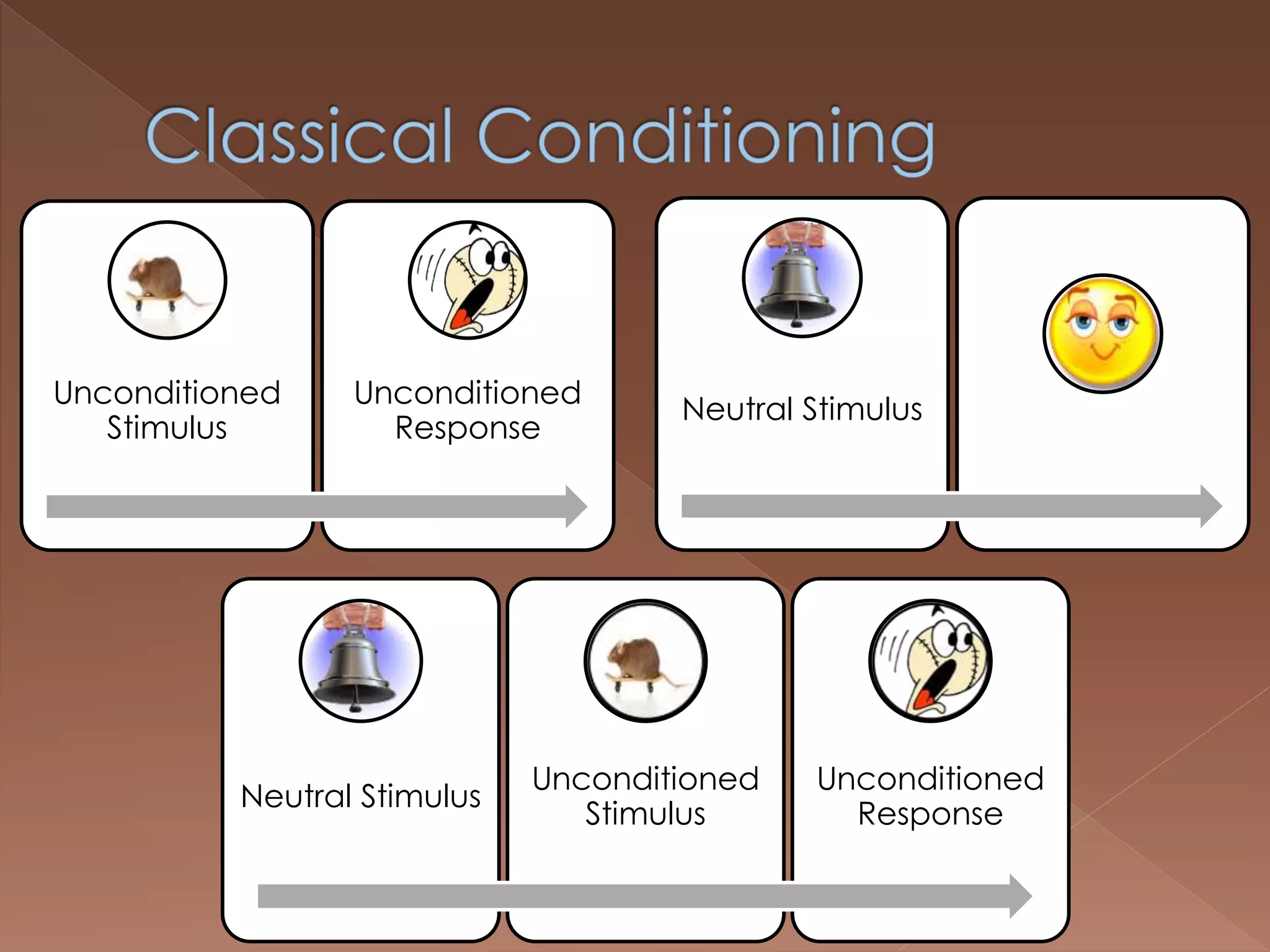
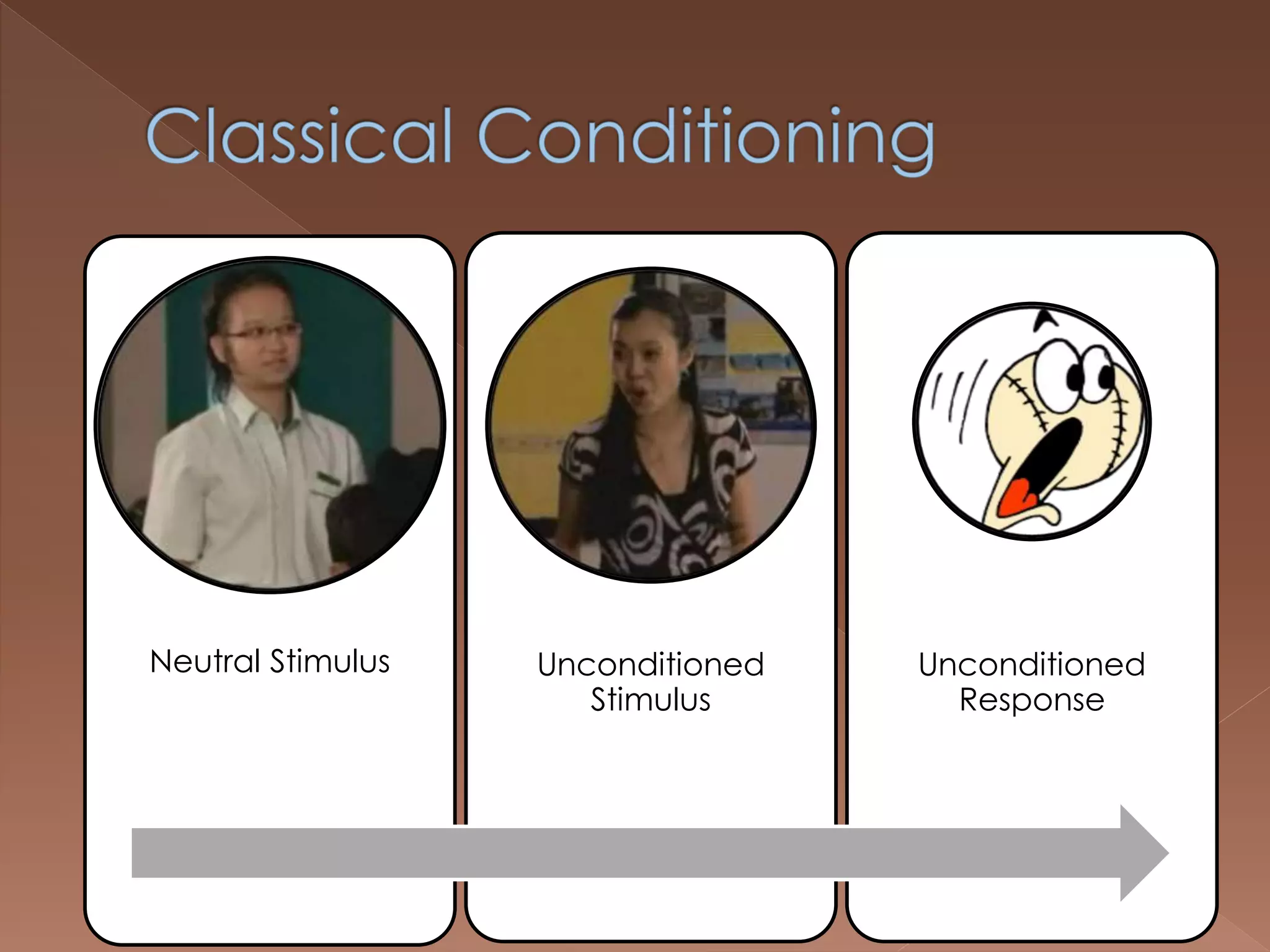
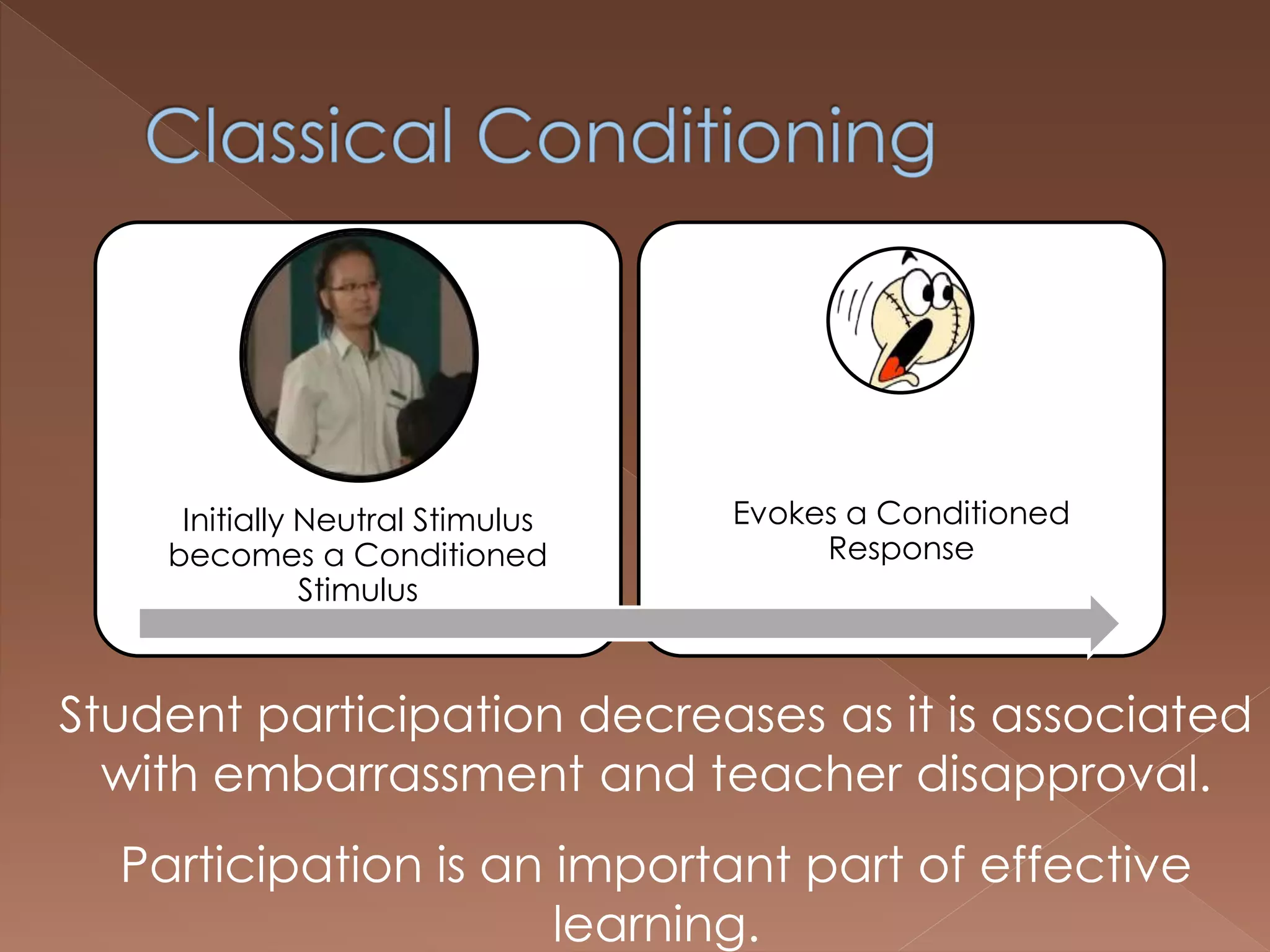
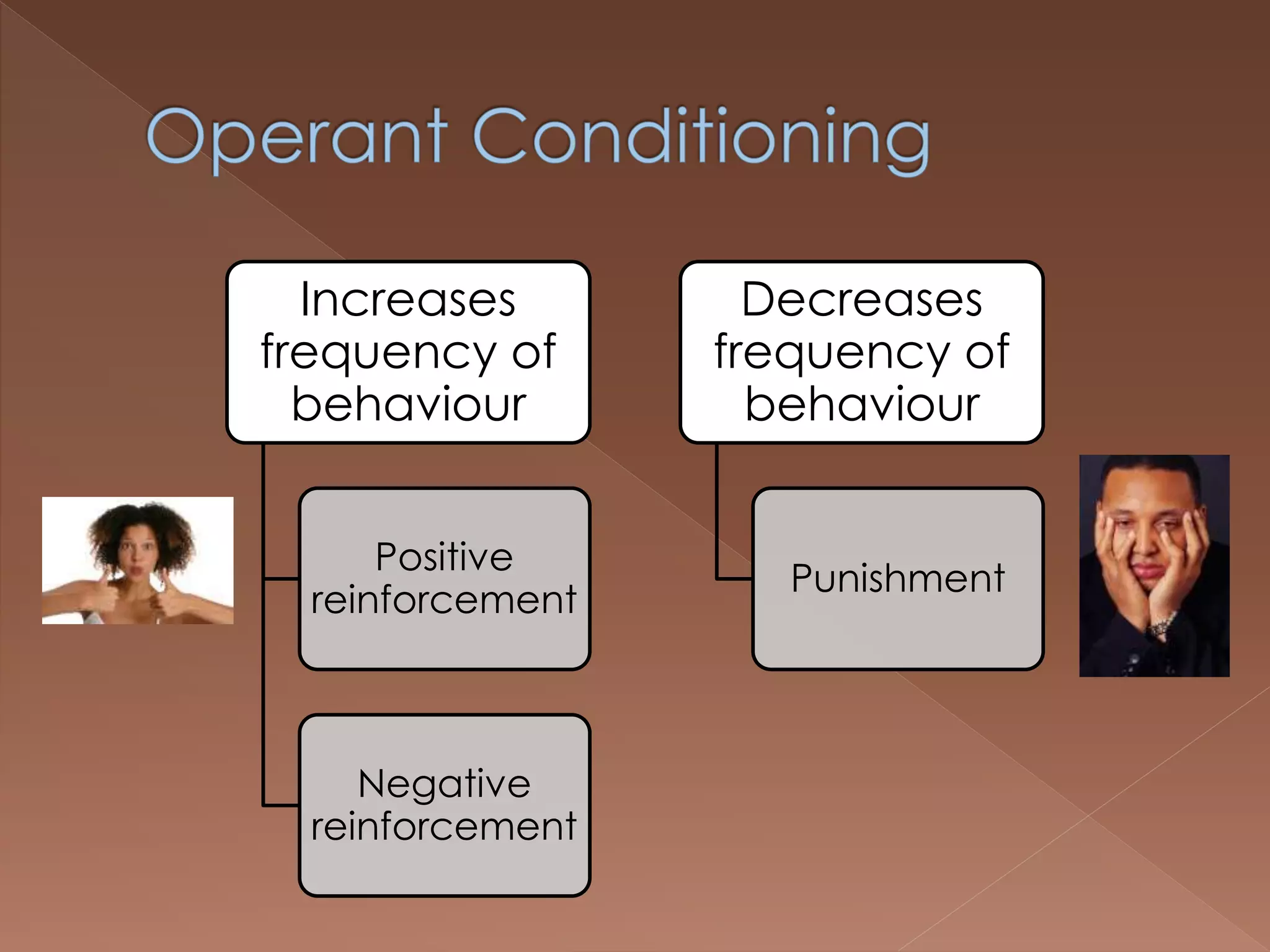
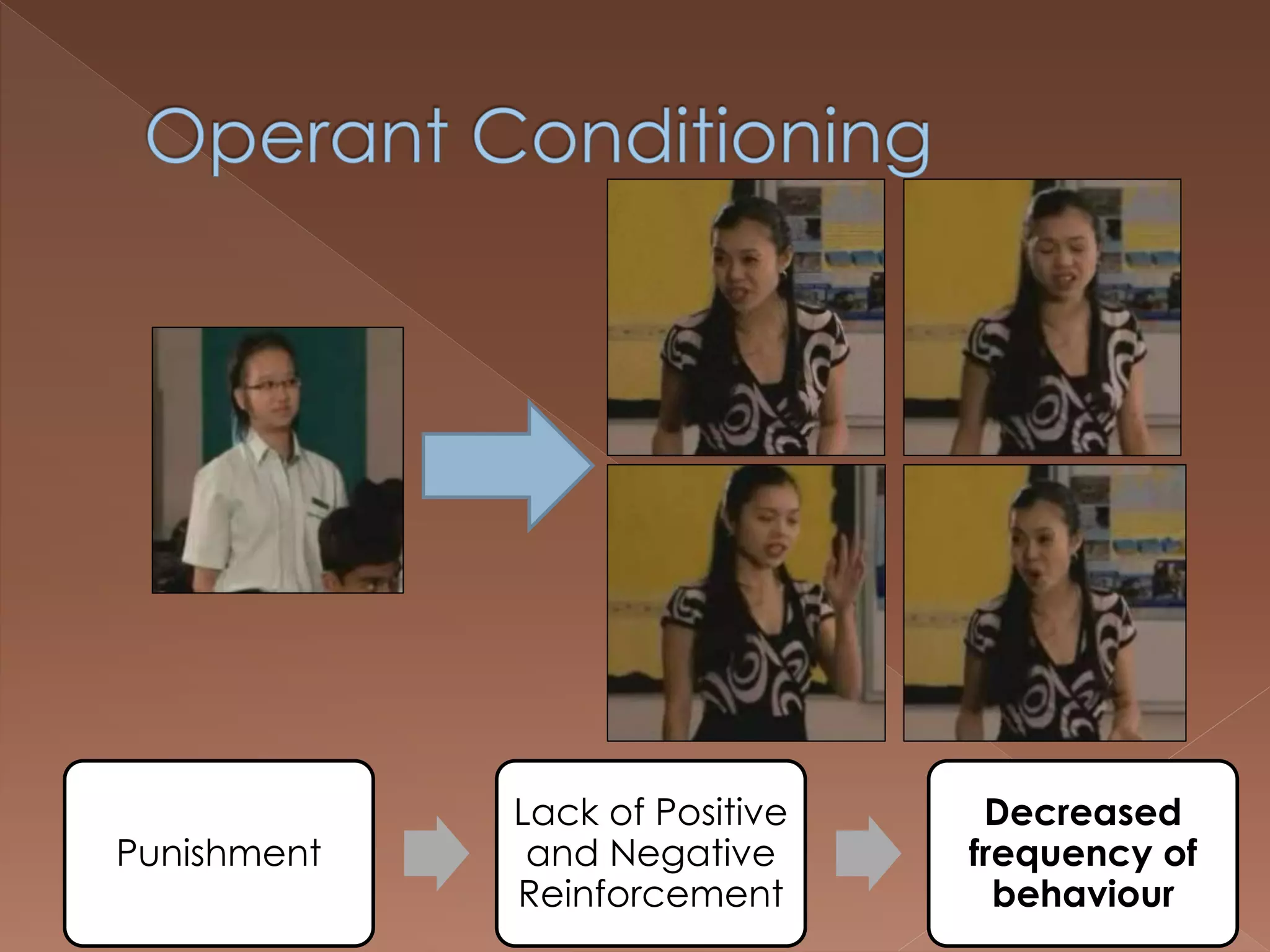
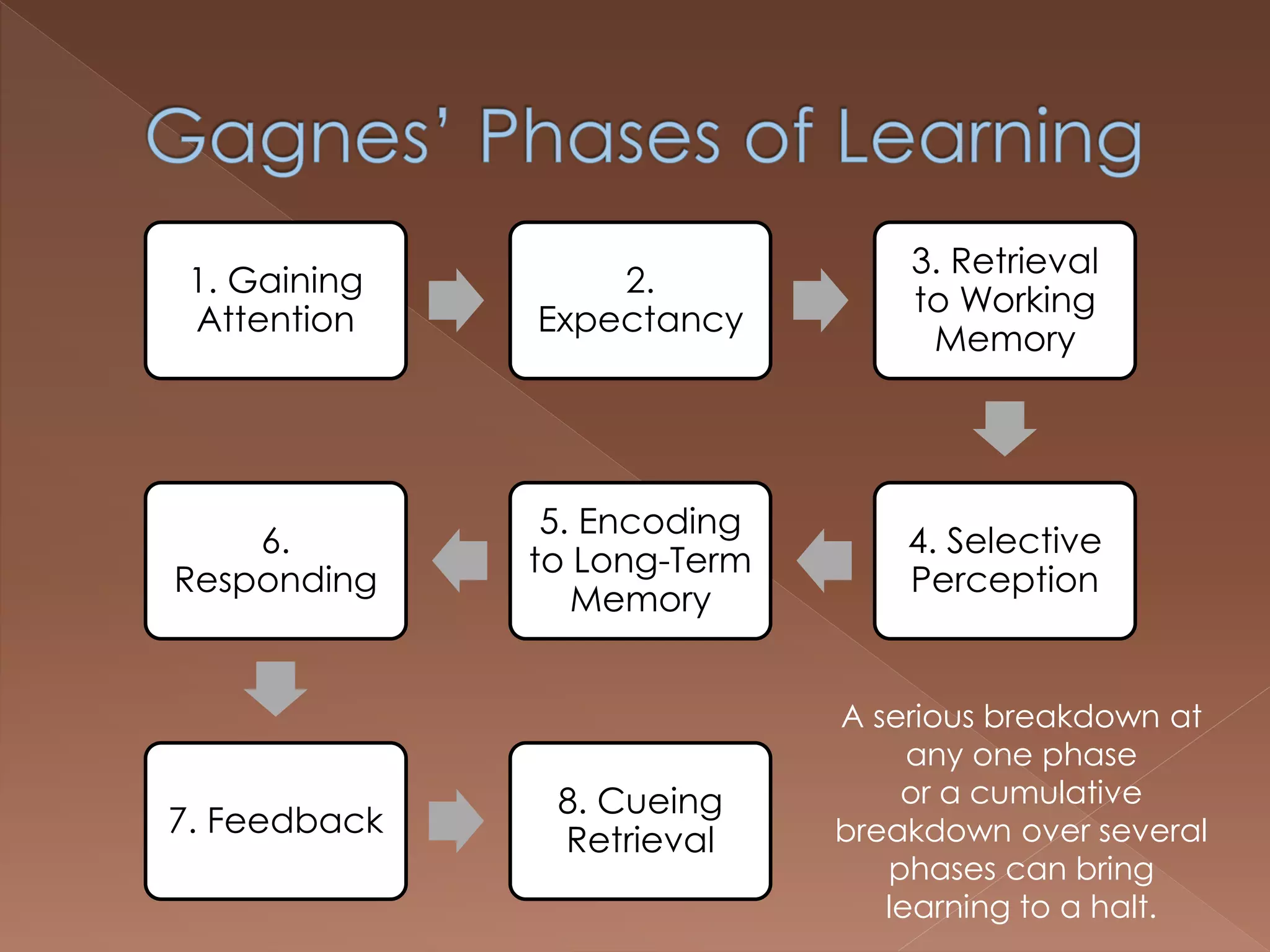
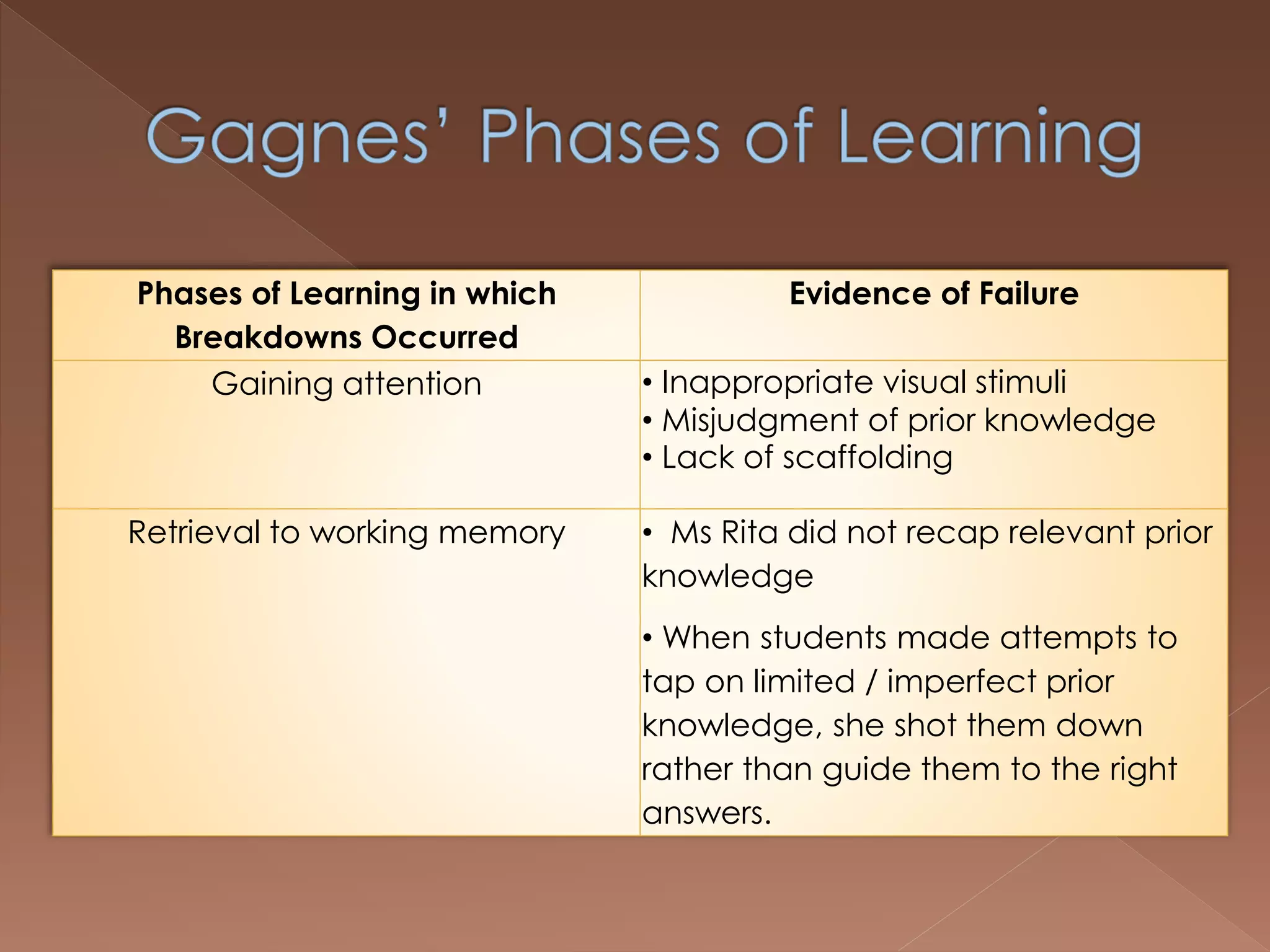
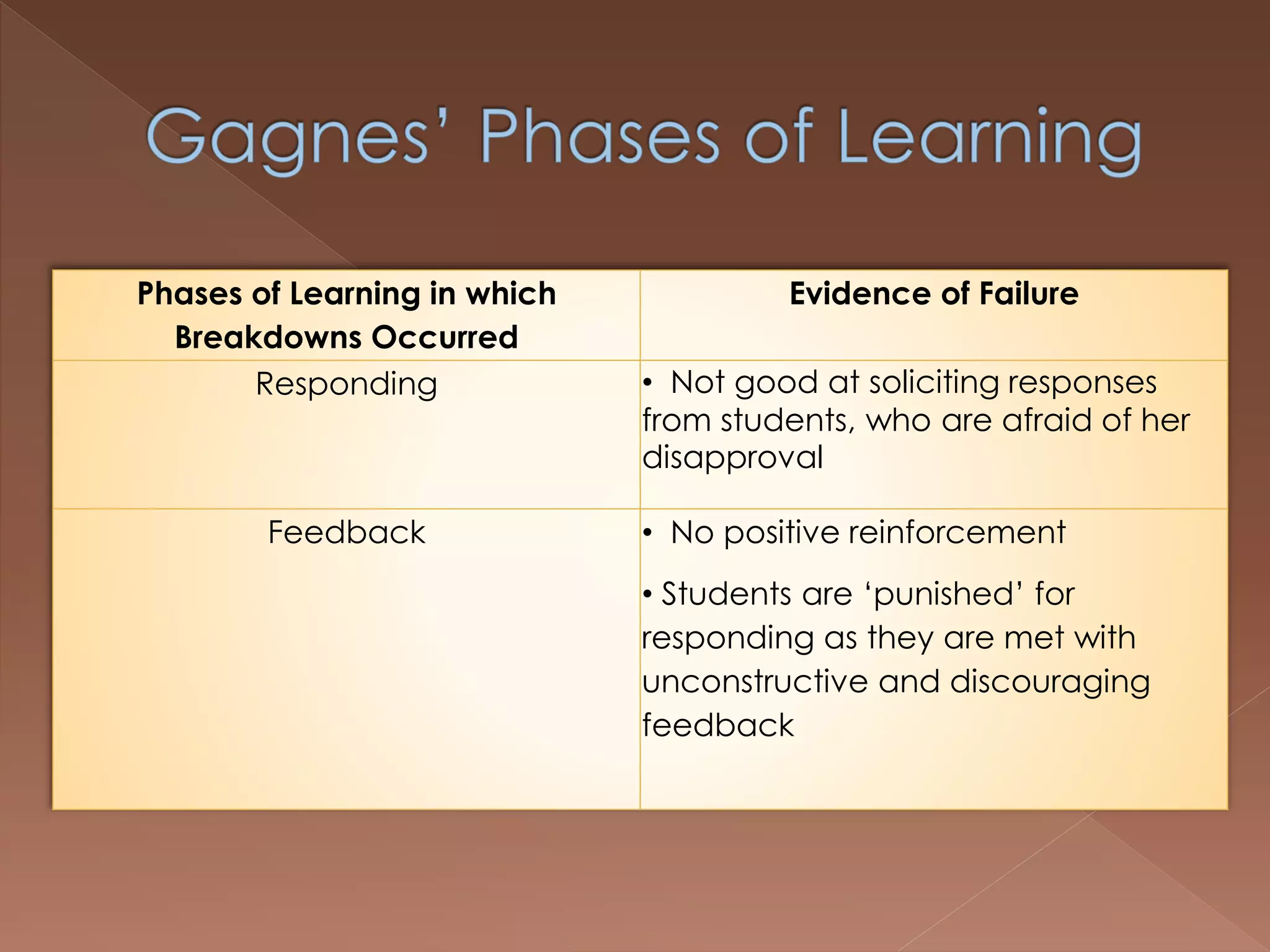
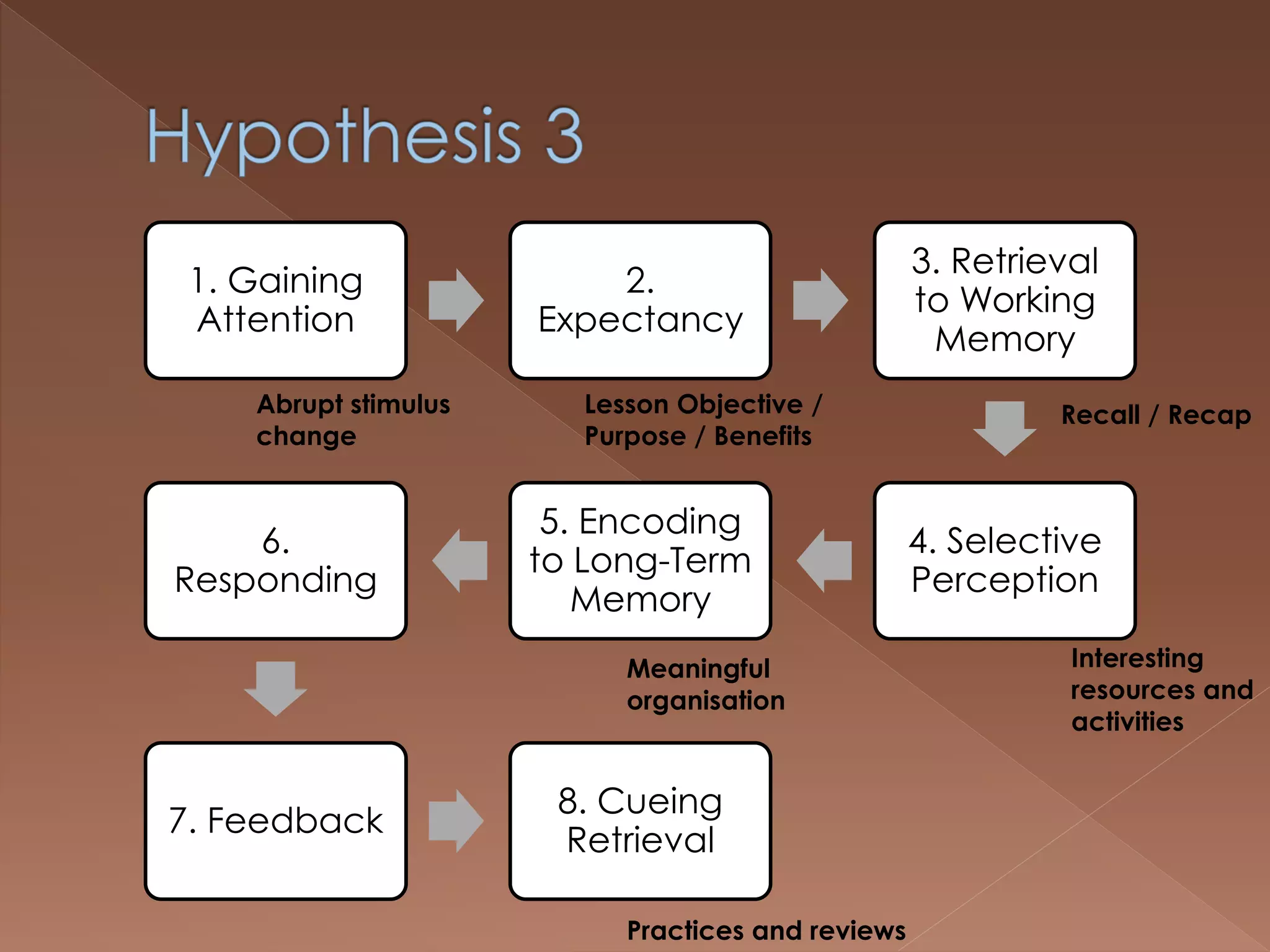
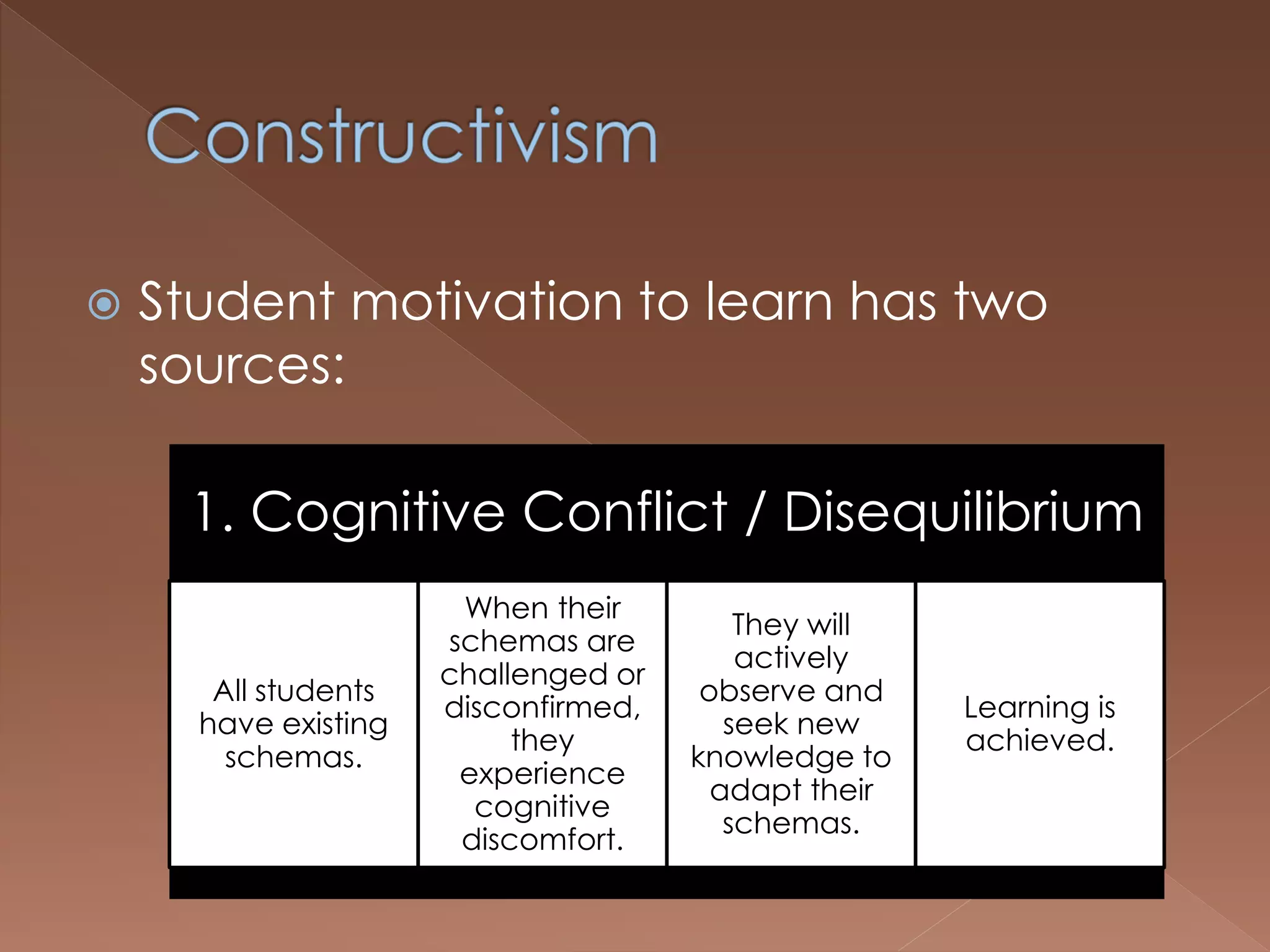
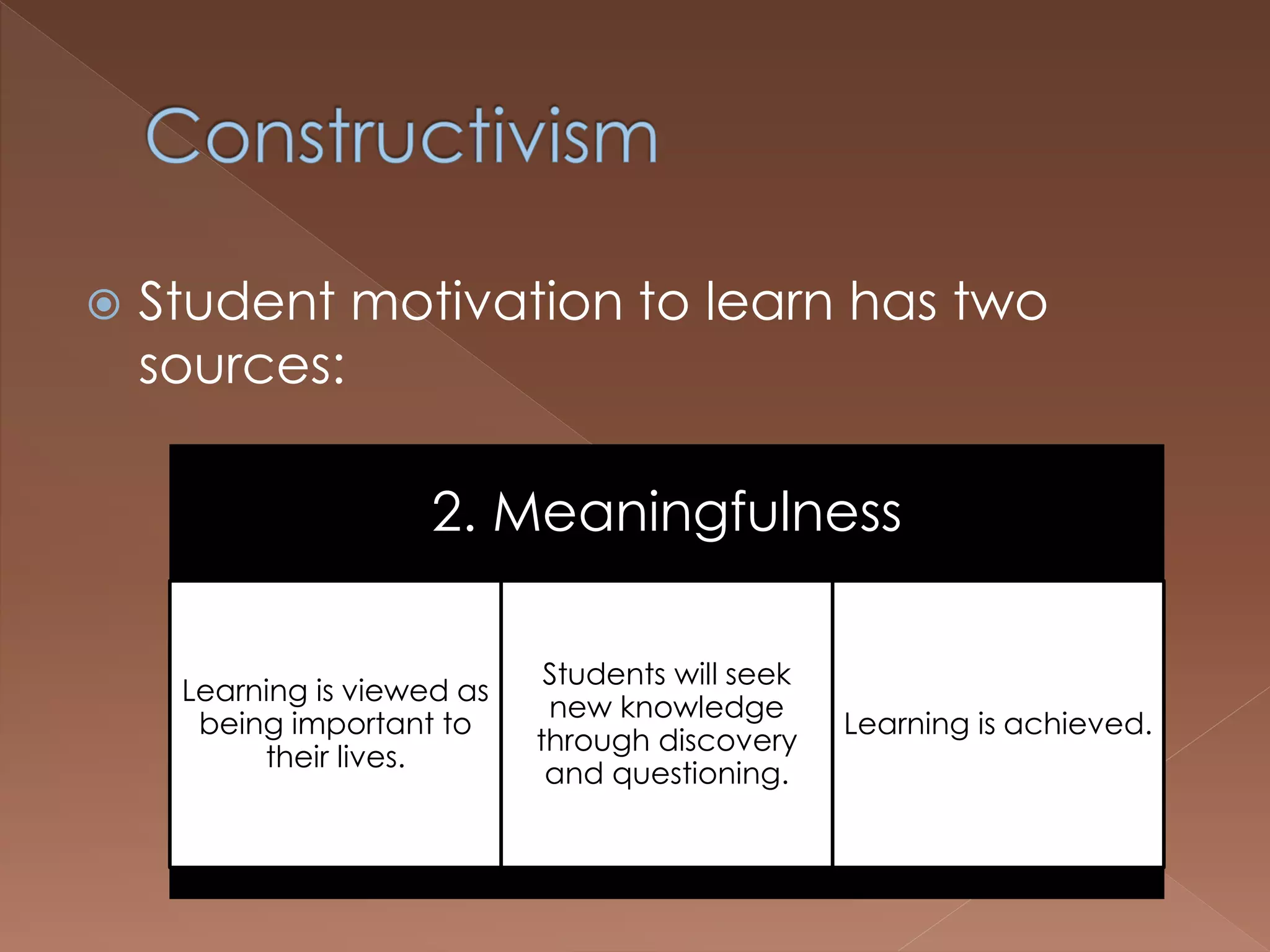
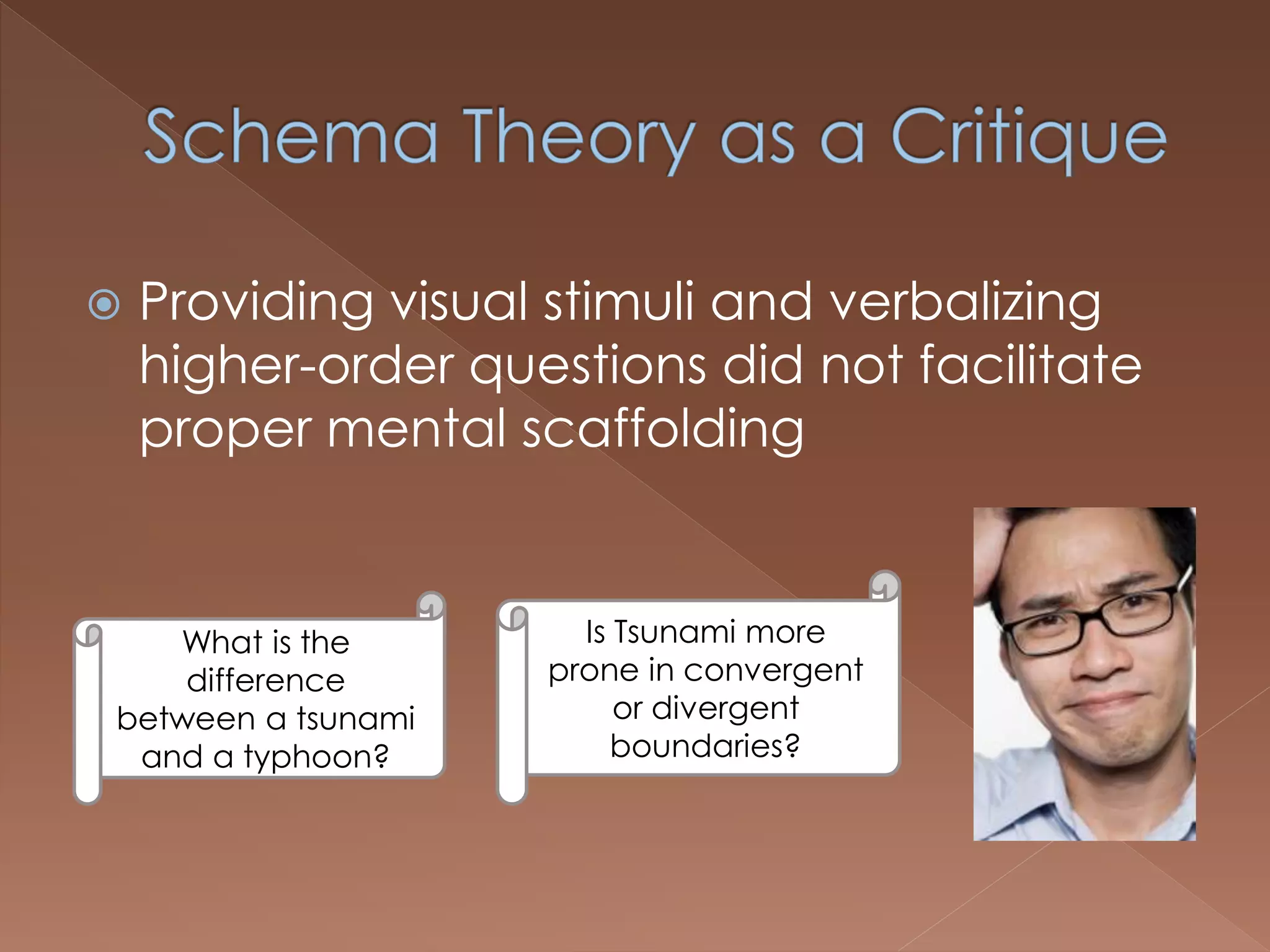
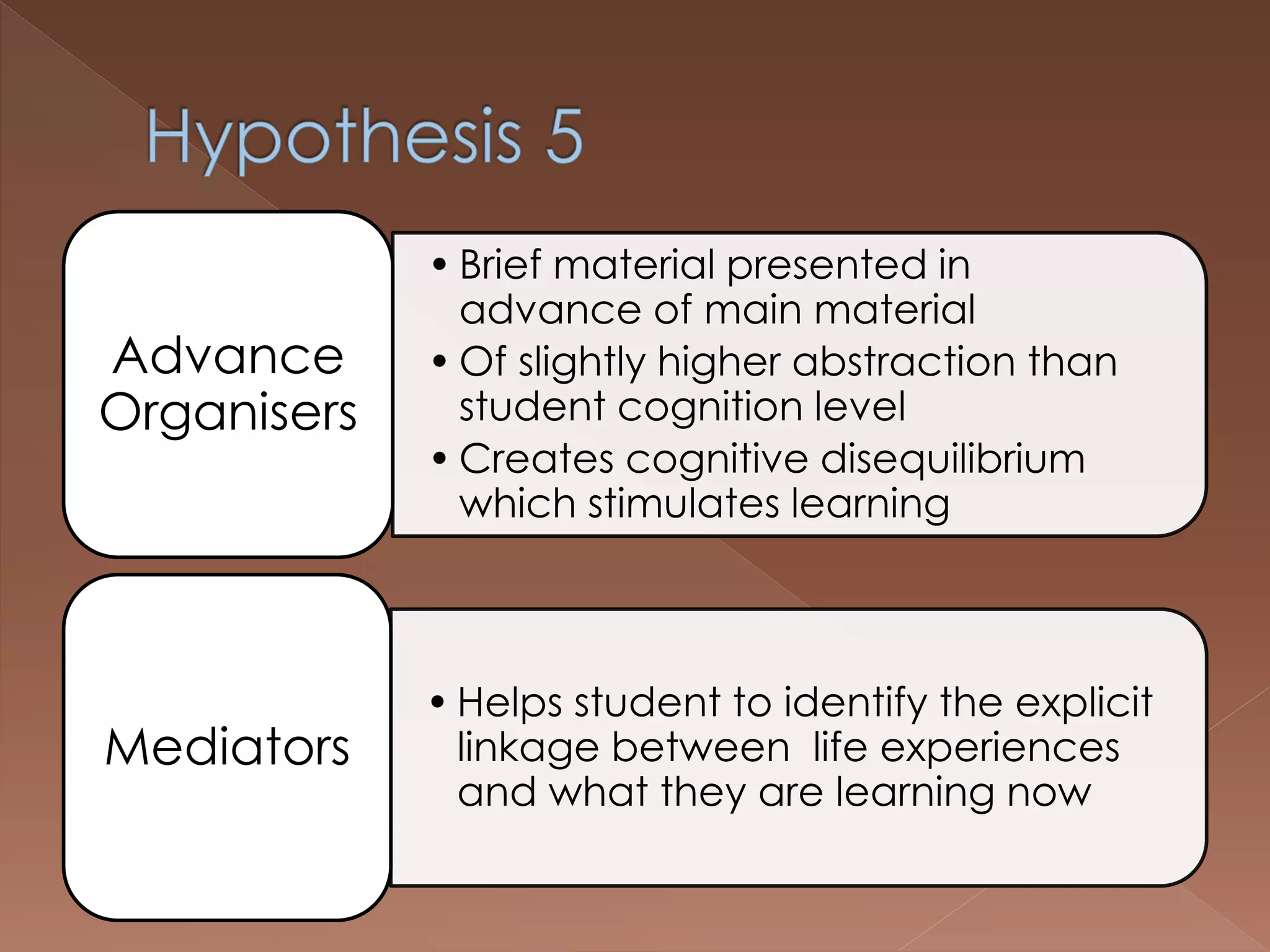
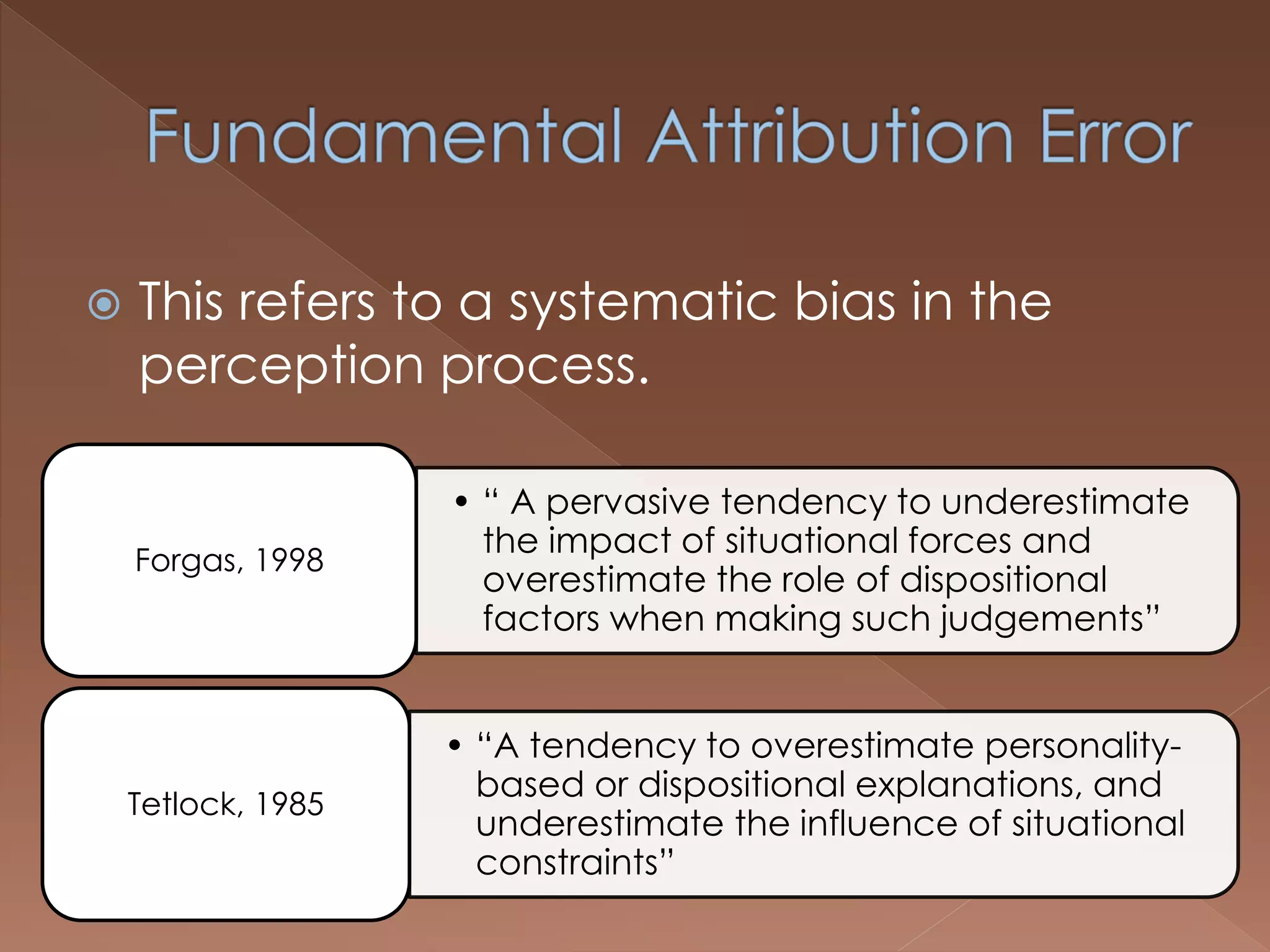
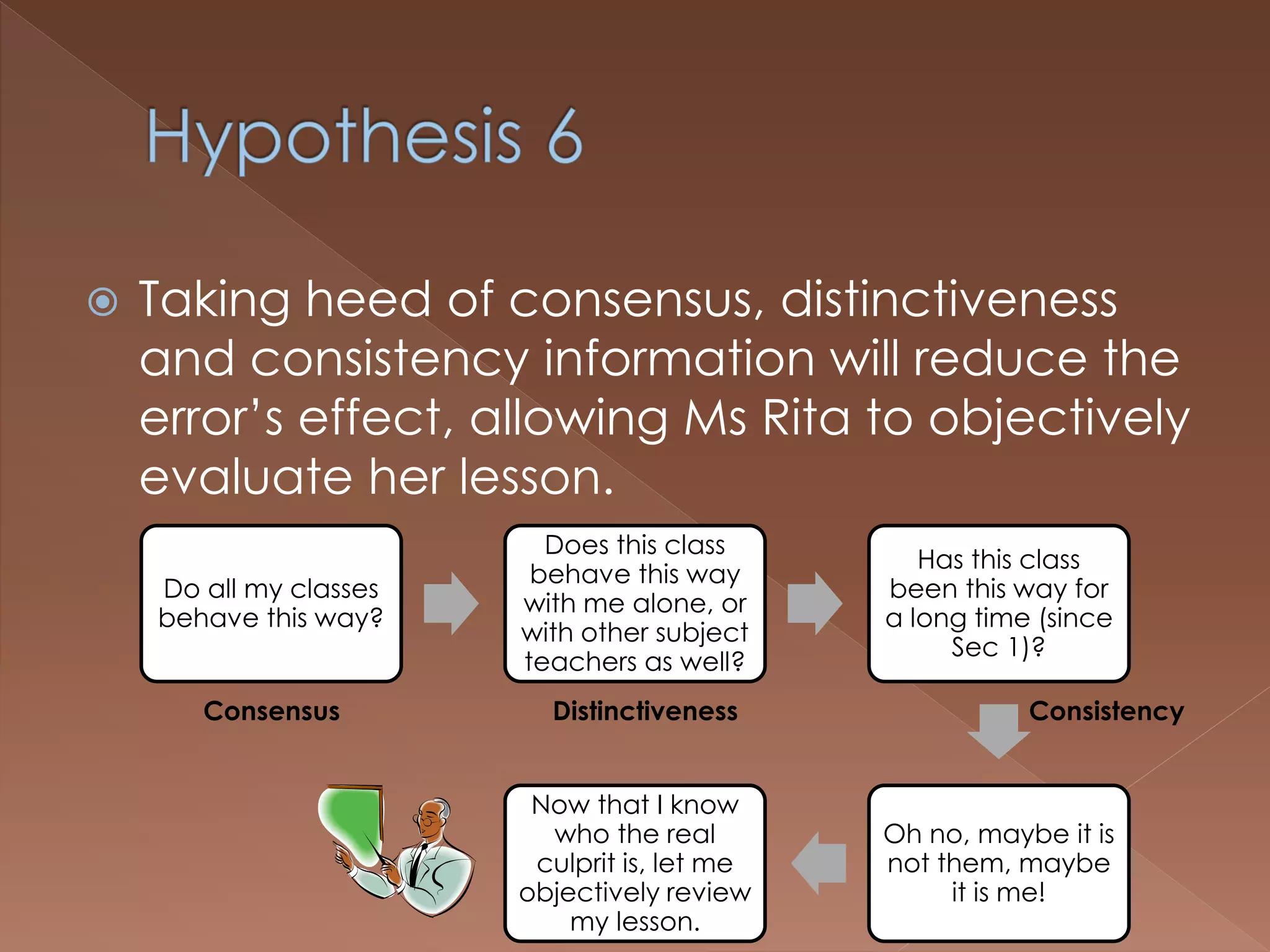
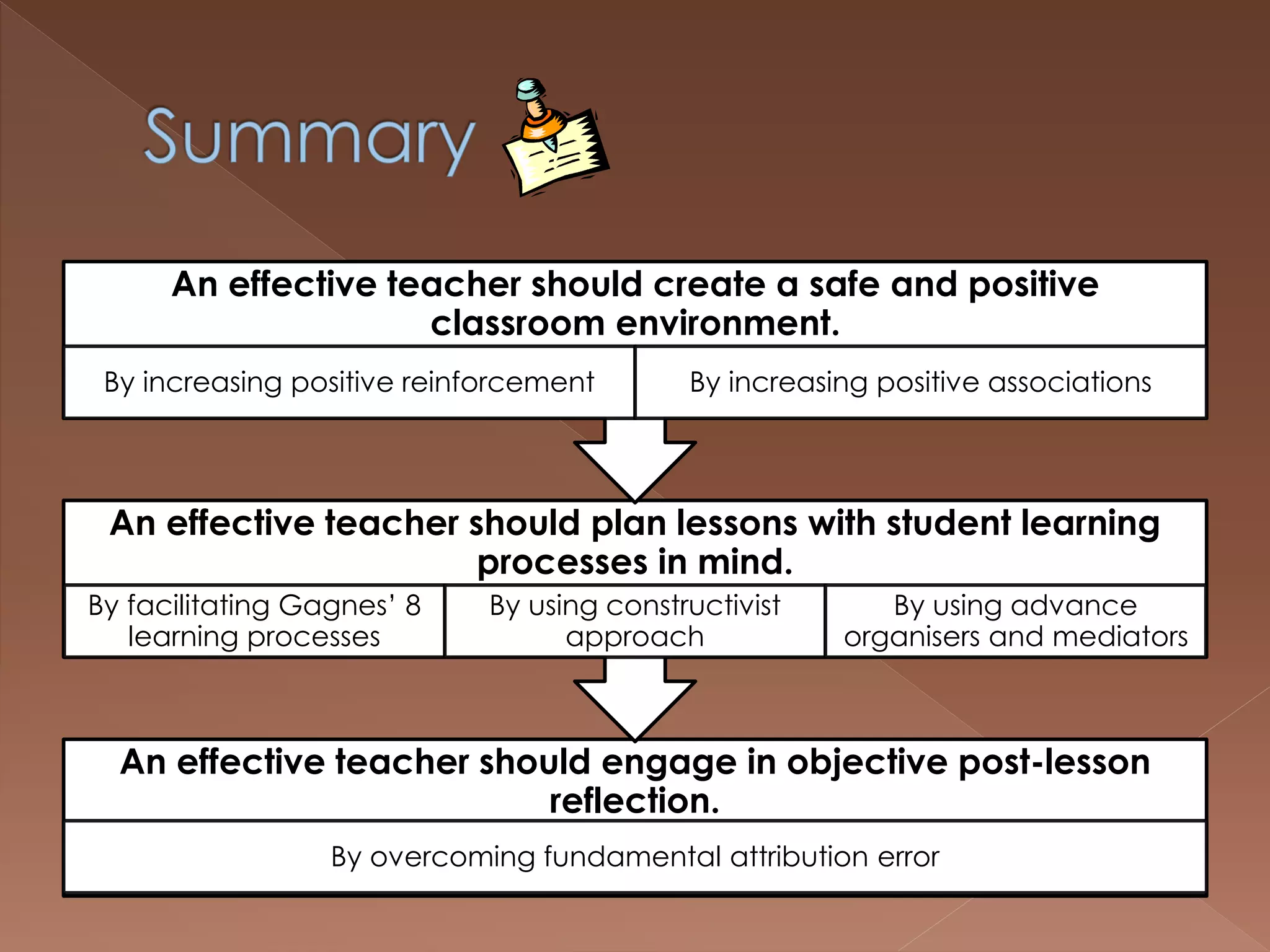
An effective teacher should engage in objective post-lesson reflection by overcoming fundamental attribution error, plan lessons with student learning processes in mind by facilitating Gagnes' 8 learning processes and using constructivist approaches with advance organizers and mediators, and create a safe positive classroom environment by increasing positive reinforcement and associations.