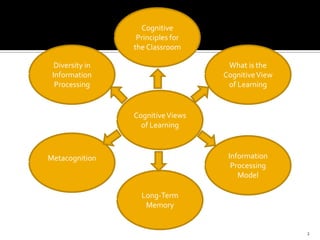
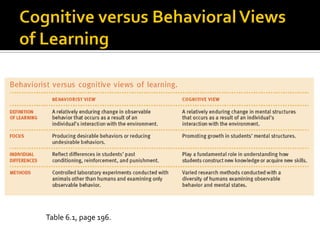
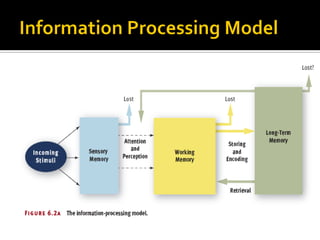
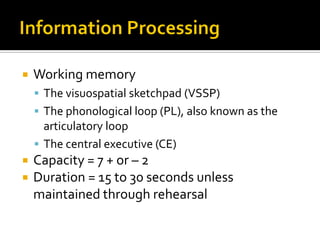
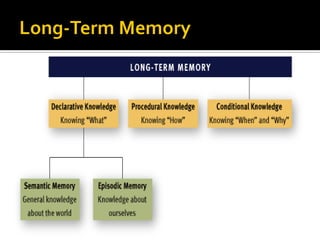
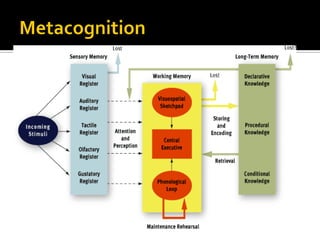
The document discusses the cognitive view of learning, including information processing models involving sensory registers, working memory, long-term memory, and retrieval processes. It also covers metacognition, individual differences in learning, and cognitive principles for instruction such as attracting attention, activating prior knowledge, preventing cognitive overload, and encouraging elaboration and organization. The cognitive view emphasizes that learning involves mental representations and schema formation through meaningful interactions with instructional content and the environment.