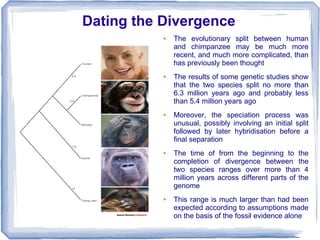
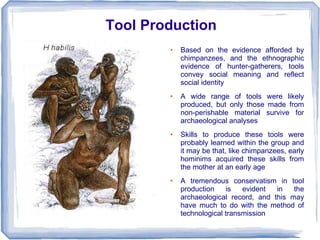
The document discusses evidence from genetics, anatomy, and behavior that traces the evolutionary path from early primates to Homo sapiens. It describes several early primate species such as Proconsul and Sivapithecus found in Africa and Asia dating back millions of years. Genetic evidence shows humans share over 99% of DNA with chimpanzees and diverged from them around 5-6 million years ago. Anatomical similarities and differences in the pelvis, feet and locomotion provide insights into the emergence of bipedalism. Higher primates display sophisticated communication including gestures, facial expressions, and tool usage, providing clues about early human behavior.