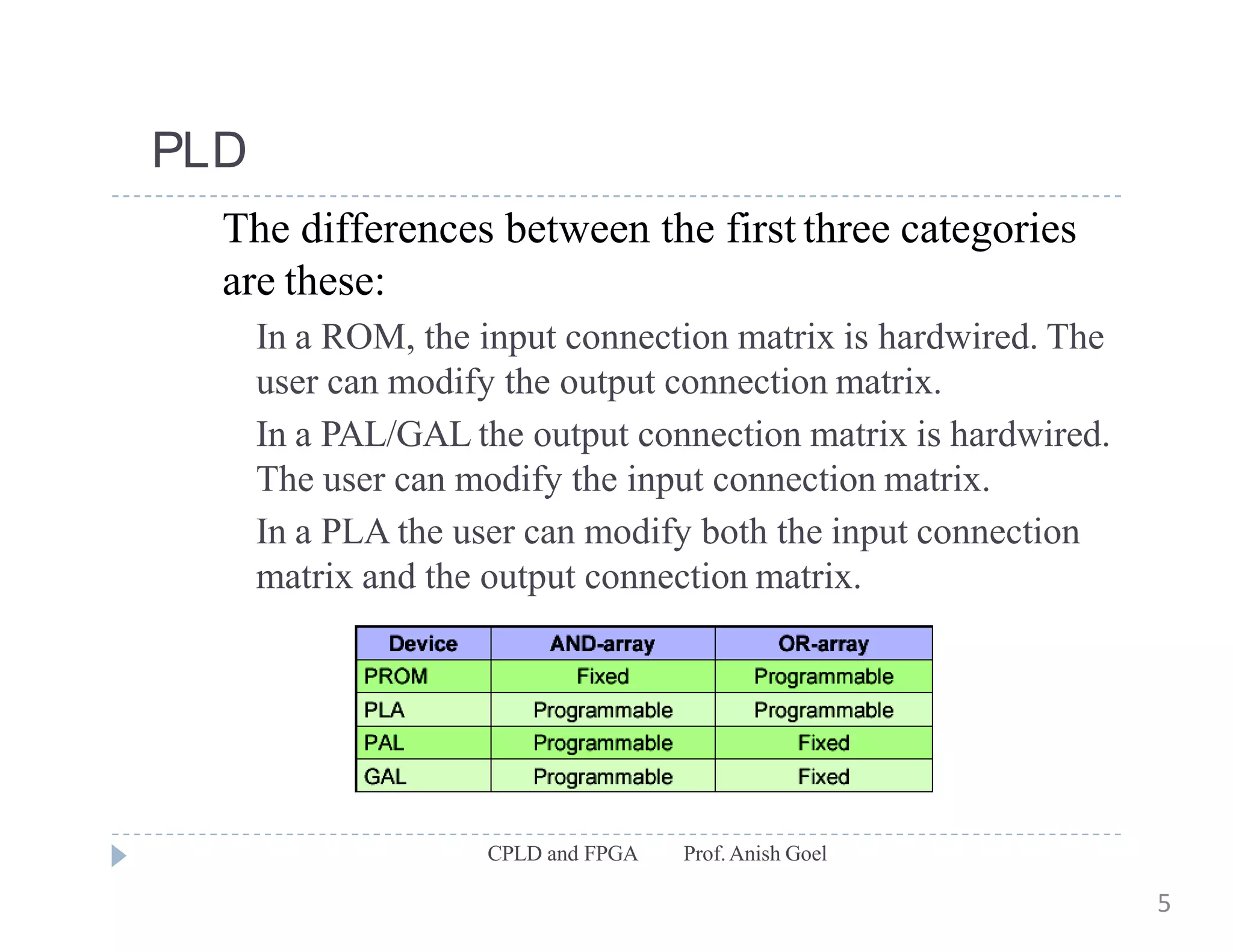
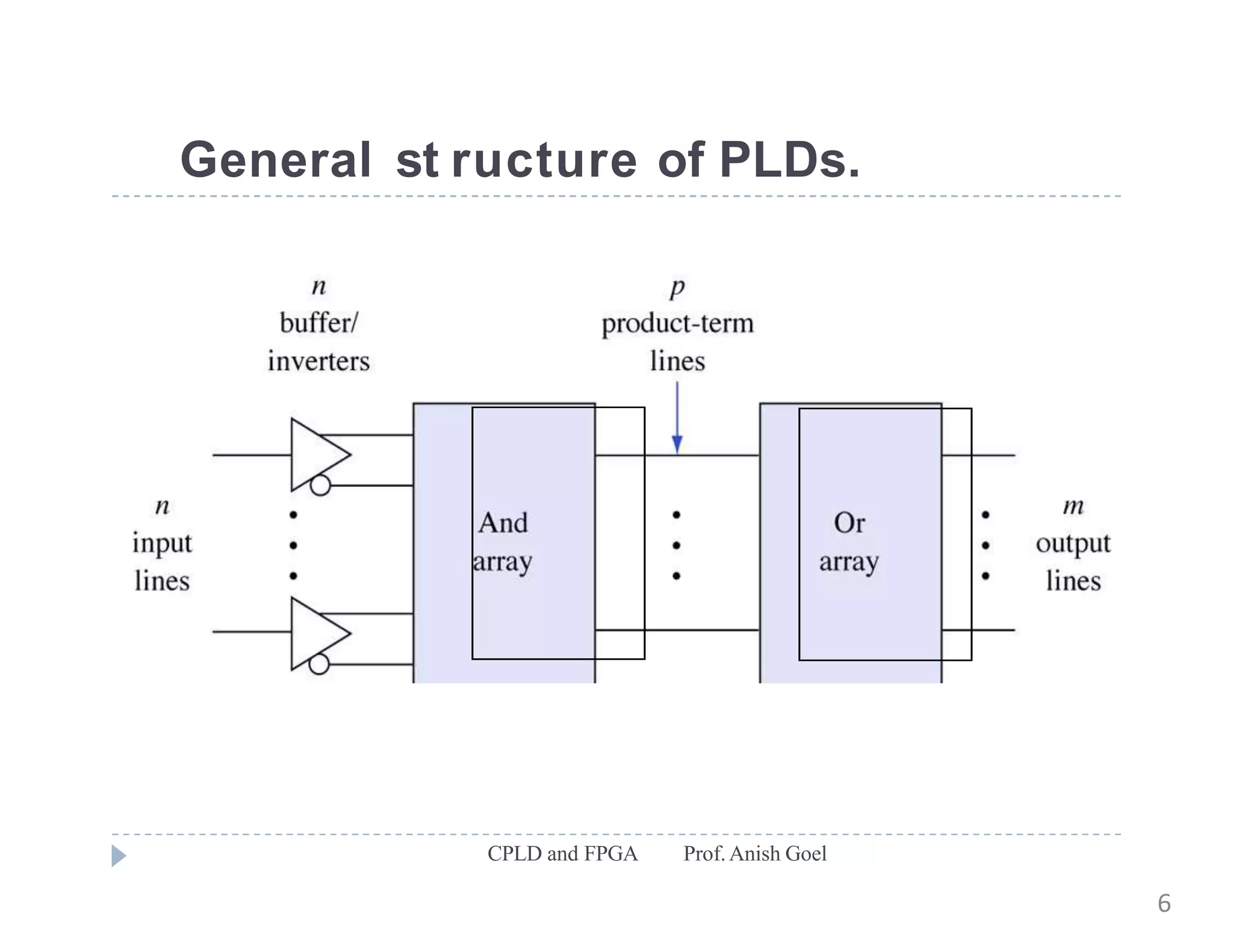
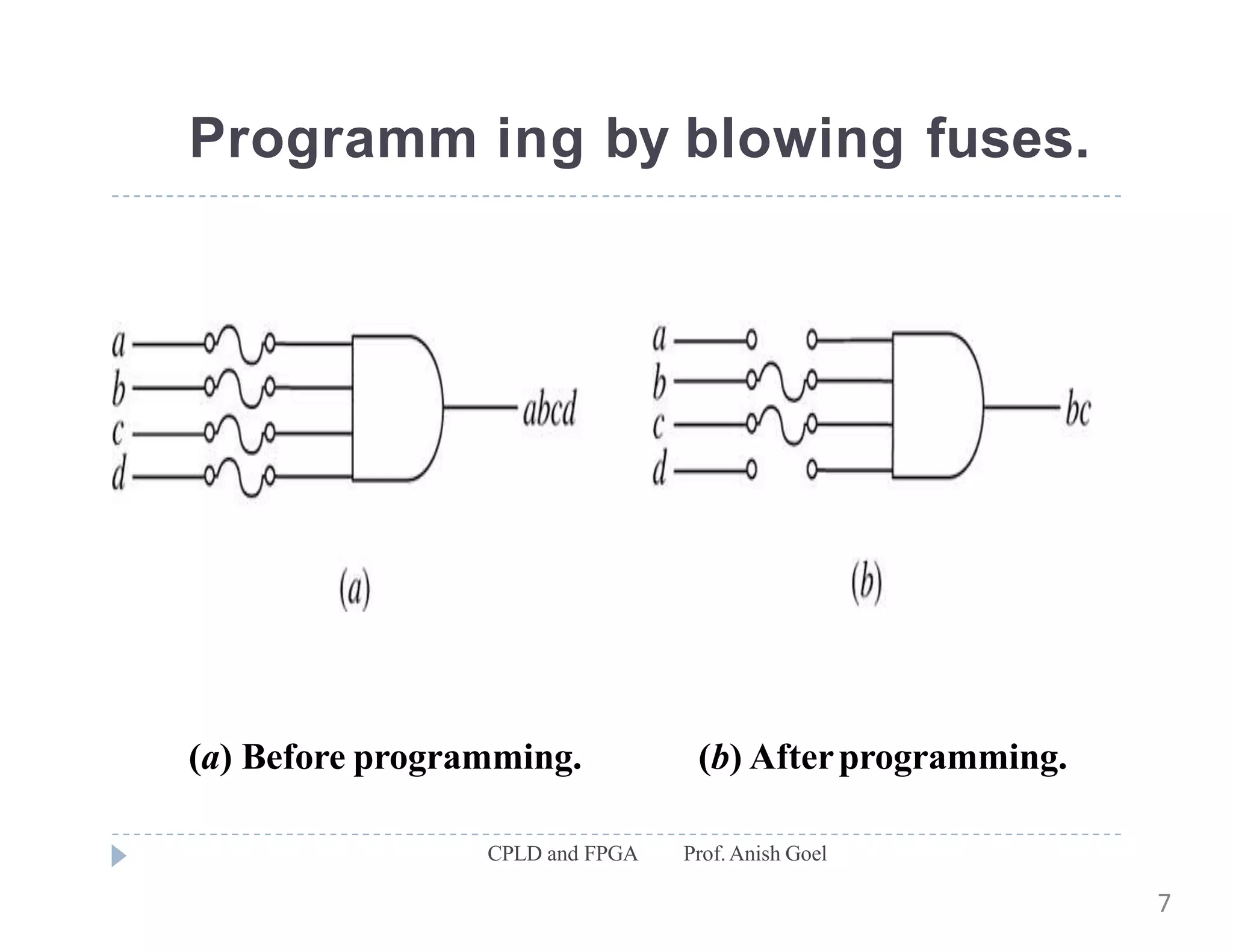
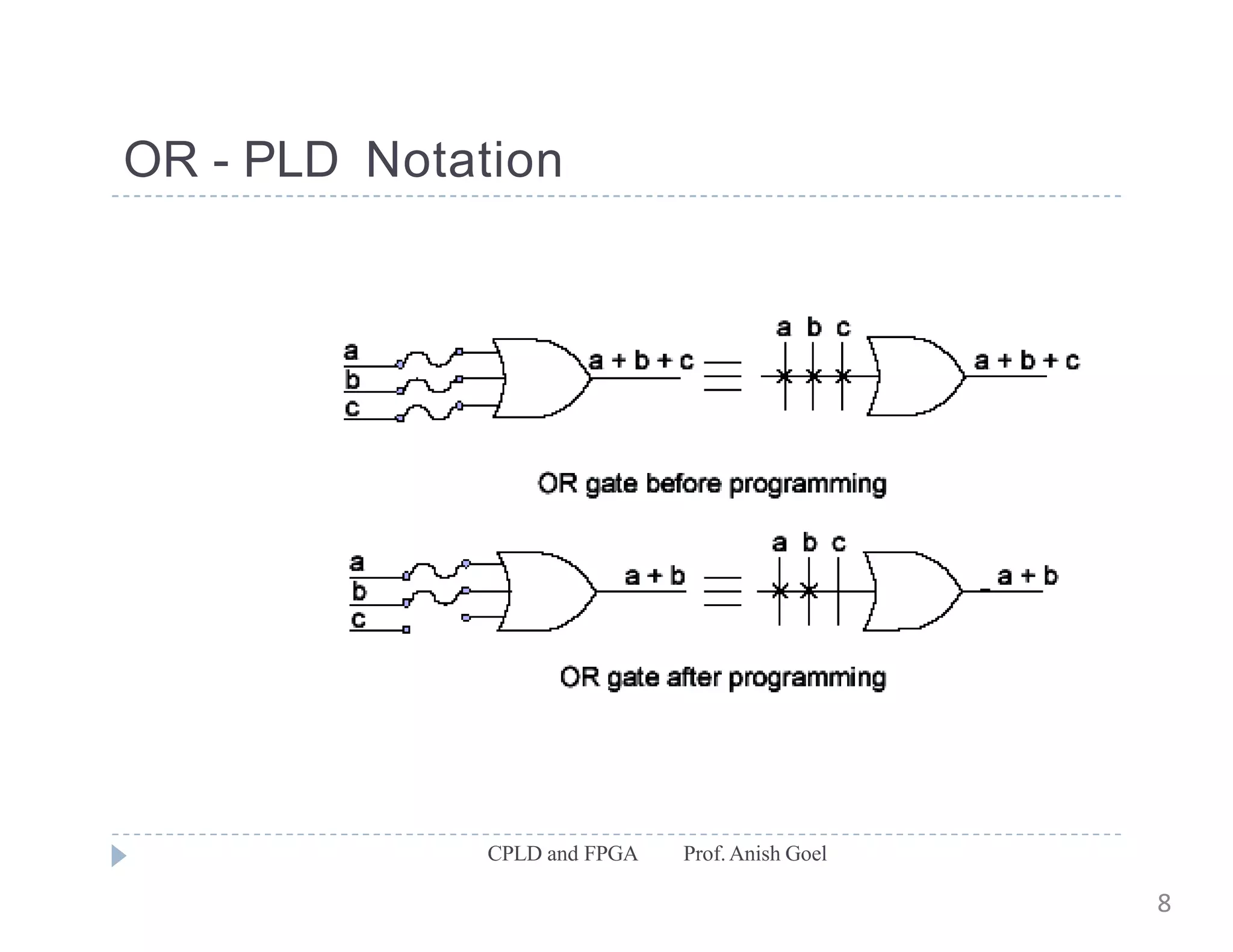
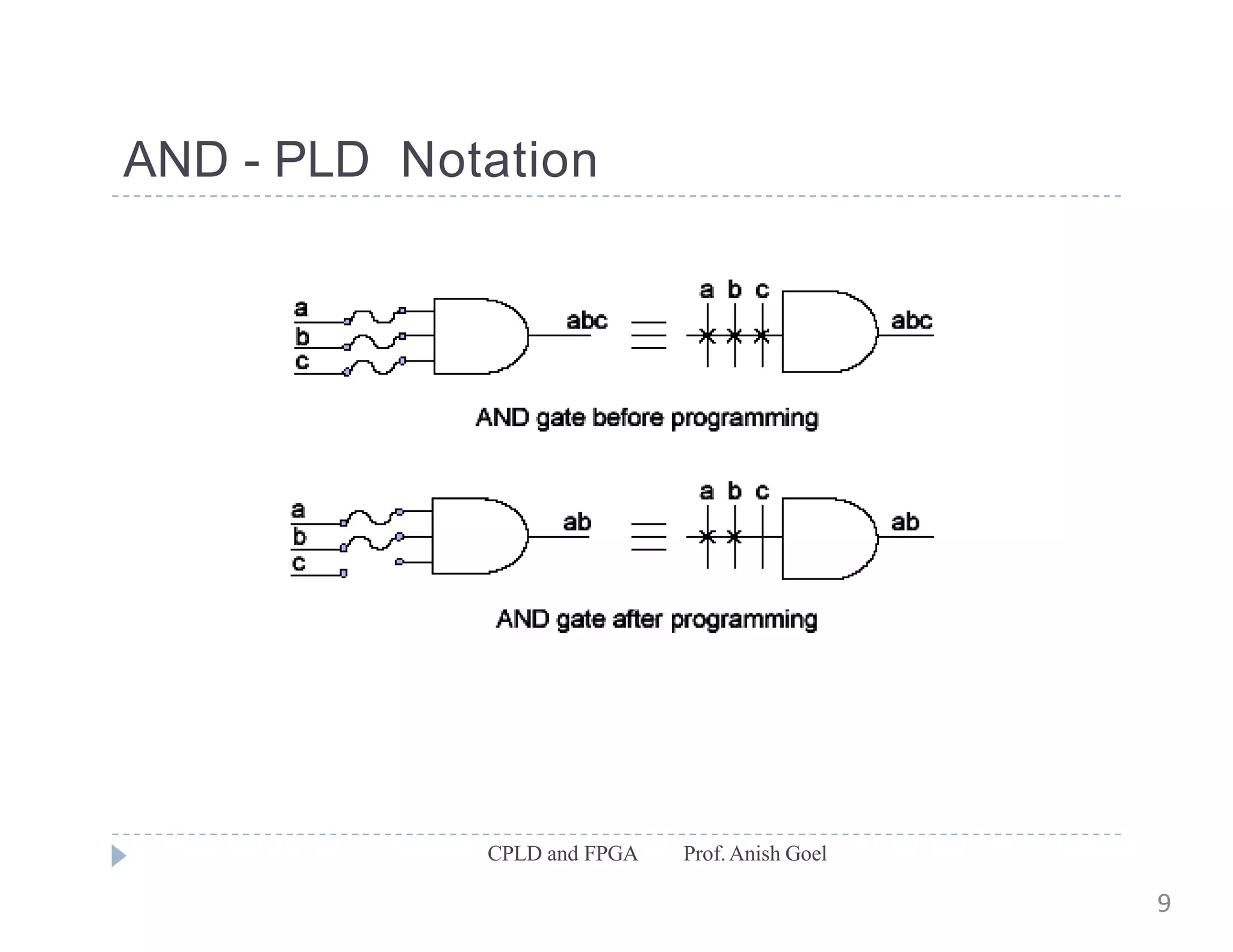
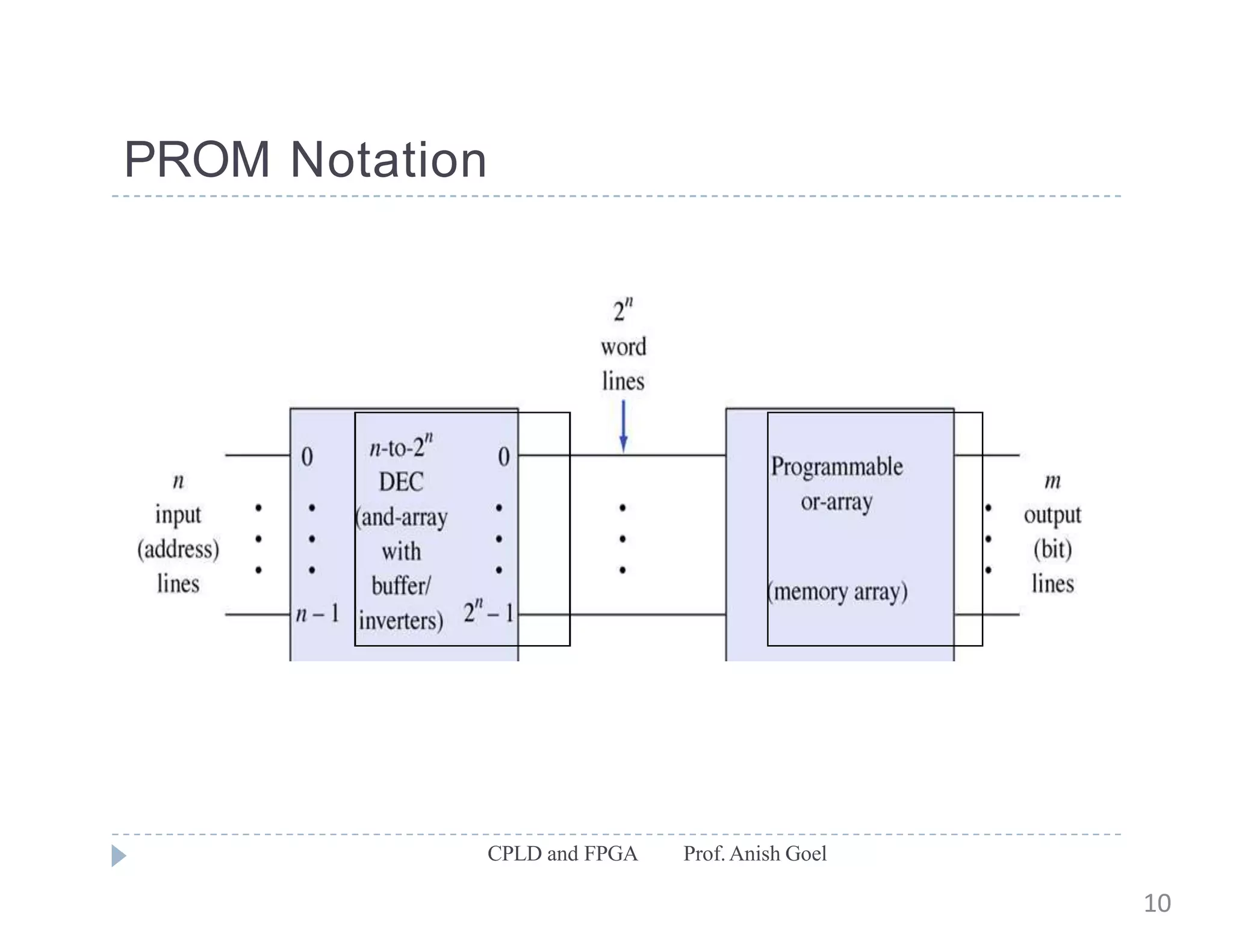
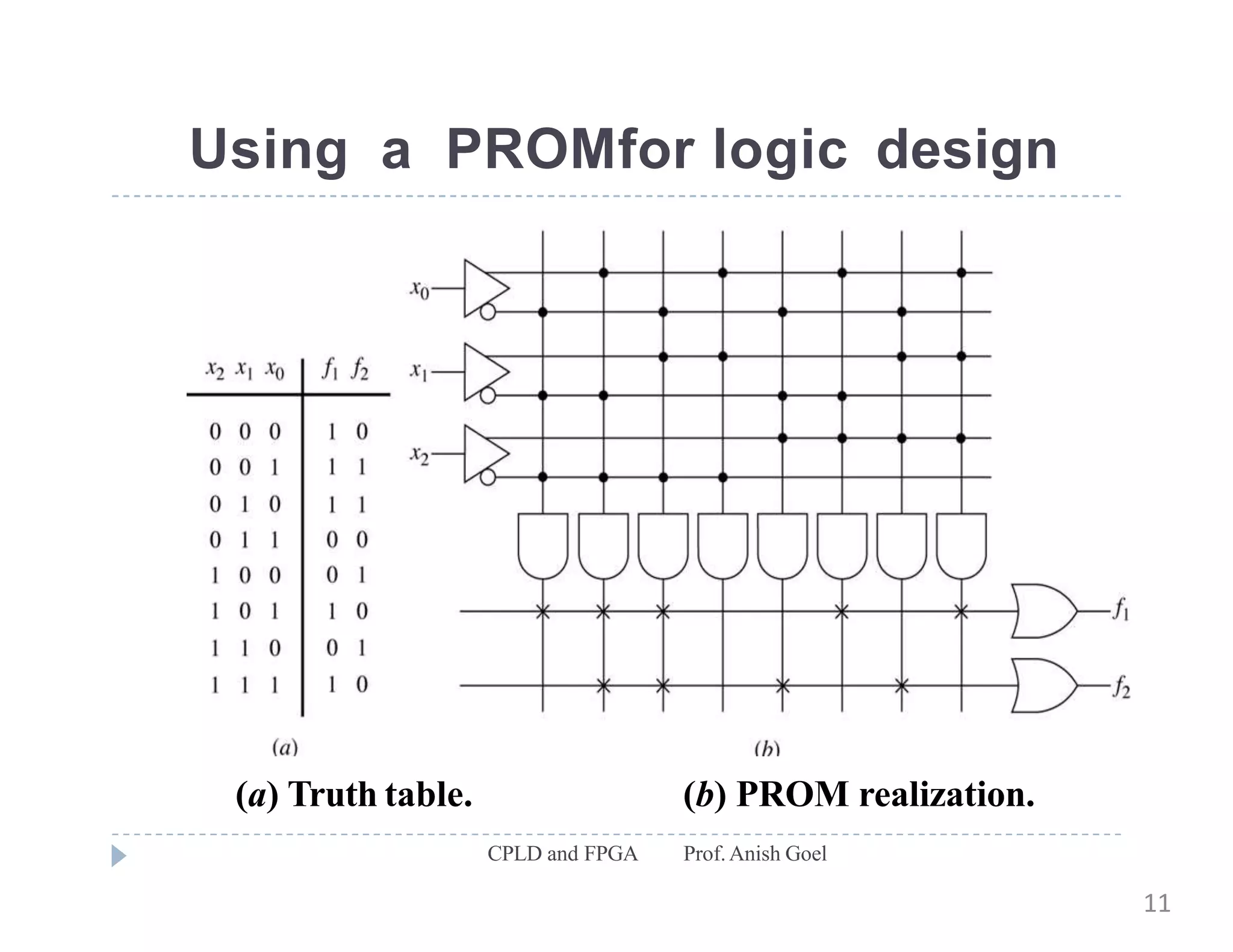
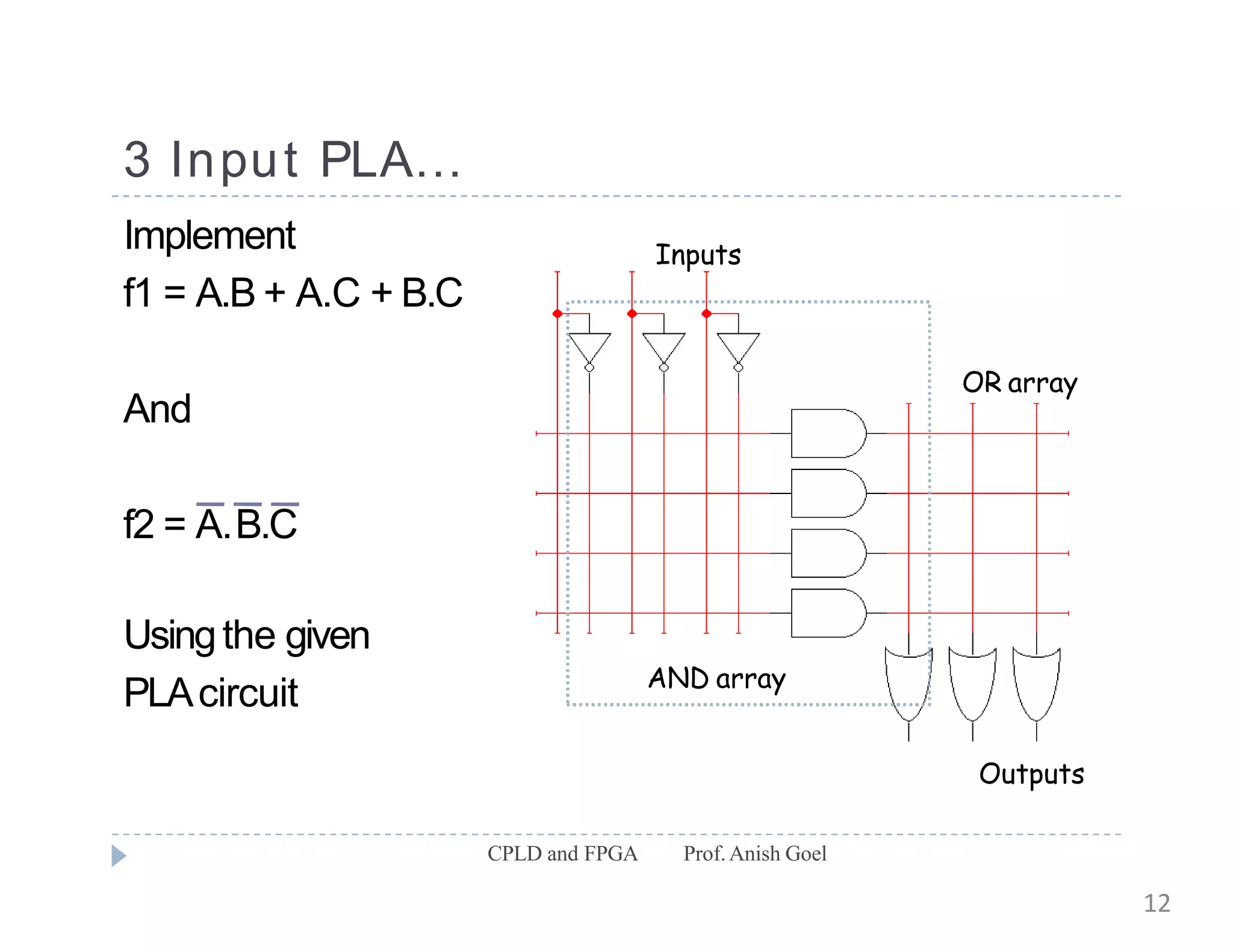
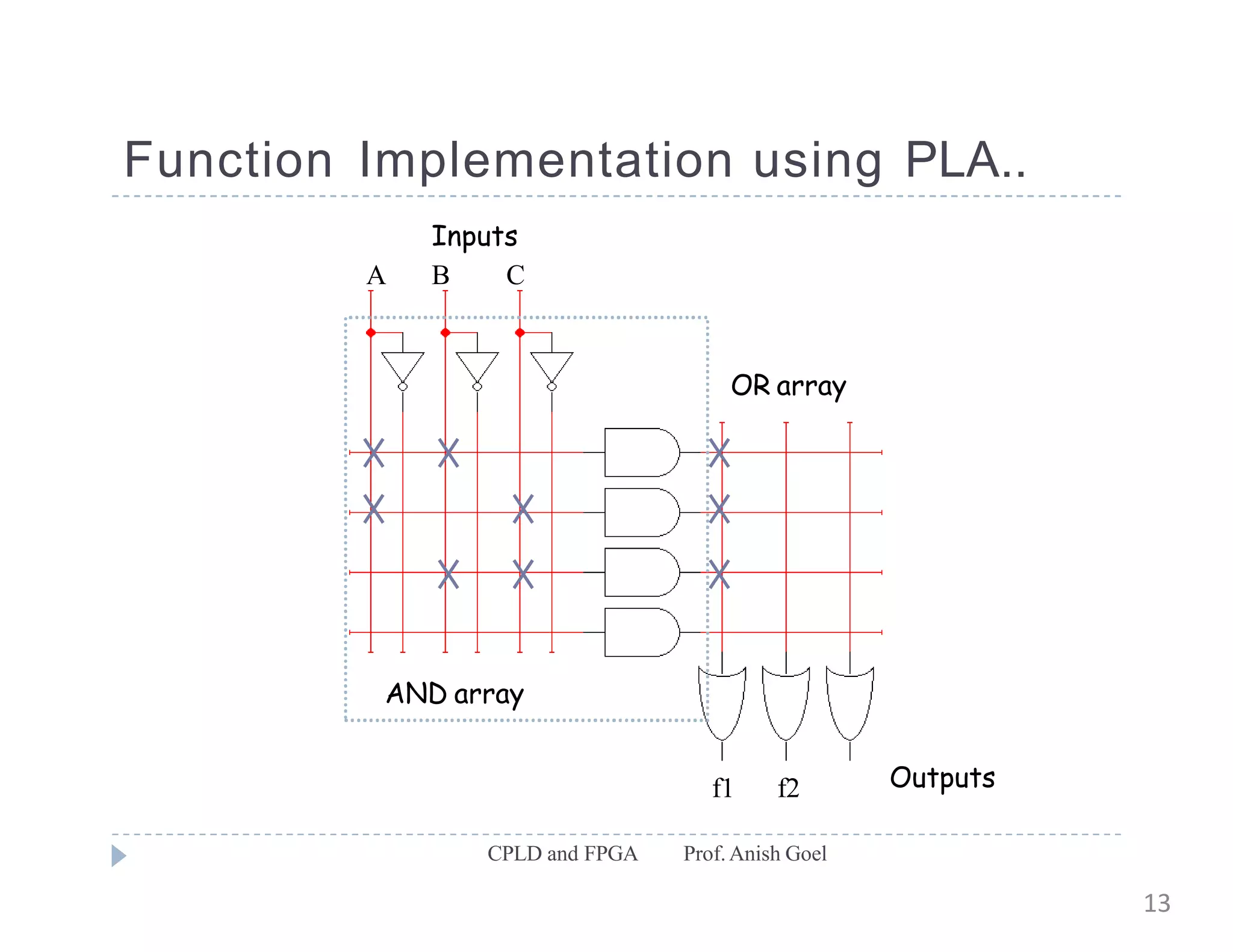
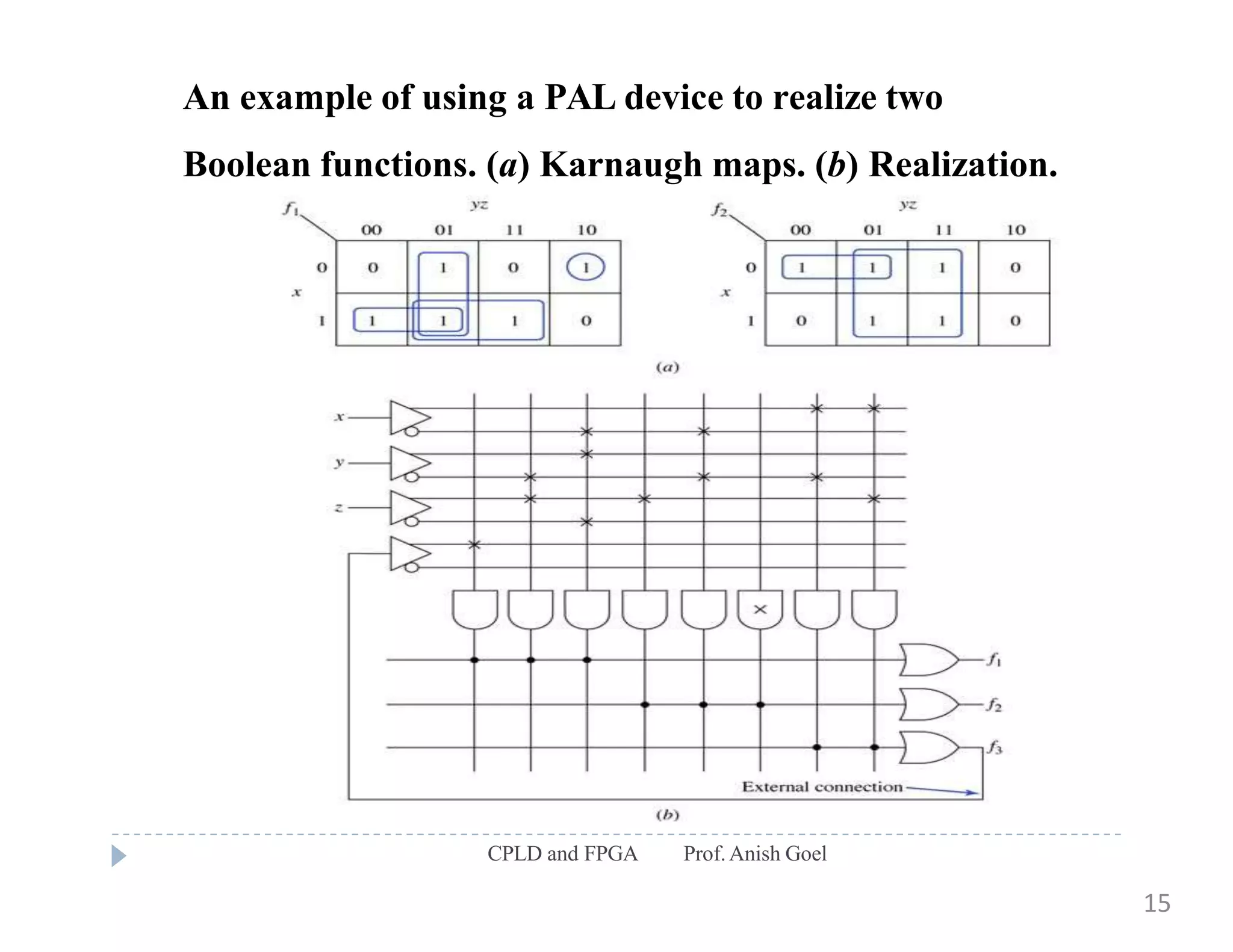
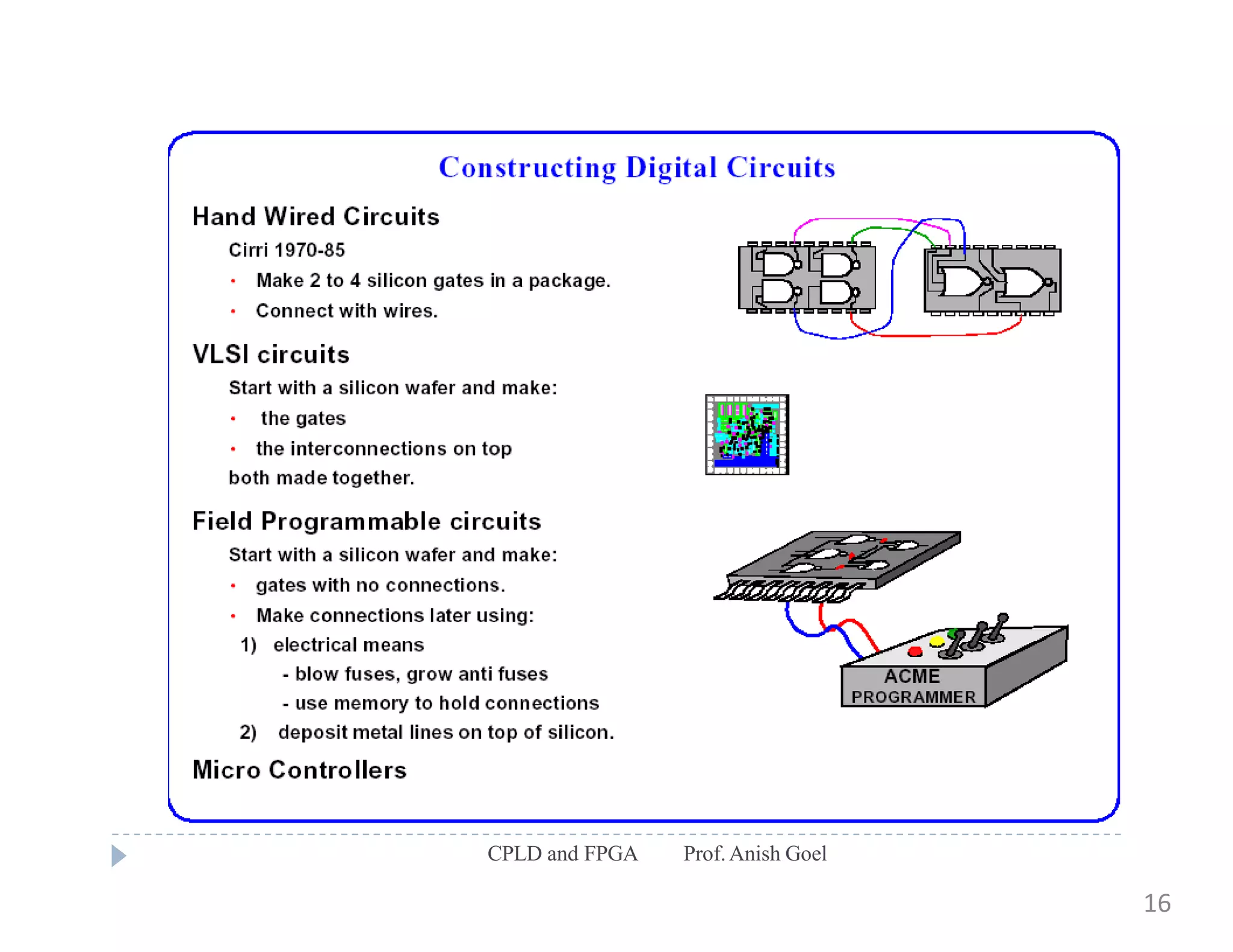
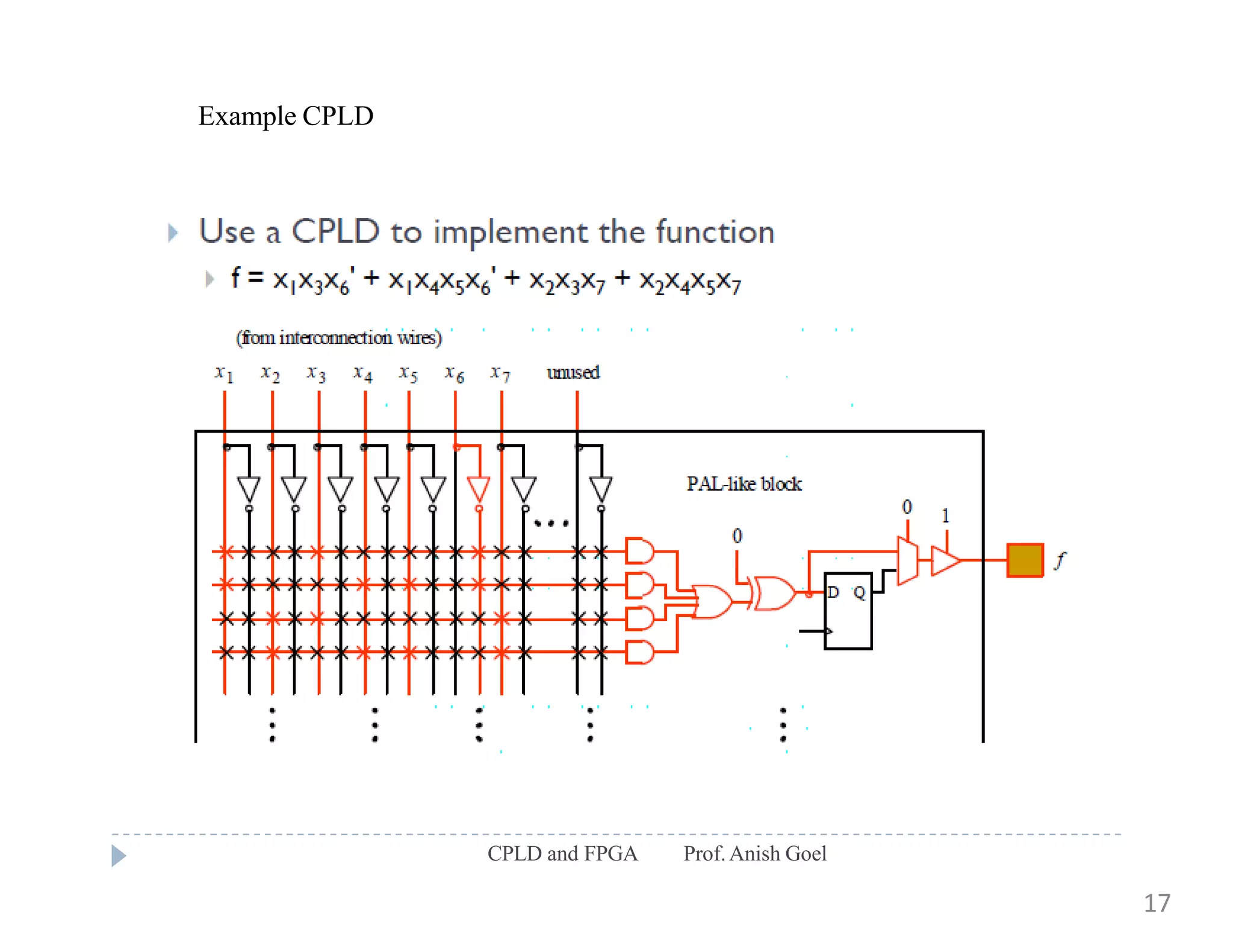
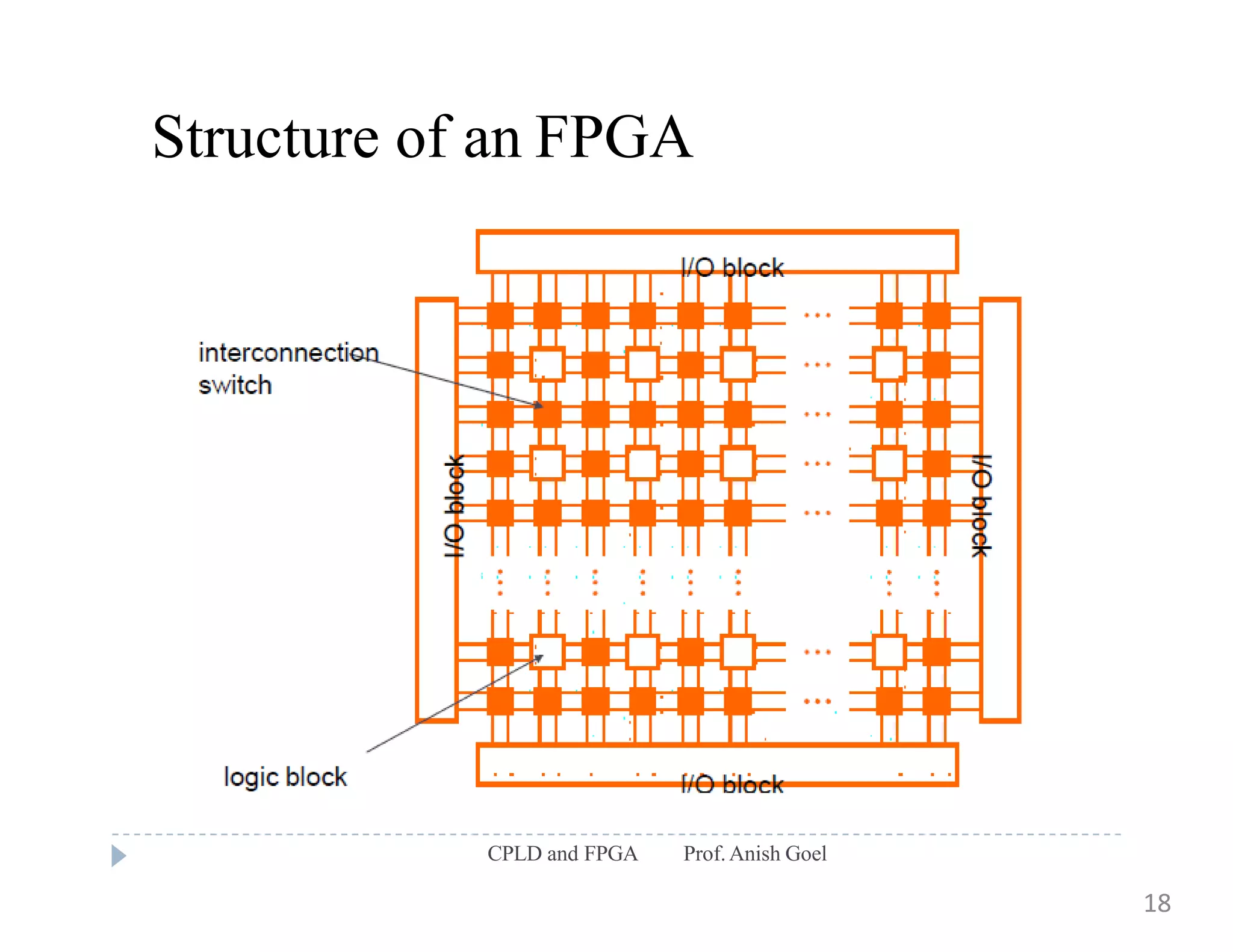
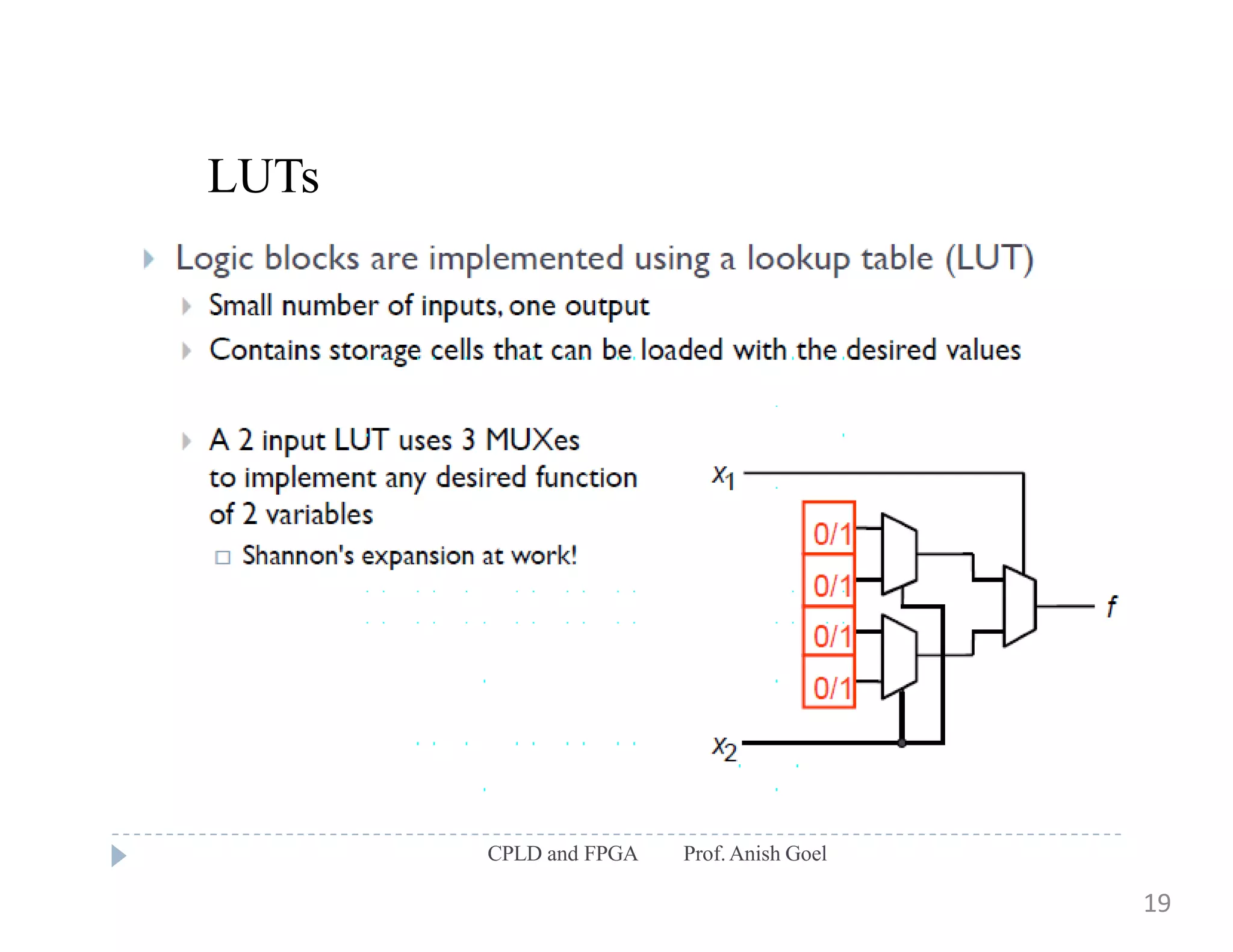
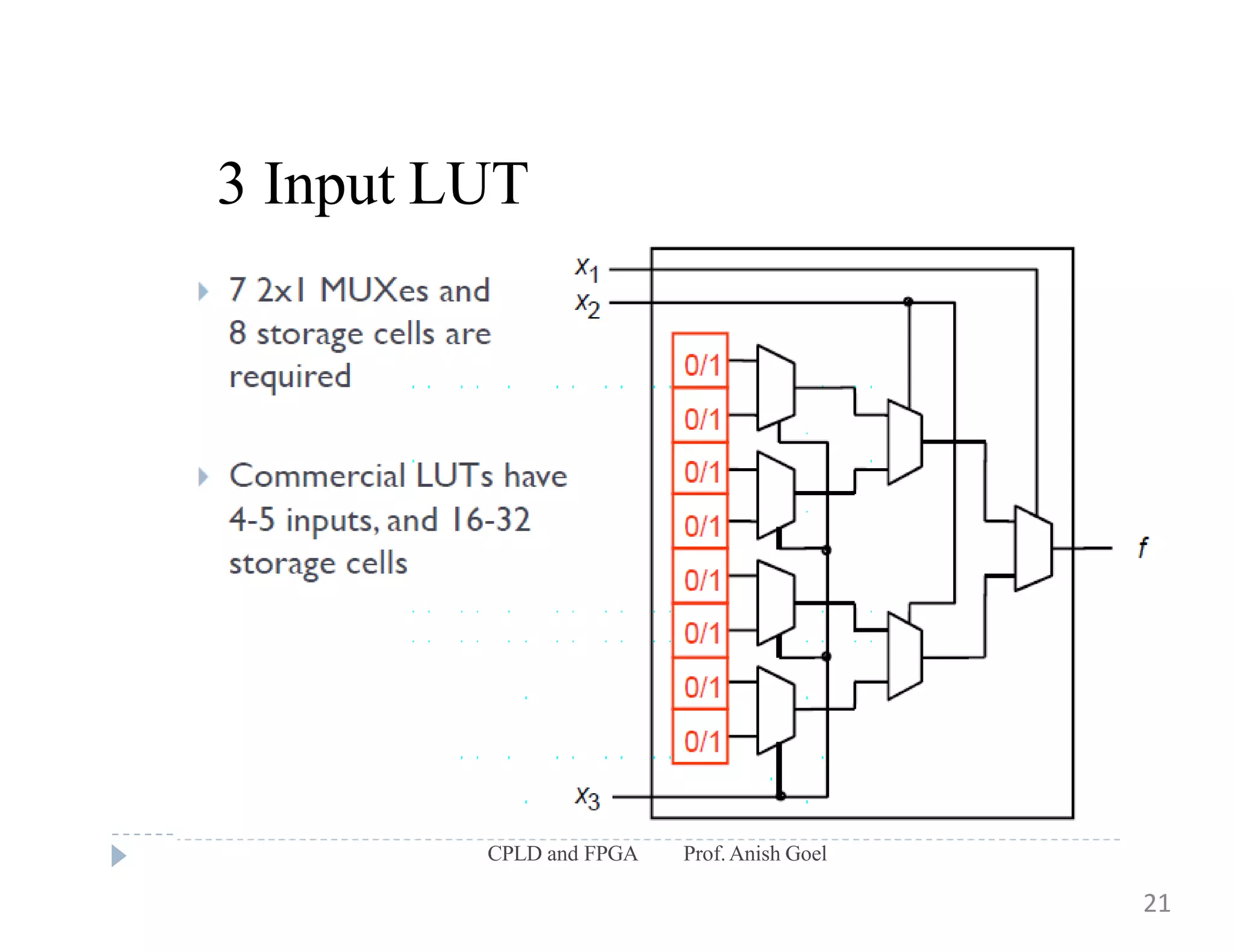
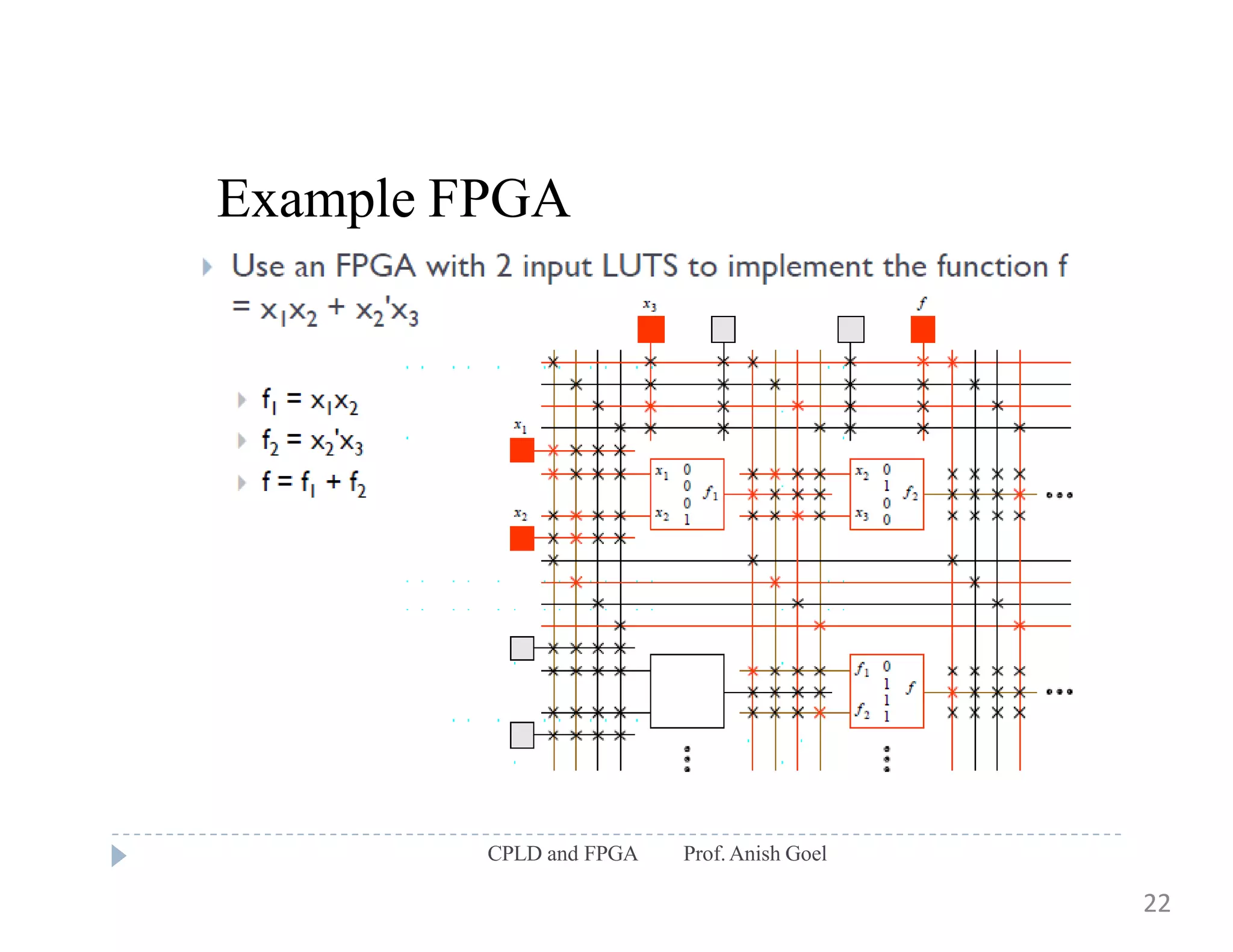
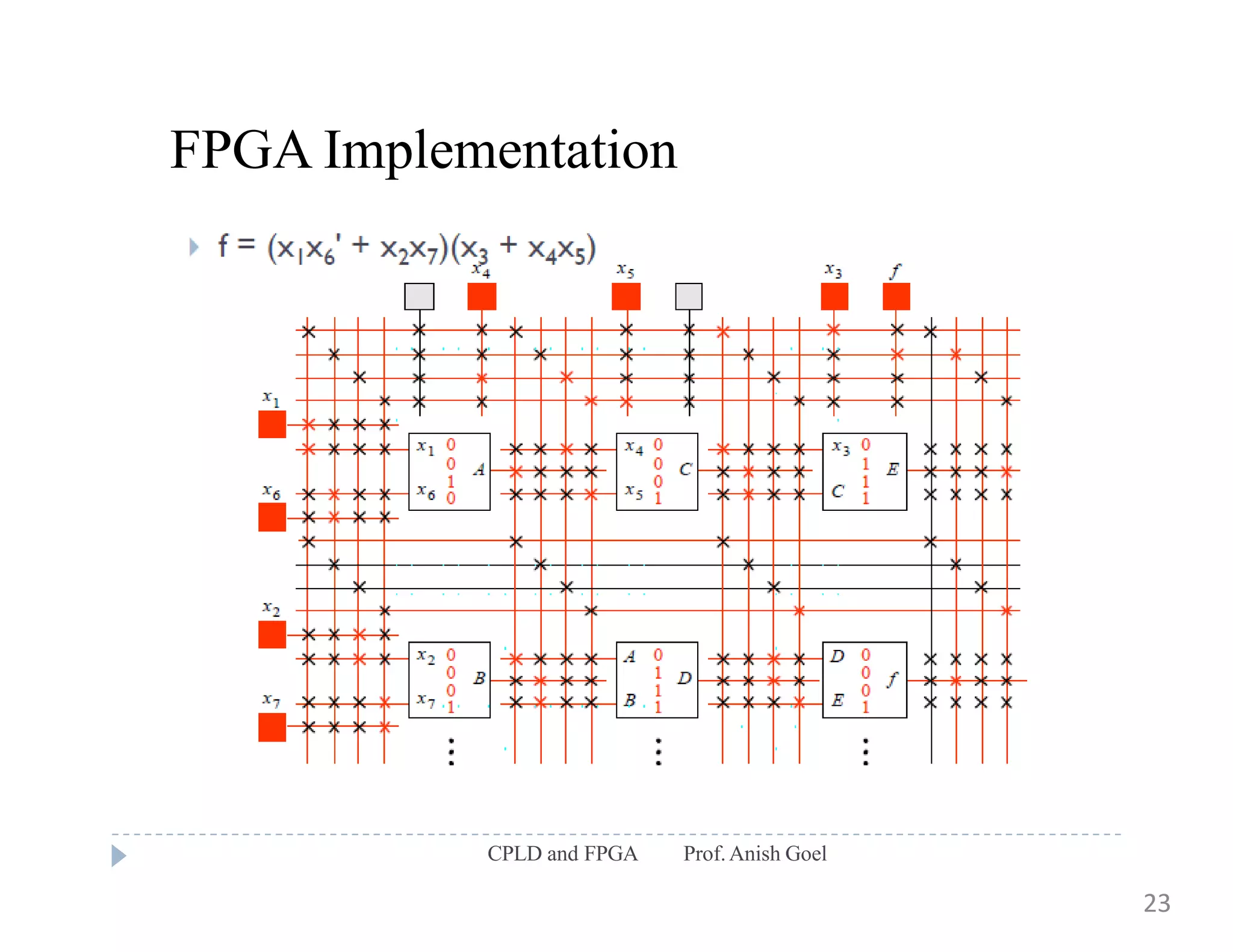
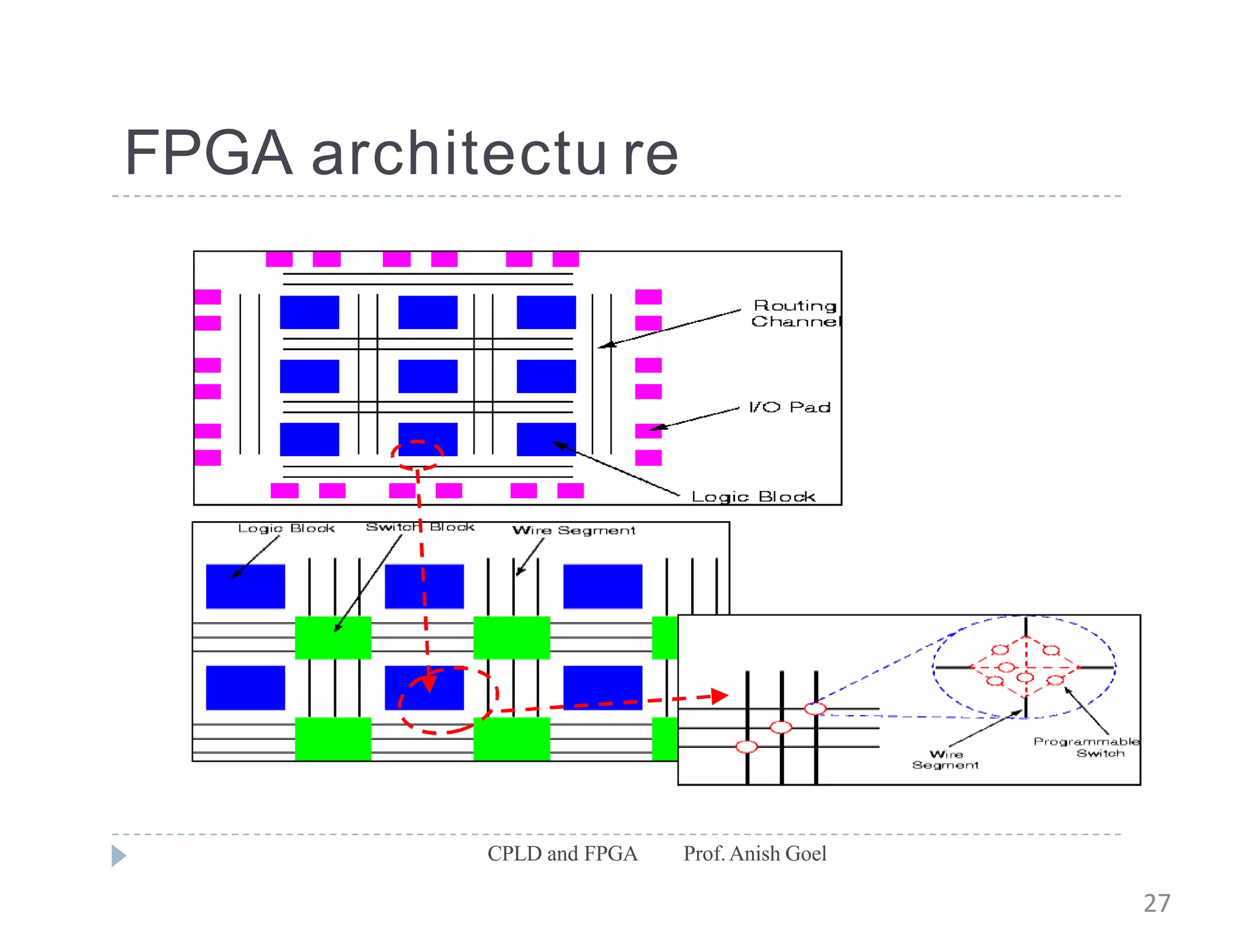
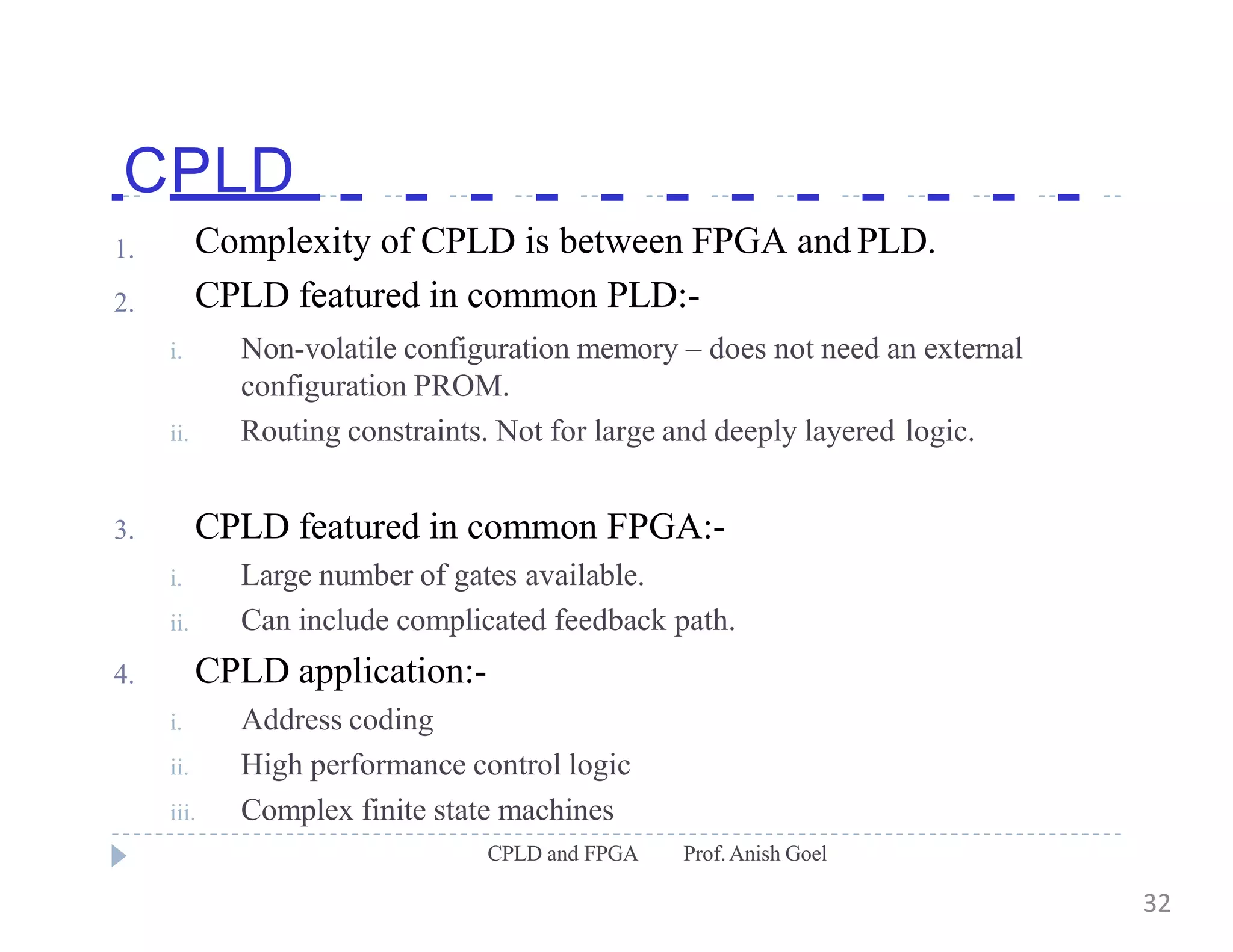
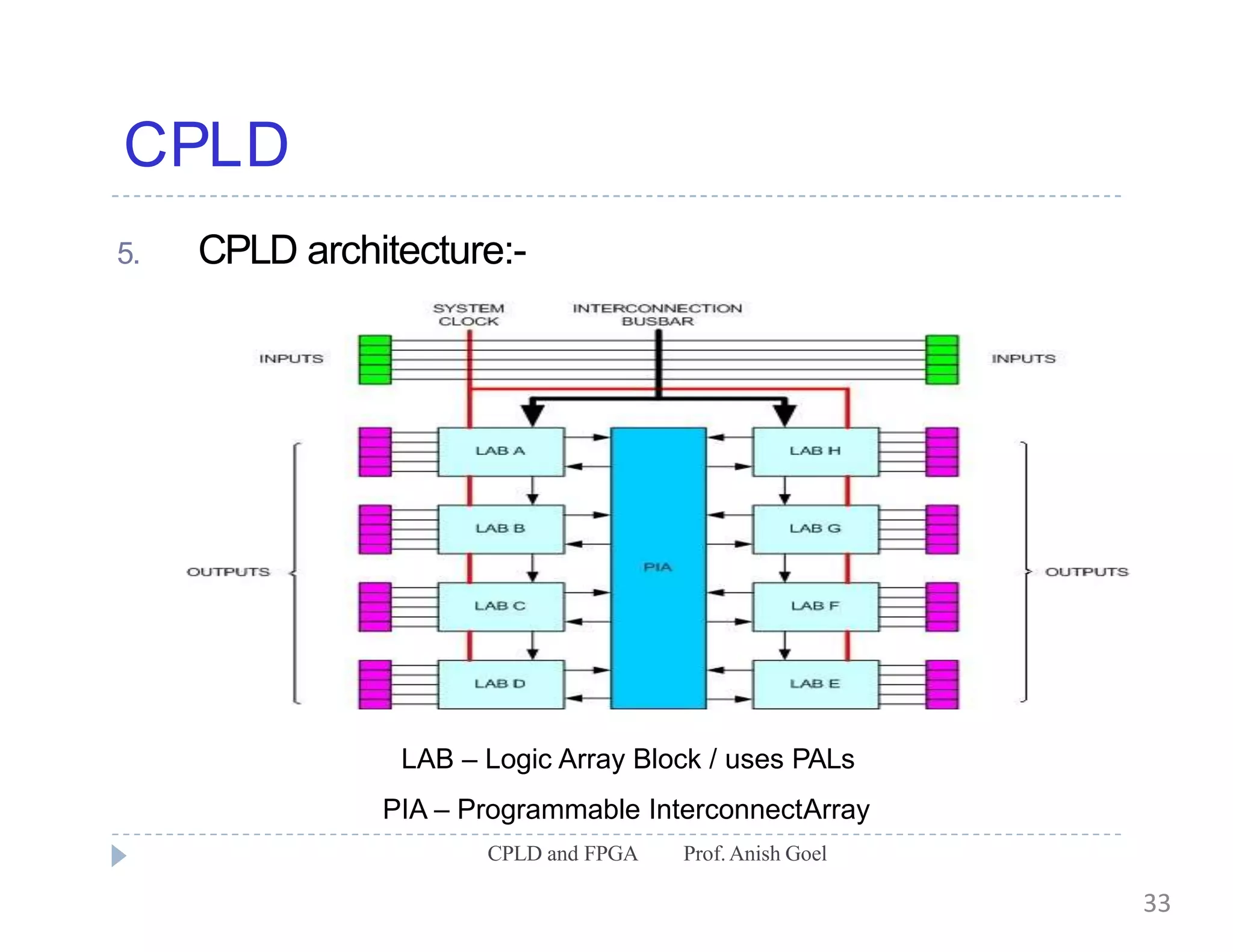
The document discusses the architecture of CPLDs and FPGAs. It begins by explaining the problems with using basic logic gates on PCBs and introduces programmable logic devices as a solution. It then describes different types of PLDs including PLA, PAL, GAL, CPLD and FPGA. CPLDs have a complexity between FPGAs and basic PLDs, containing non-volatile memory and supporting larger logic than PLDs. FPGAs contain logic cells, interconnects, and can implement thousands of gates. The document provides examples of implementing logic with different PLDs and describes the architecture and programming of CPLDs and FPGAs.