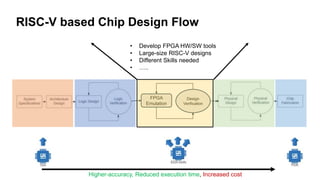
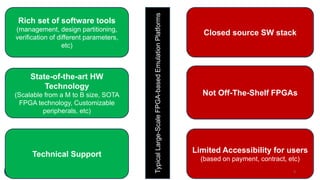
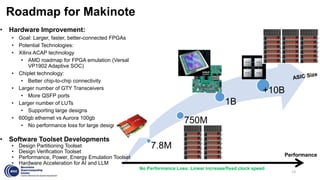
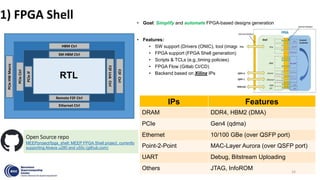
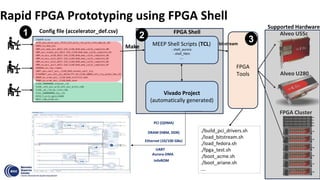
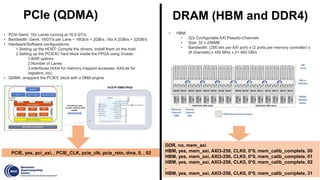
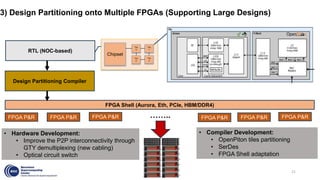
This document summarizes an FPGA-based emulation platform called Makinote developed by BSC for prototyping large-scale RISC-V designs. It discusses the Makinote hardware platform consisting of an FPGA cluster with over 100 FPGAs and software tools. The tools include an FPGA shell for design implementation, integration with OpenPiton, and design partitioning across multiple FPGAs. Design verification methods using the FPGA platform aim to speed up verification by 3 orders of magnitude compared to simulation. Makinote is intended as an open platform for research collaboration in contrast to closed commercial emulation systems.