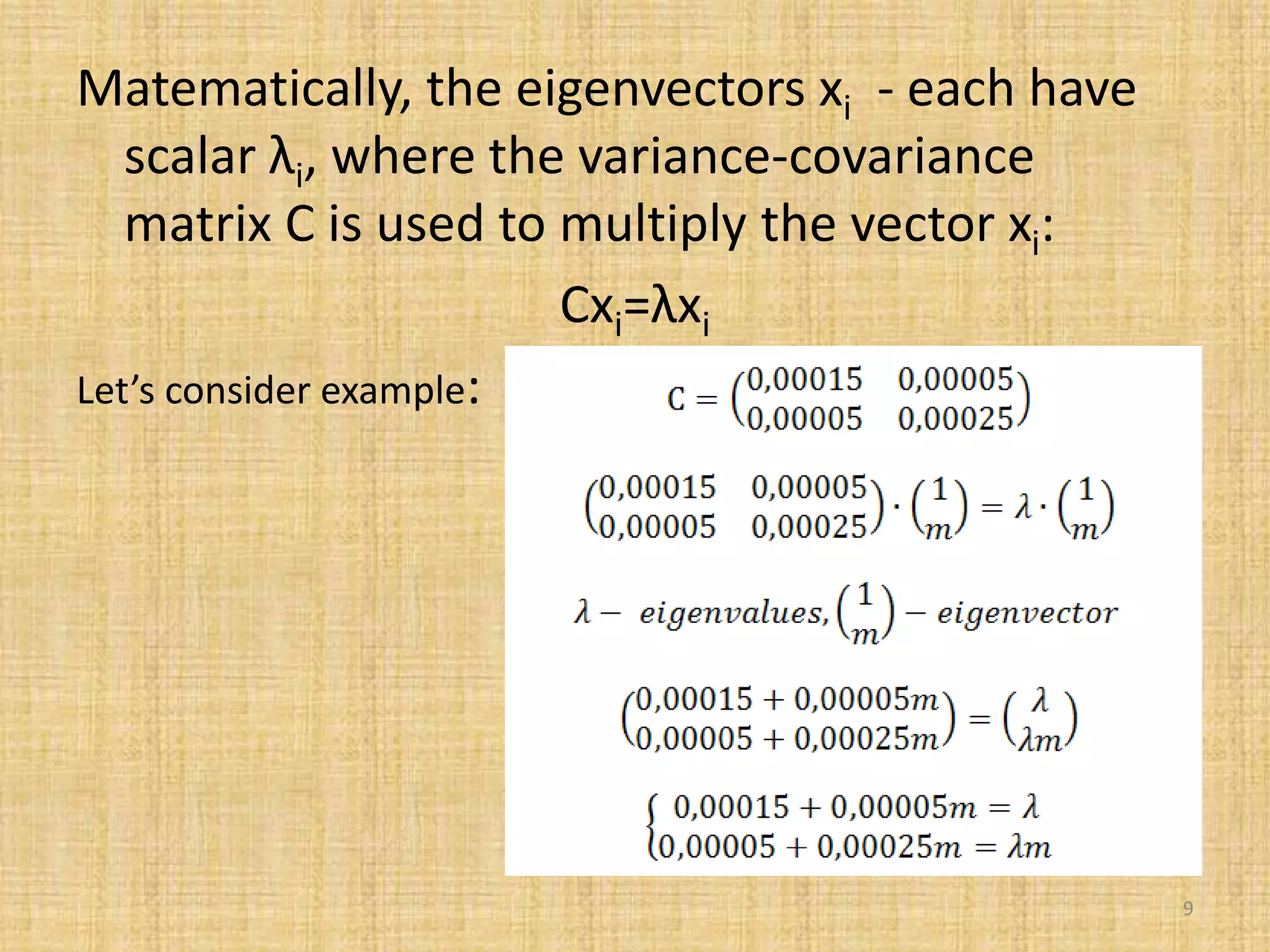
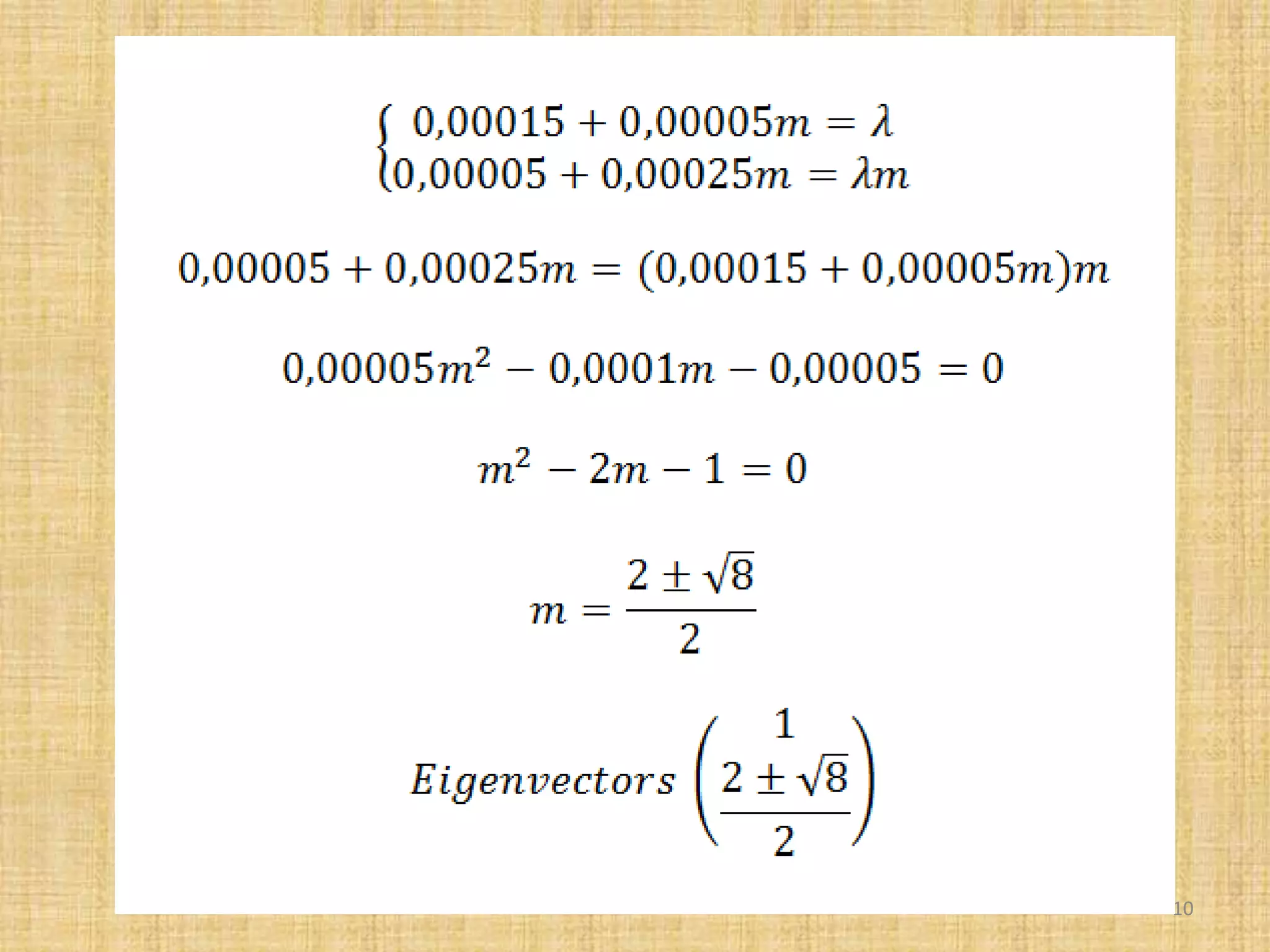
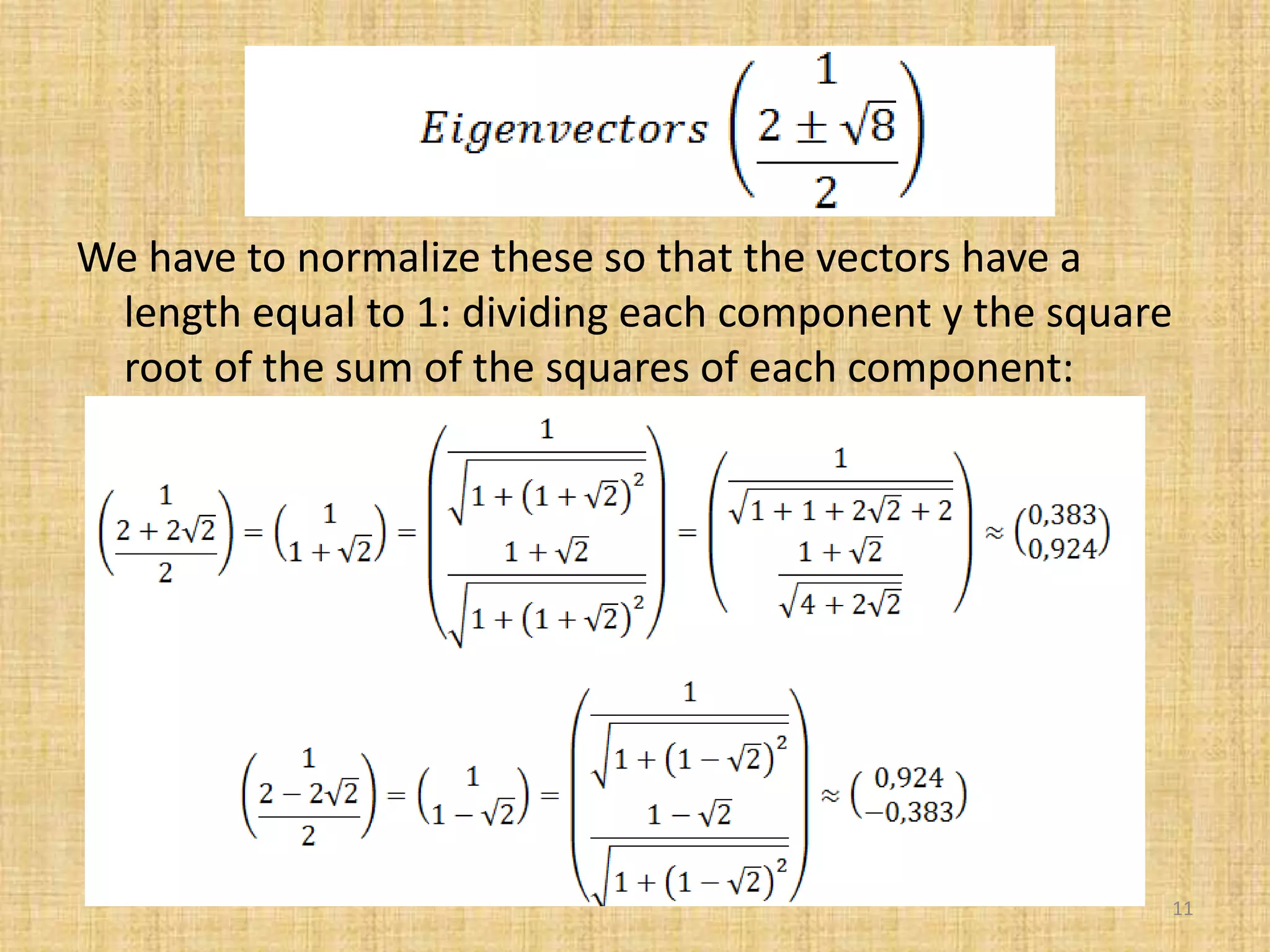
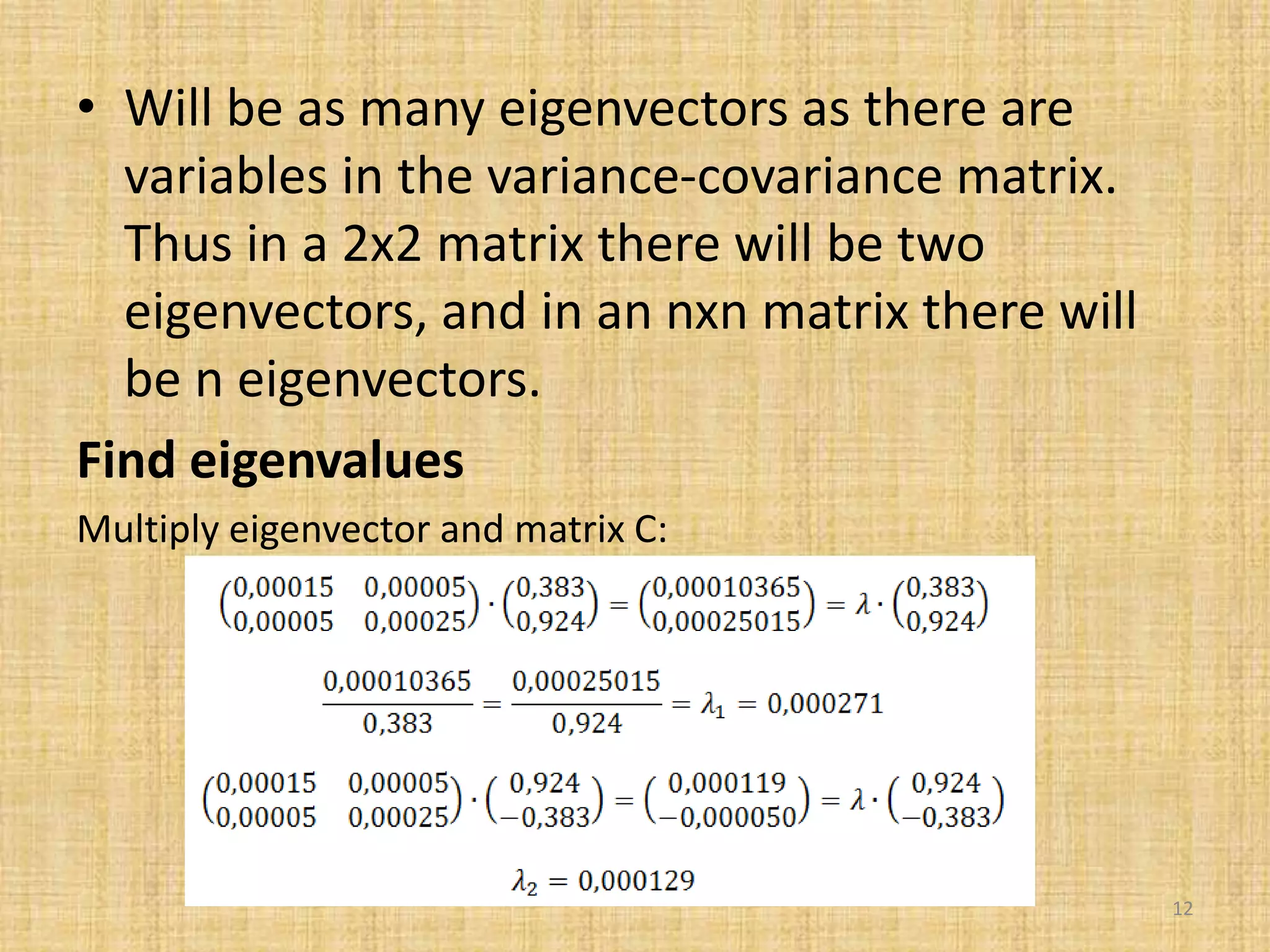
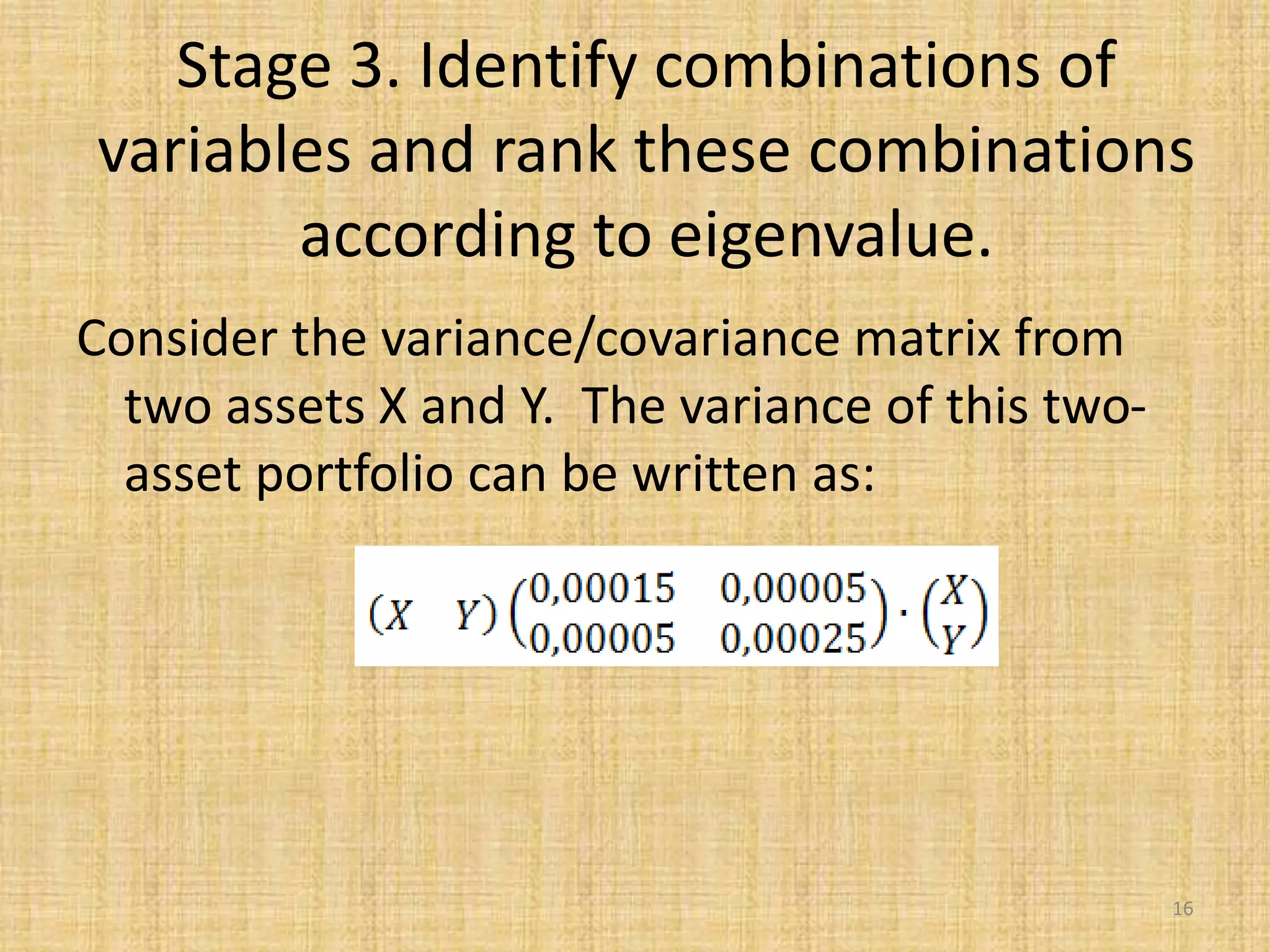
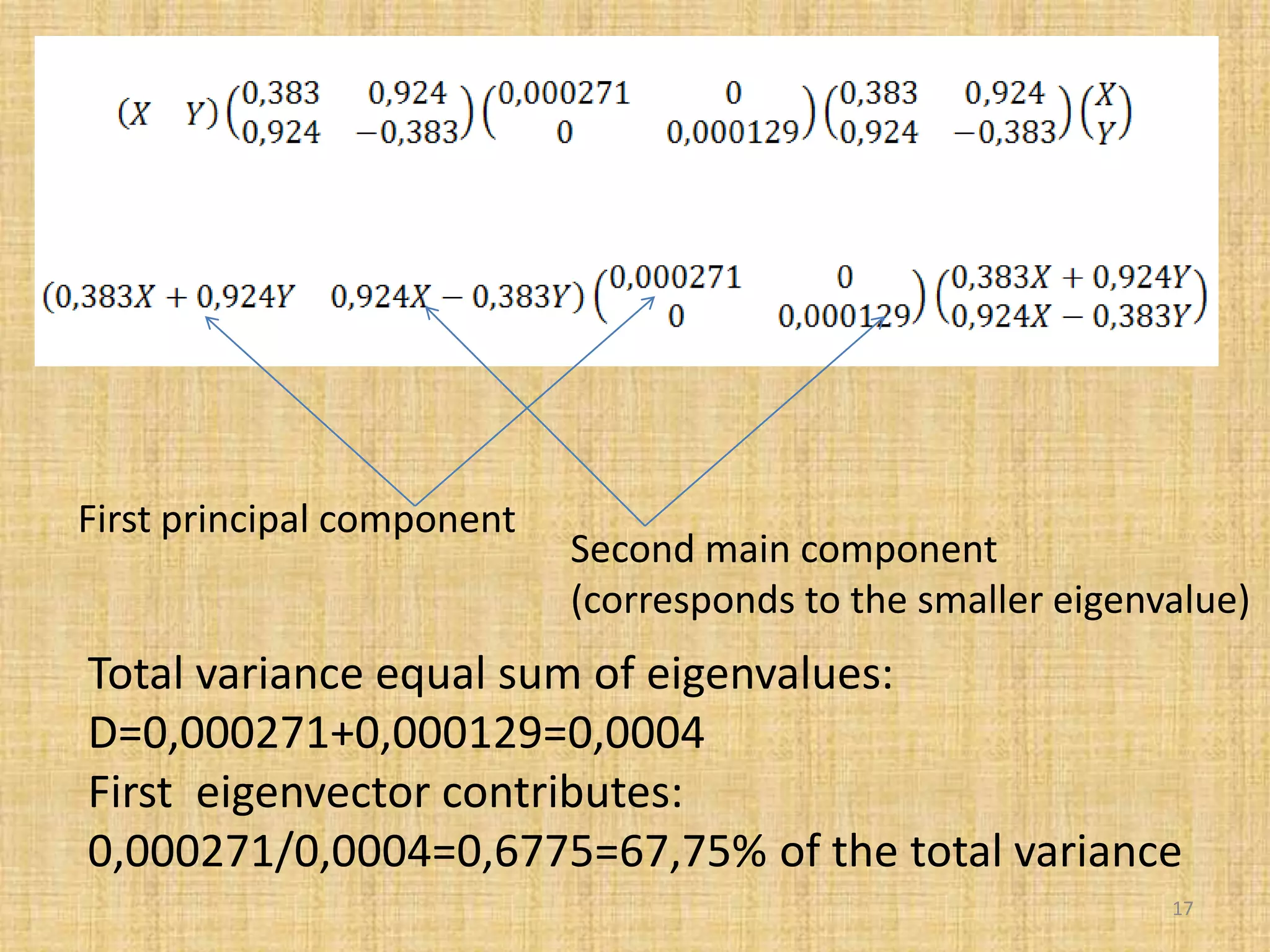
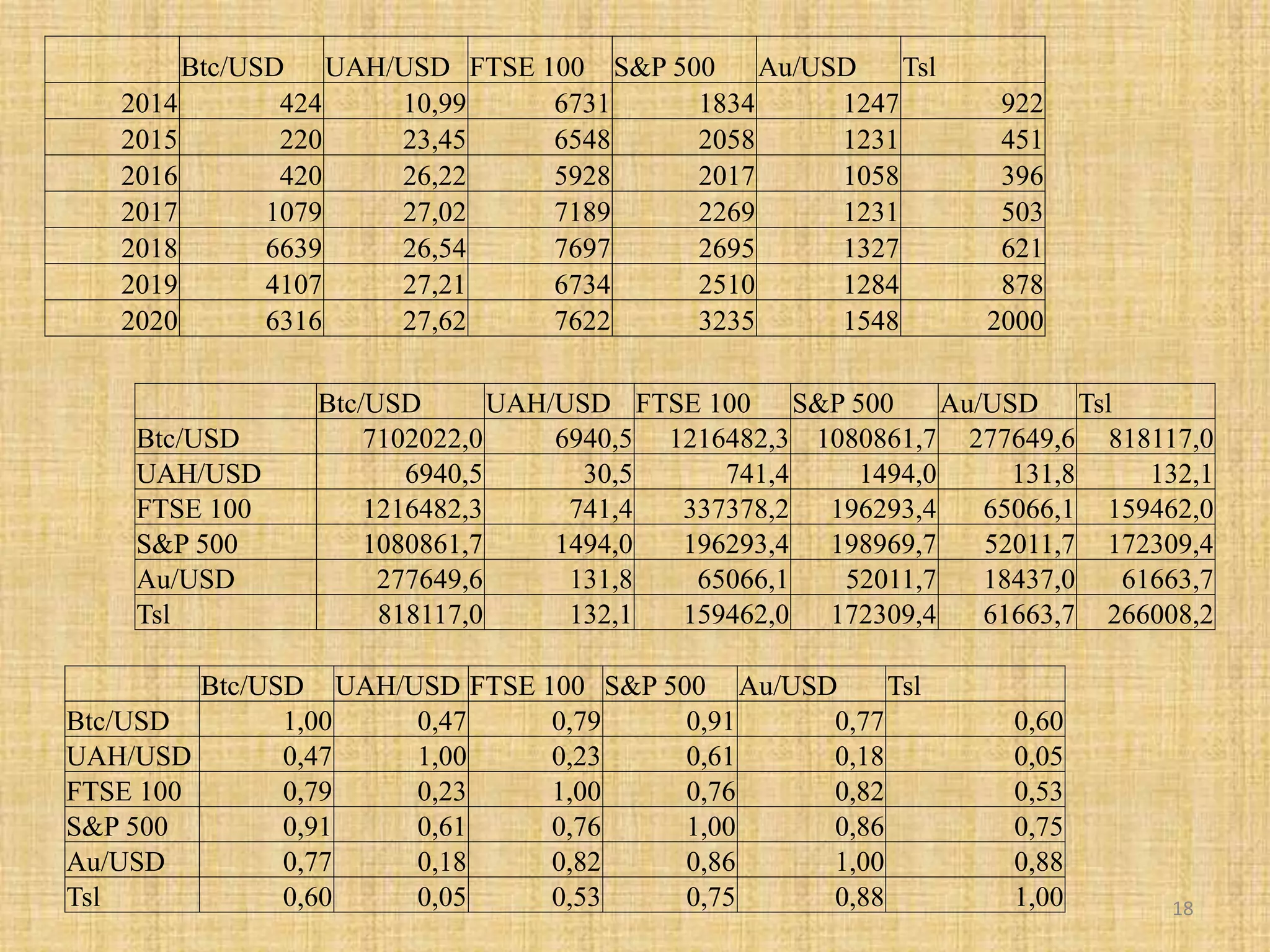
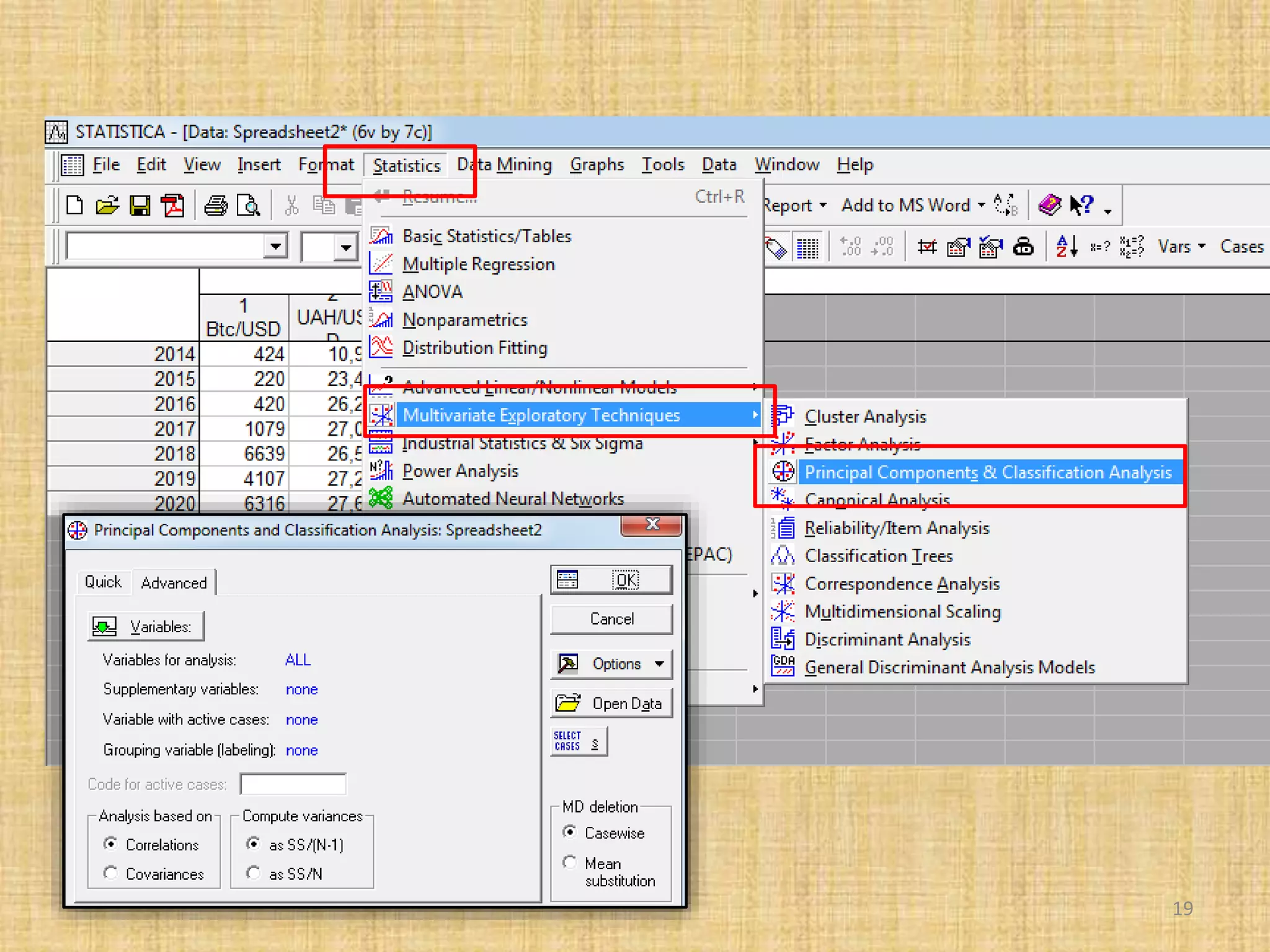
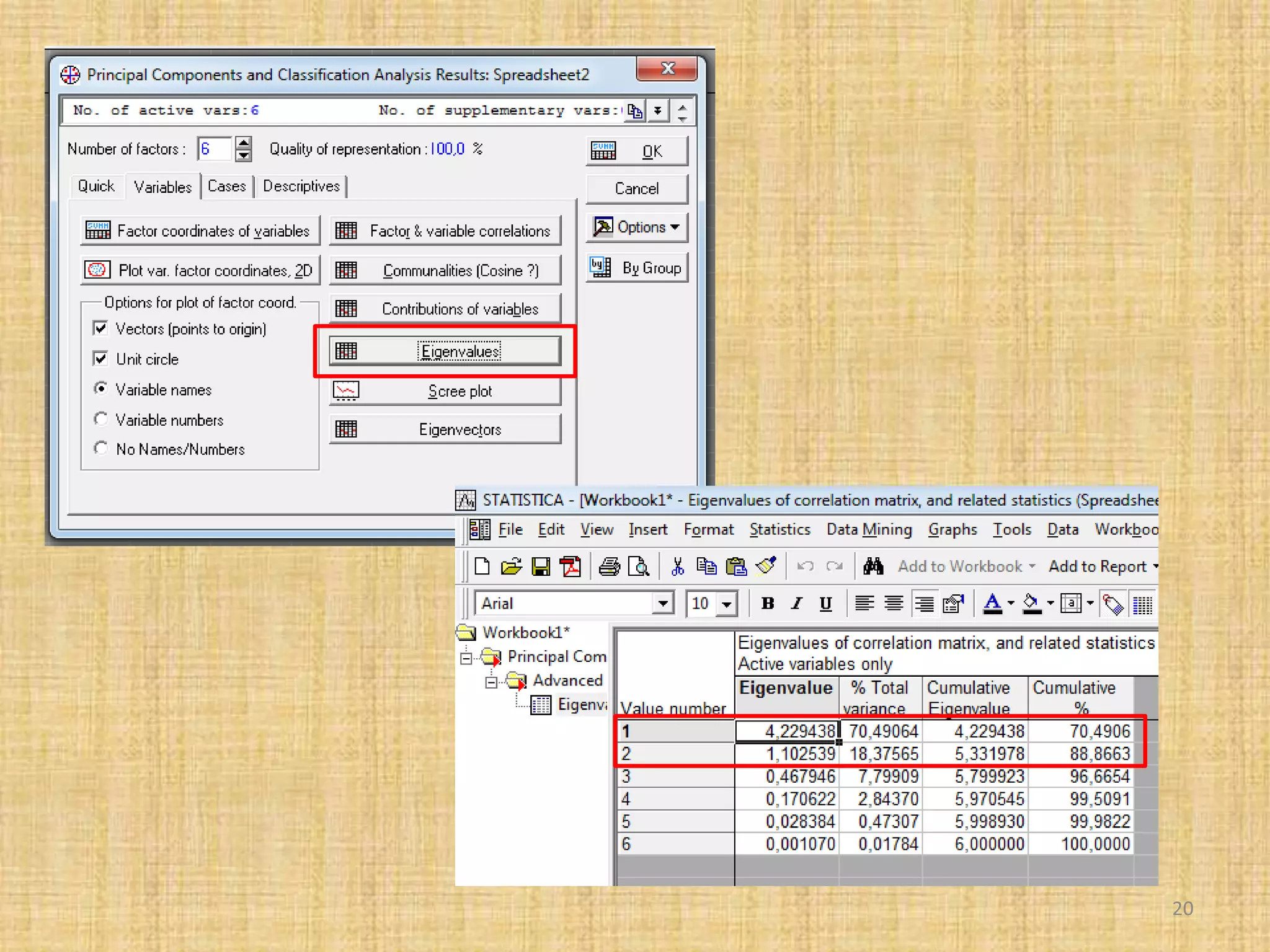
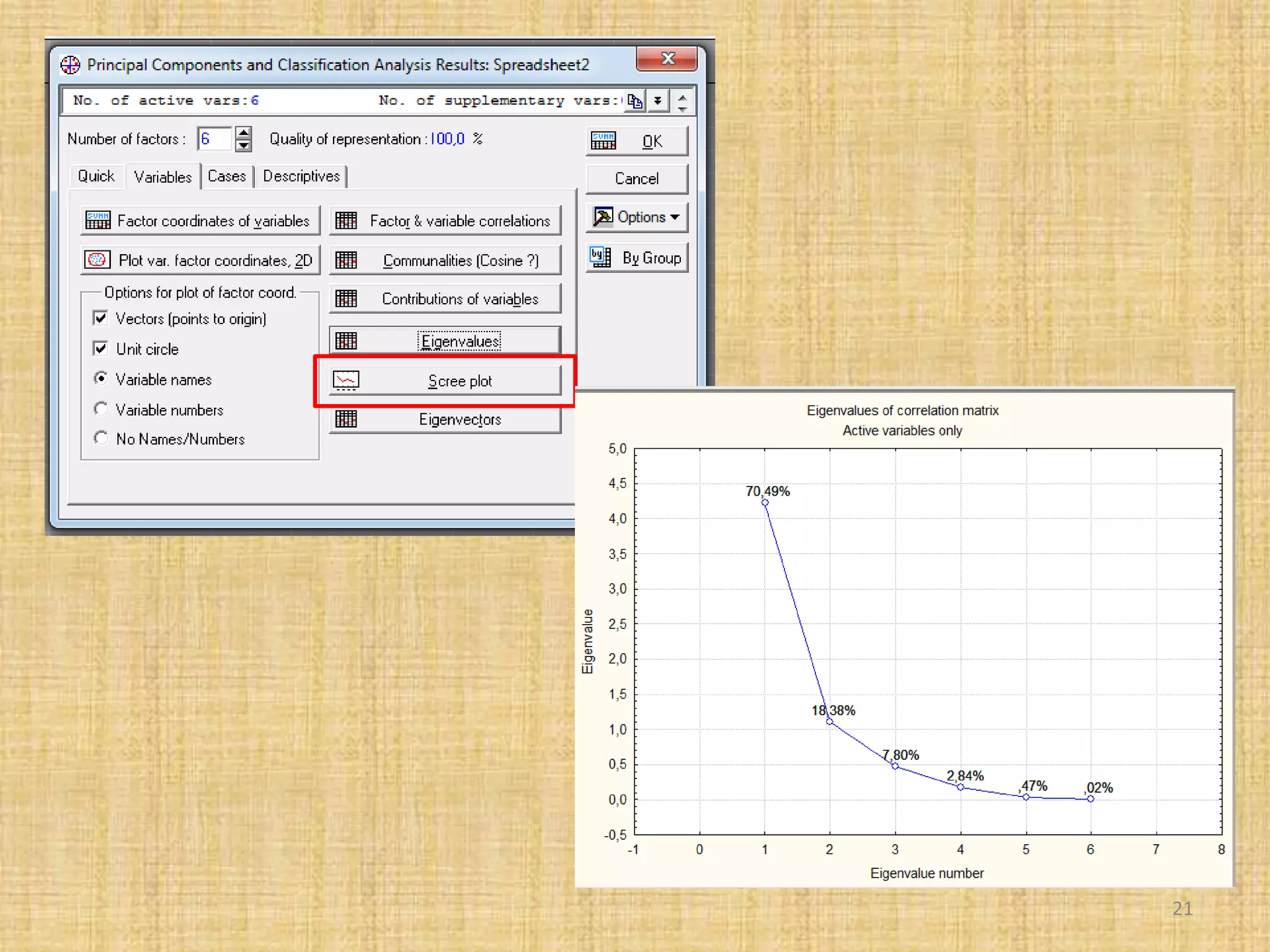
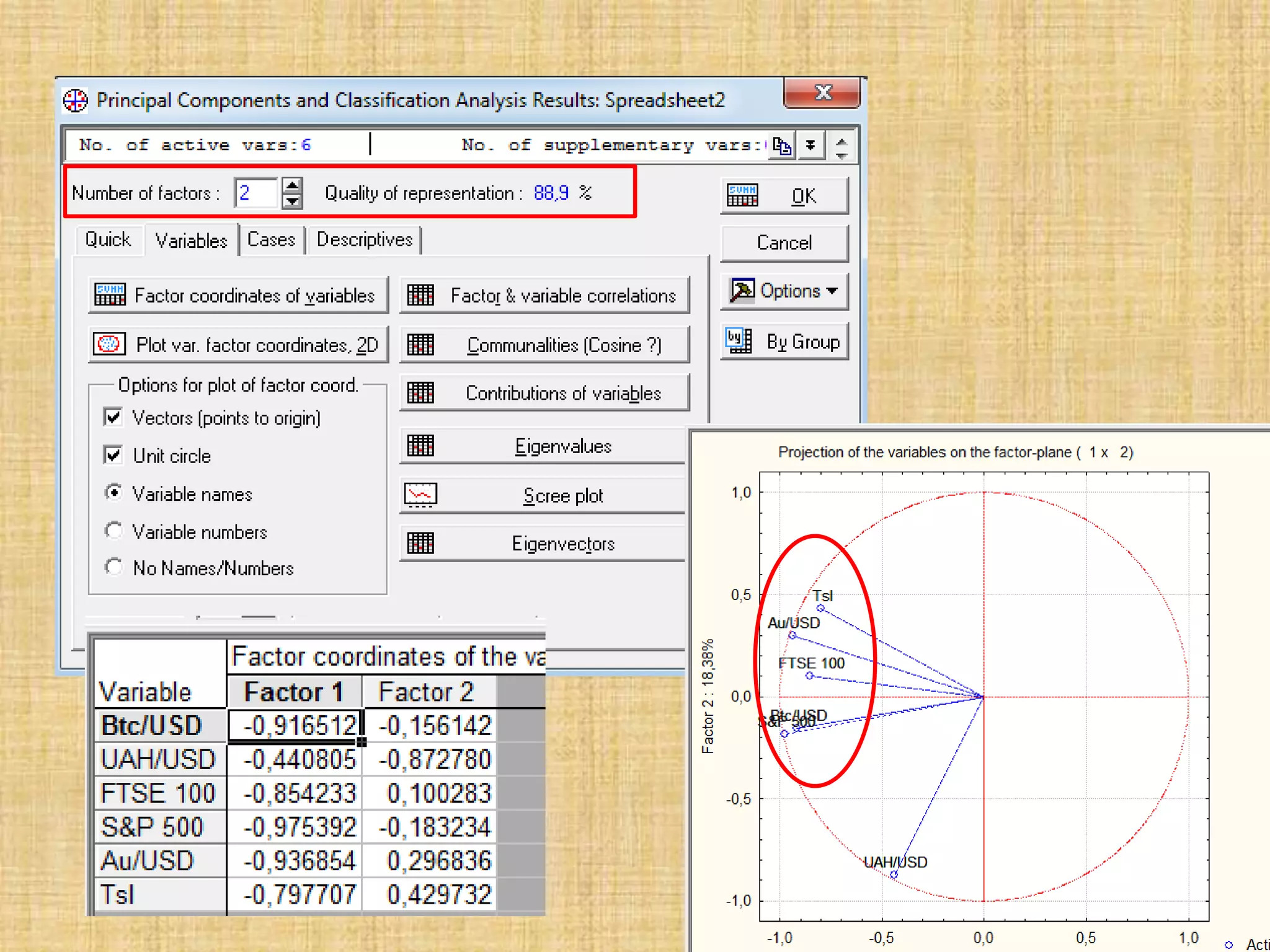
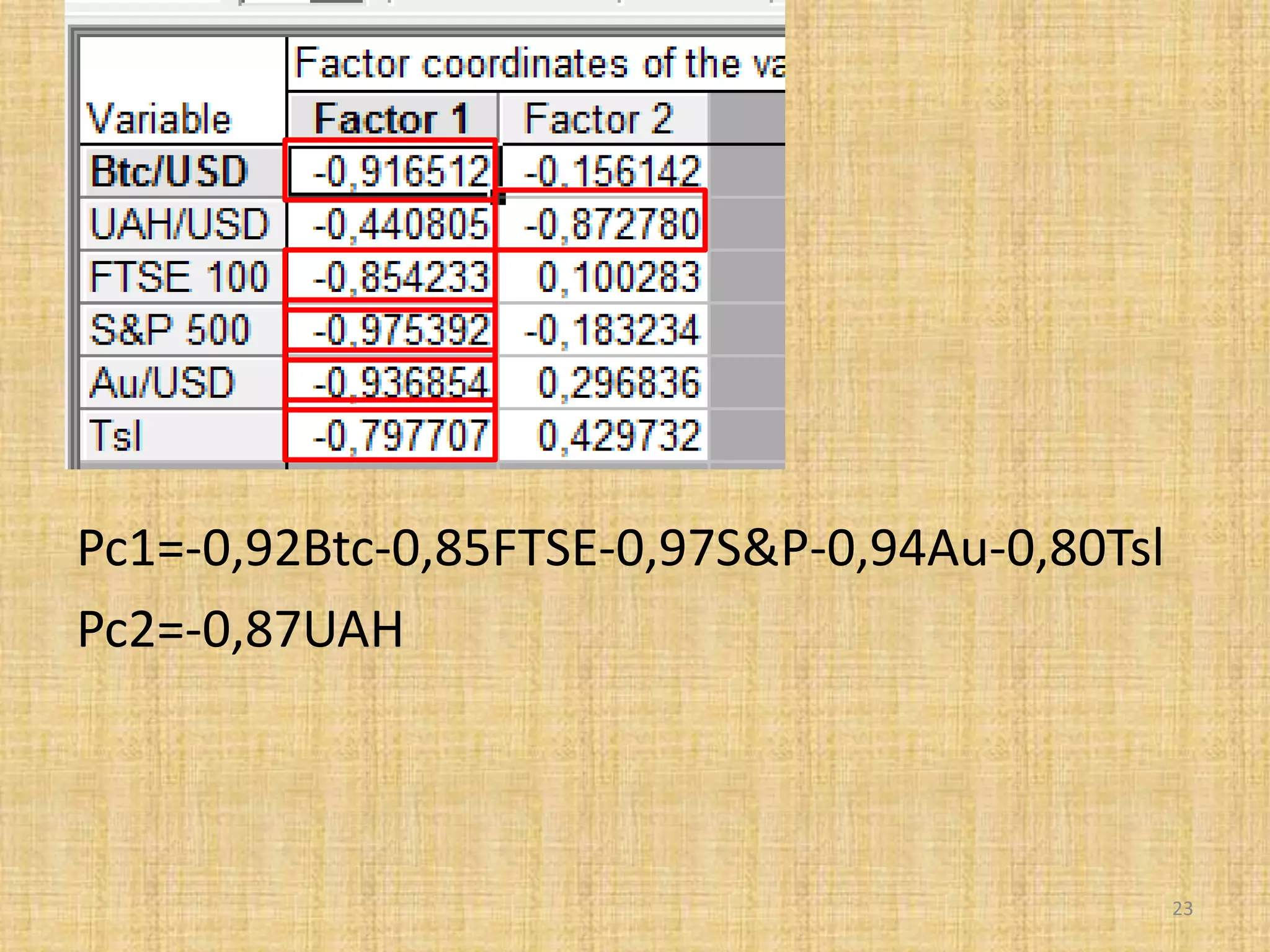
The document discusses multivariate analysis techniques, specifically principal components analysis (PCA) and factor analysis (FA), emphasizing their application in understanding data structure. It outlines the stages of PCA, including finding eigenvectors and eigenvalues, constructing matrices, and identifying ranked combinations of variables. Additionally, it highlights the purpose of PCA in reducing data dimensionality and interpreting variance in datasets.