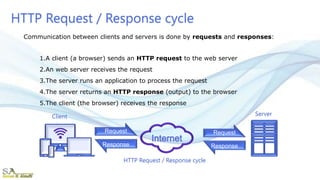
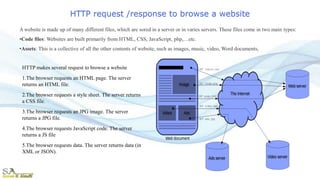
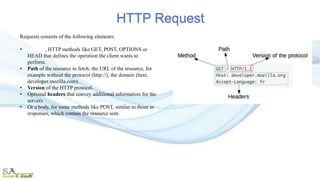
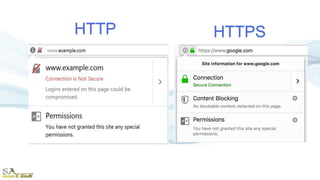
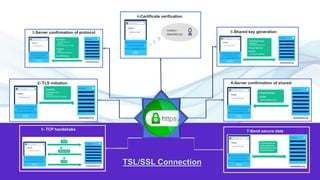
The document provides an overview of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and its secure variant, HTTPS, outlining their features, functionalities, and the request/response cycle. HTTP is a connectionless, stateless protocol used to transfer various data types over the web, while HTTPS adds security through encryption using TLS and SSL. Key differences between HTTP and HTTPS include security measures, port usage, and their applications in transferring sensitive information.