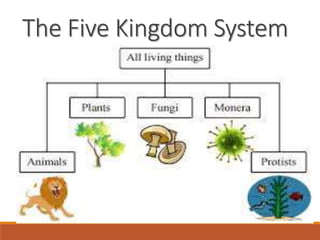
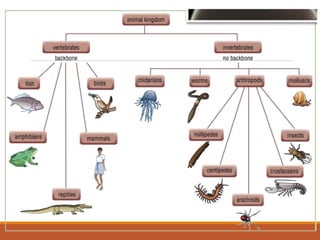
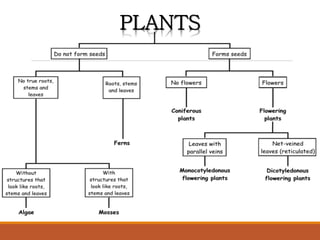
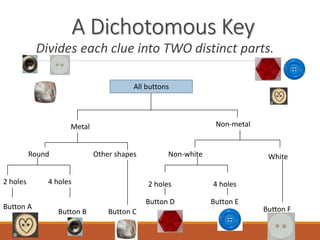
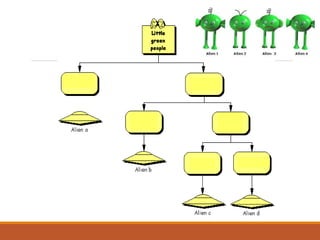
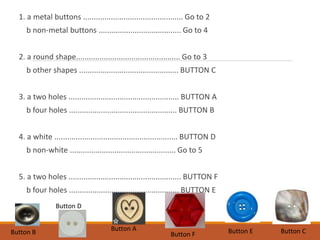
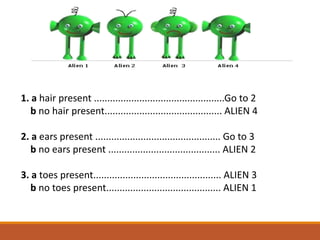
The document discusses the classification of living things, describing how Aristotle was one of the first to classify organisms into groups based on their characteristics. It explains that today Carolus Linnaeus' system of binomial nomenclature, which assigns every species a two-part scientific name, is still used. The document also outlines the five kingdom system of classification and provides examples of how dichotomous keys can be used to classify organisms based on distinguishing characteristics.