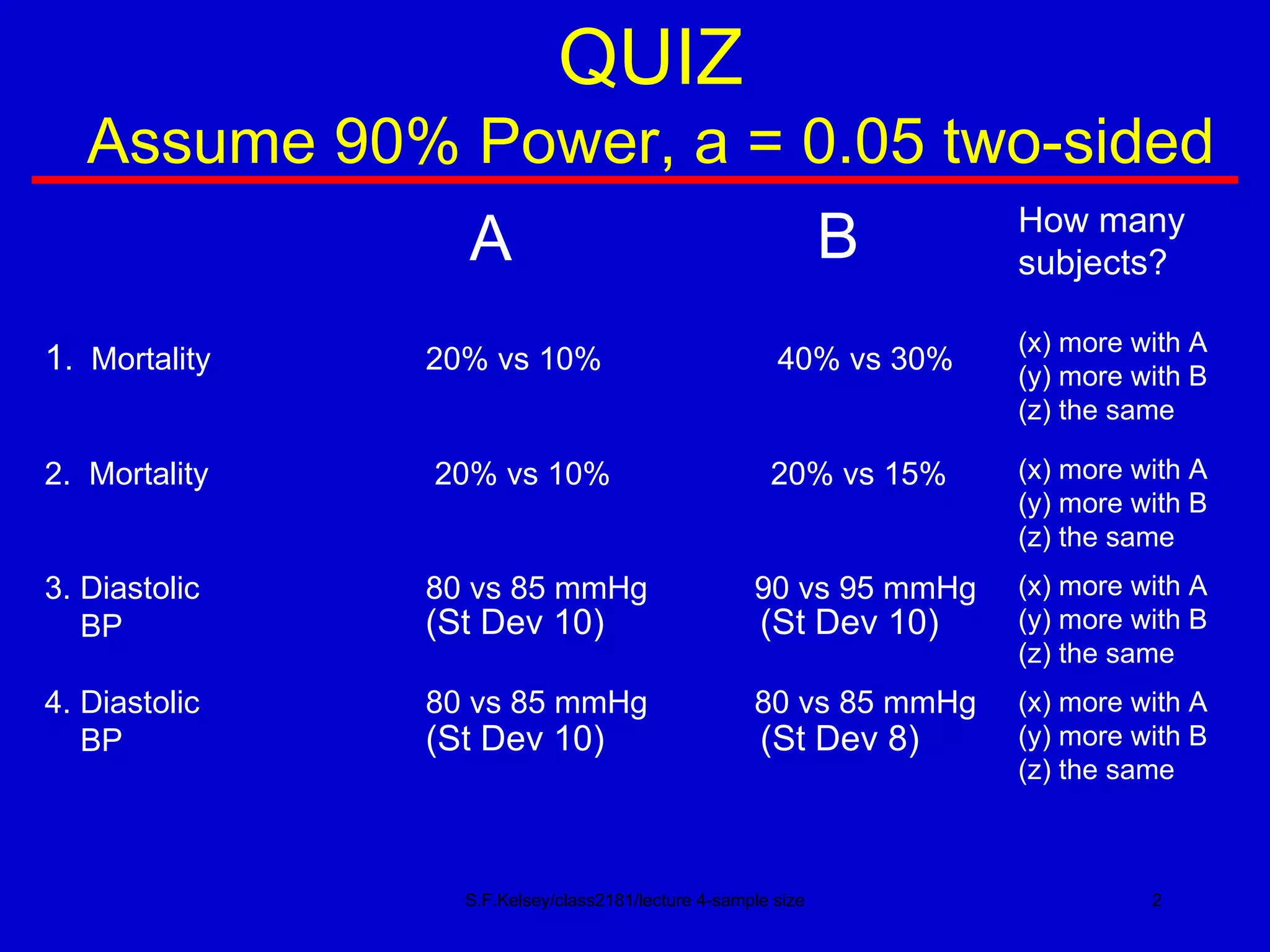
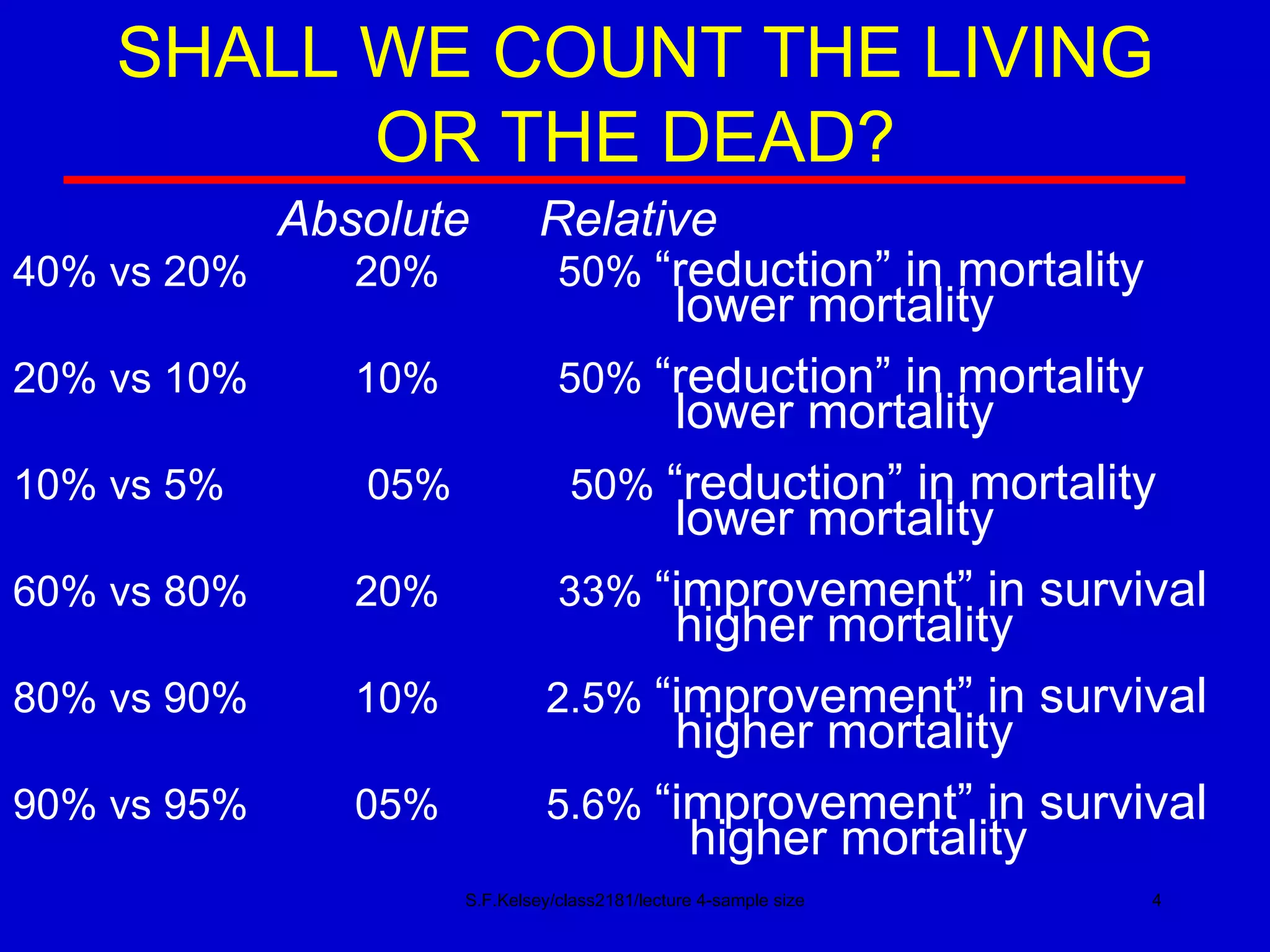
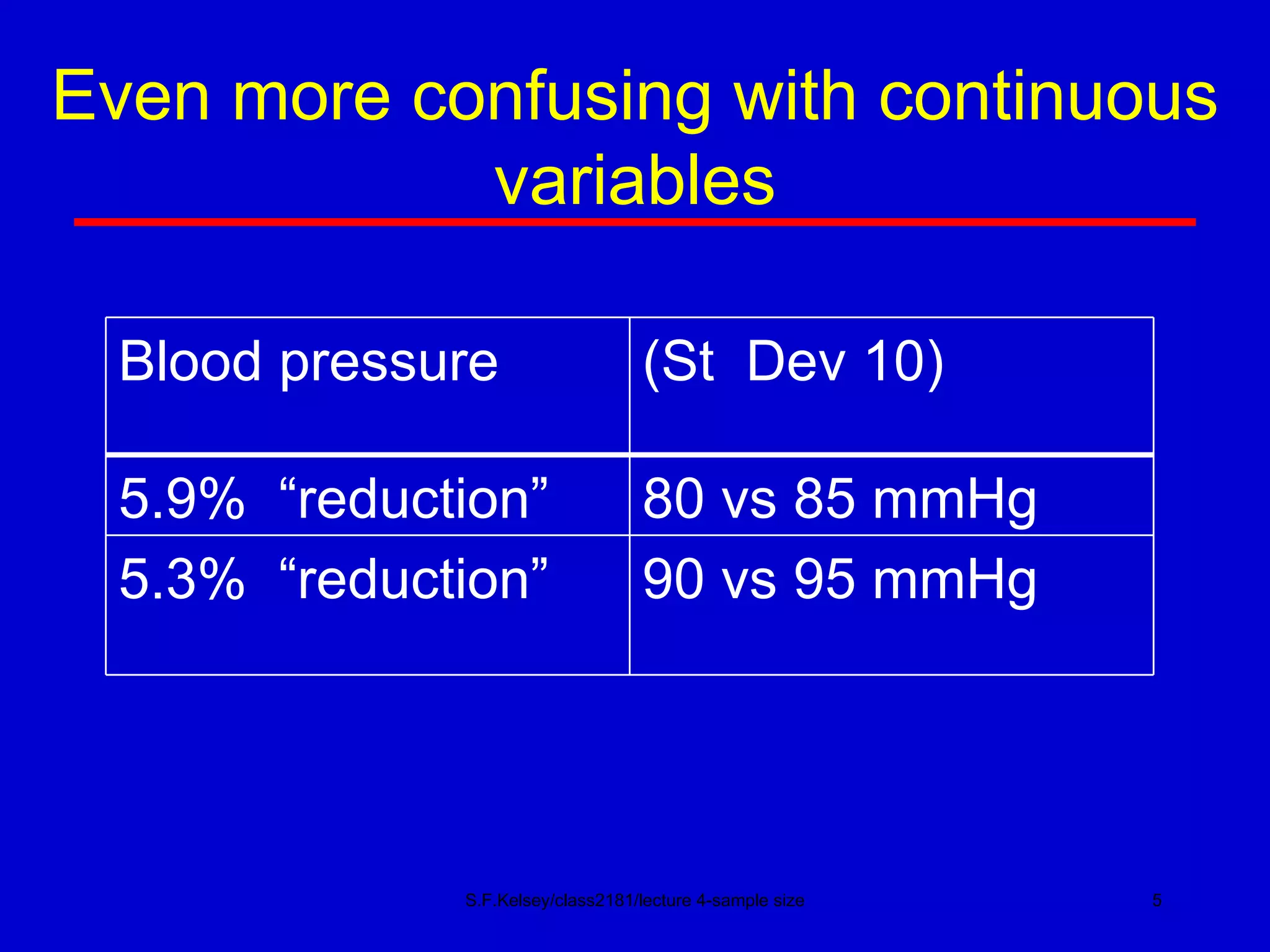
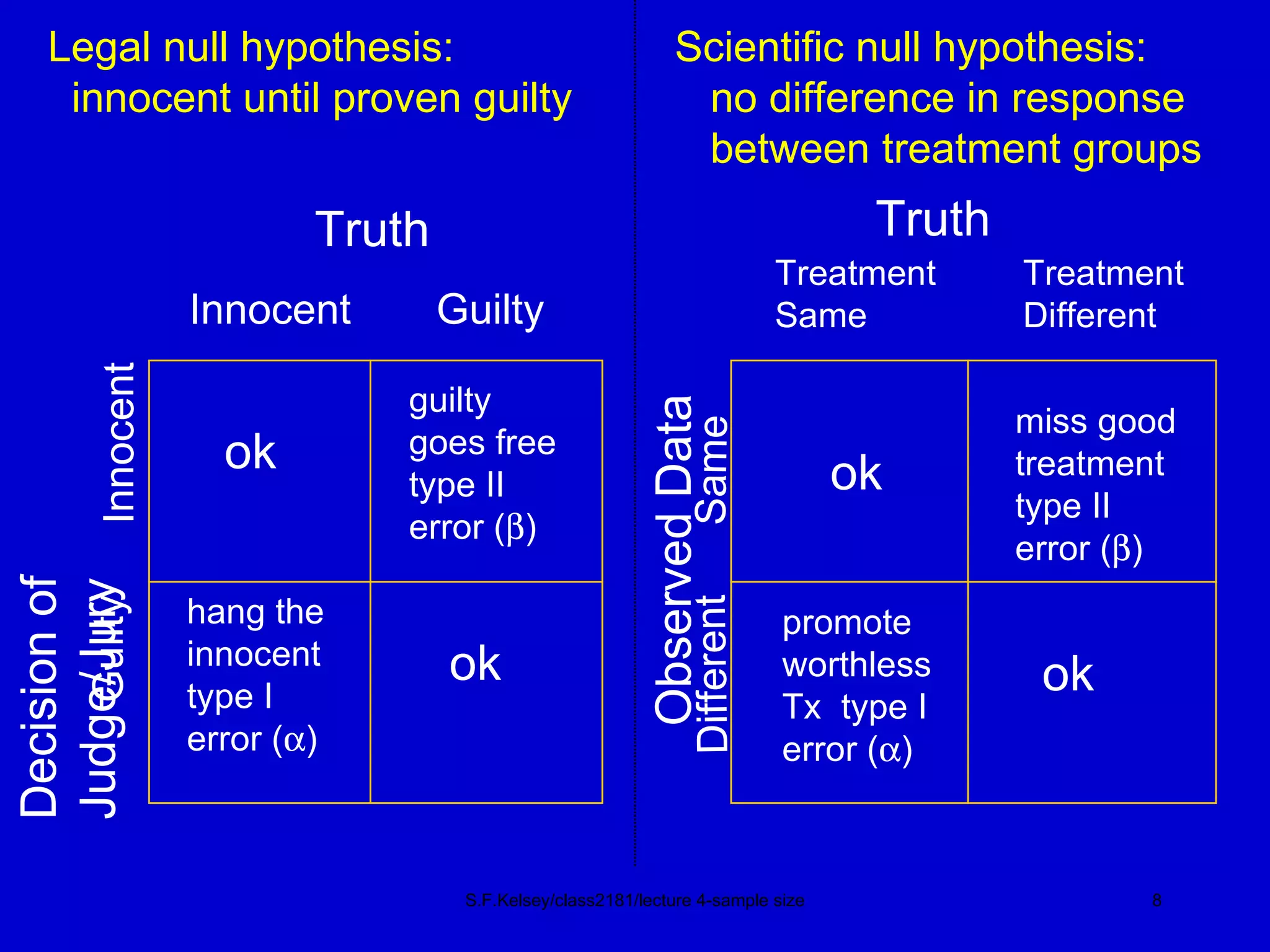
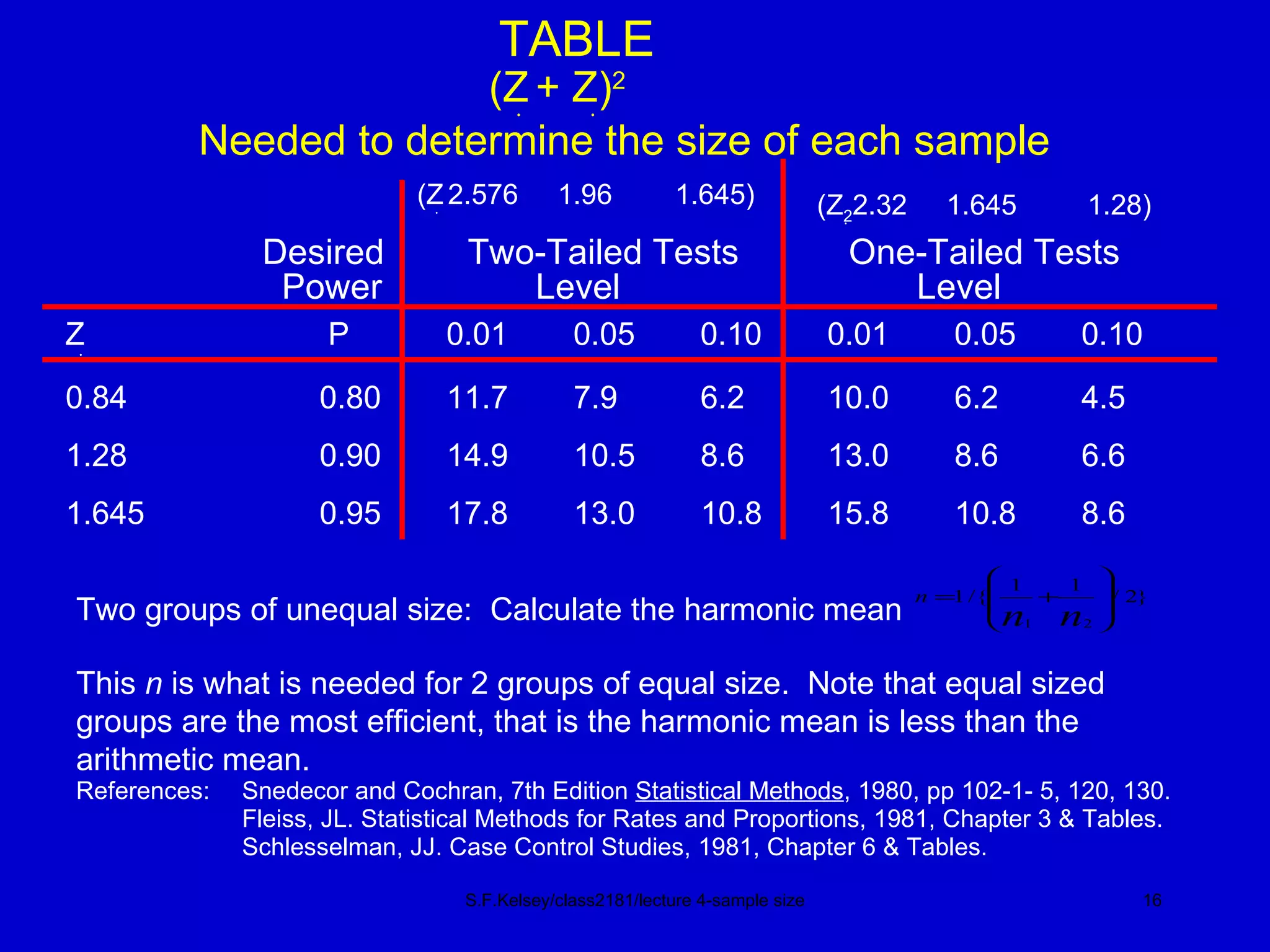
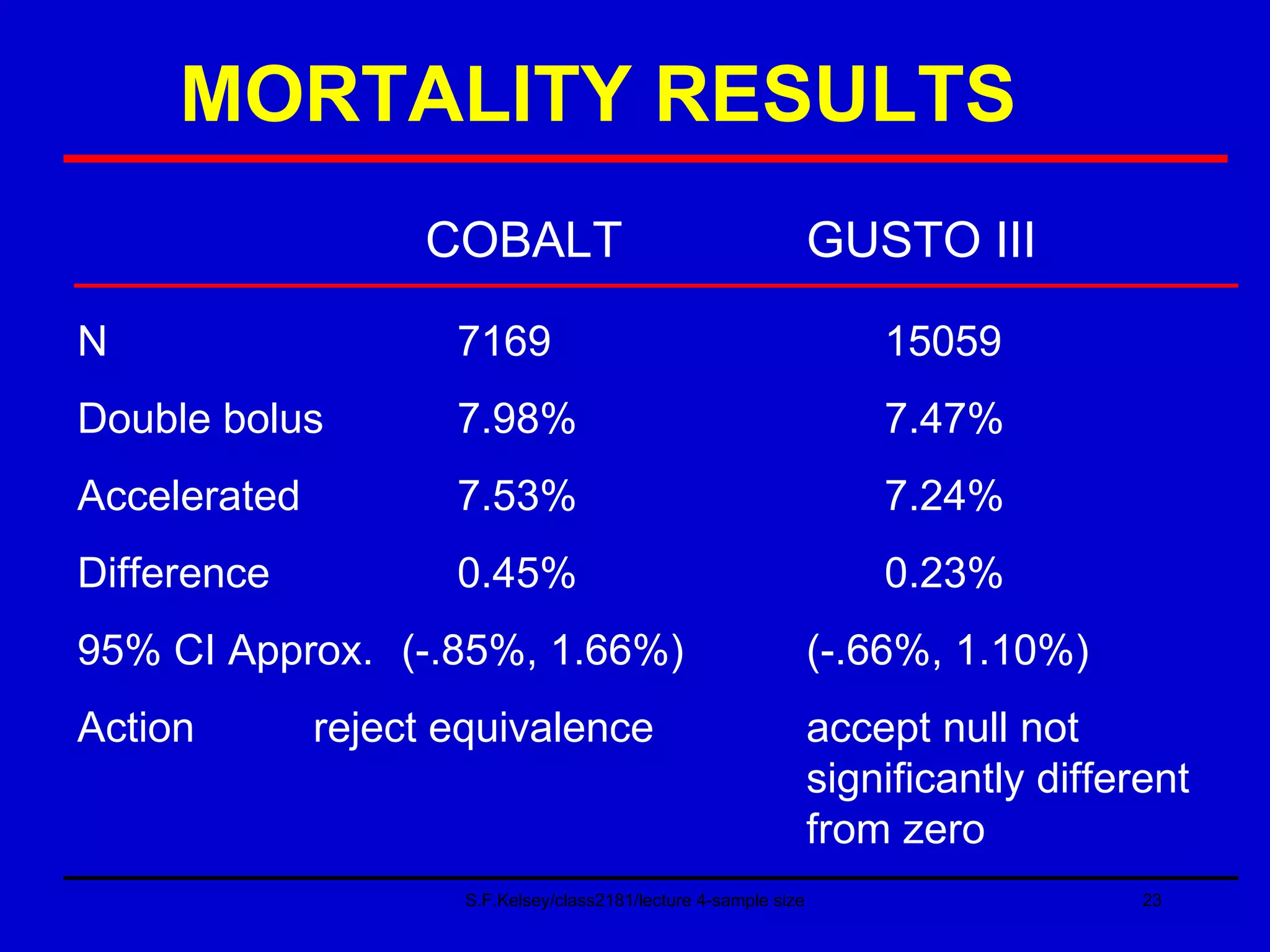
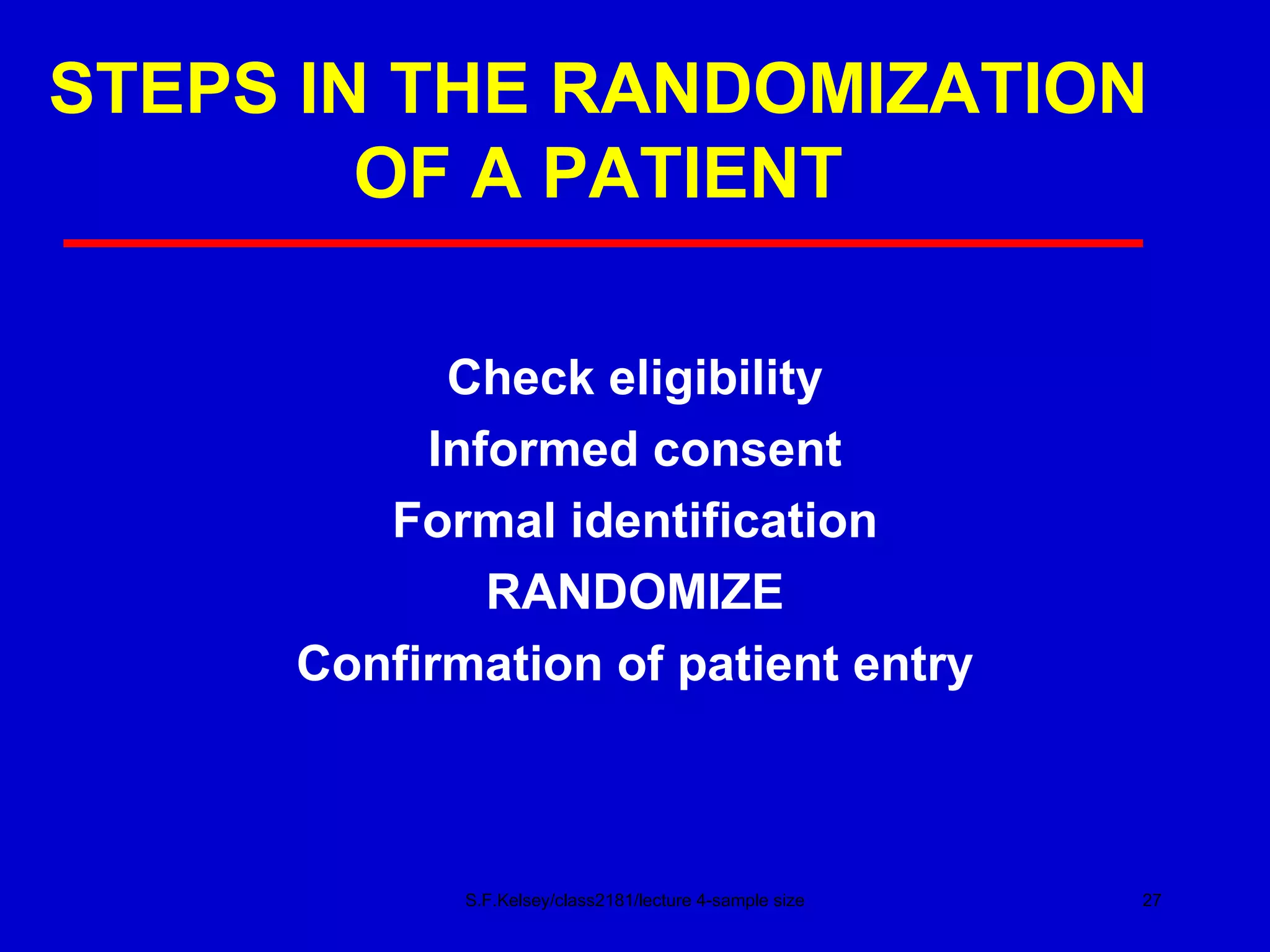
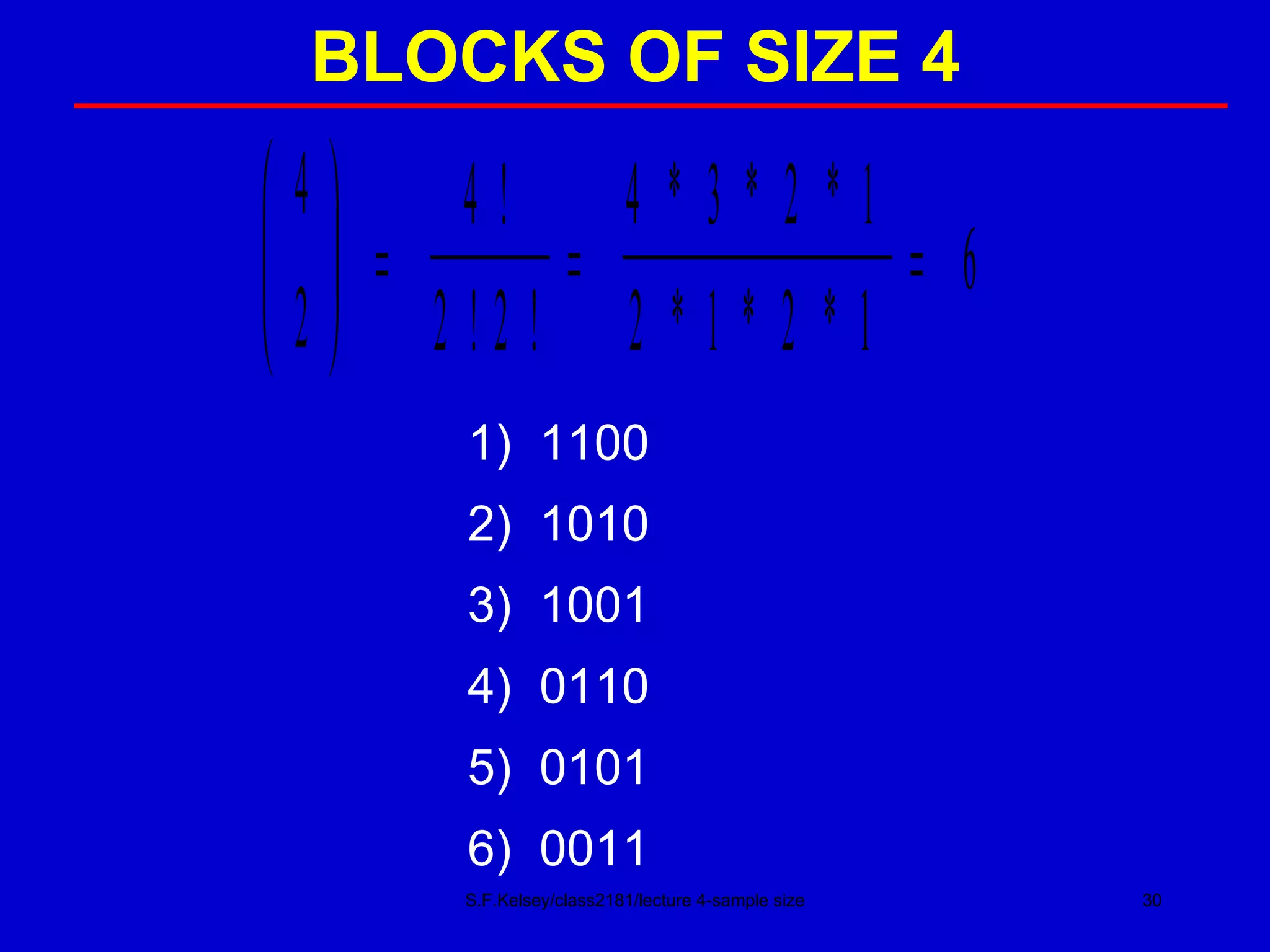
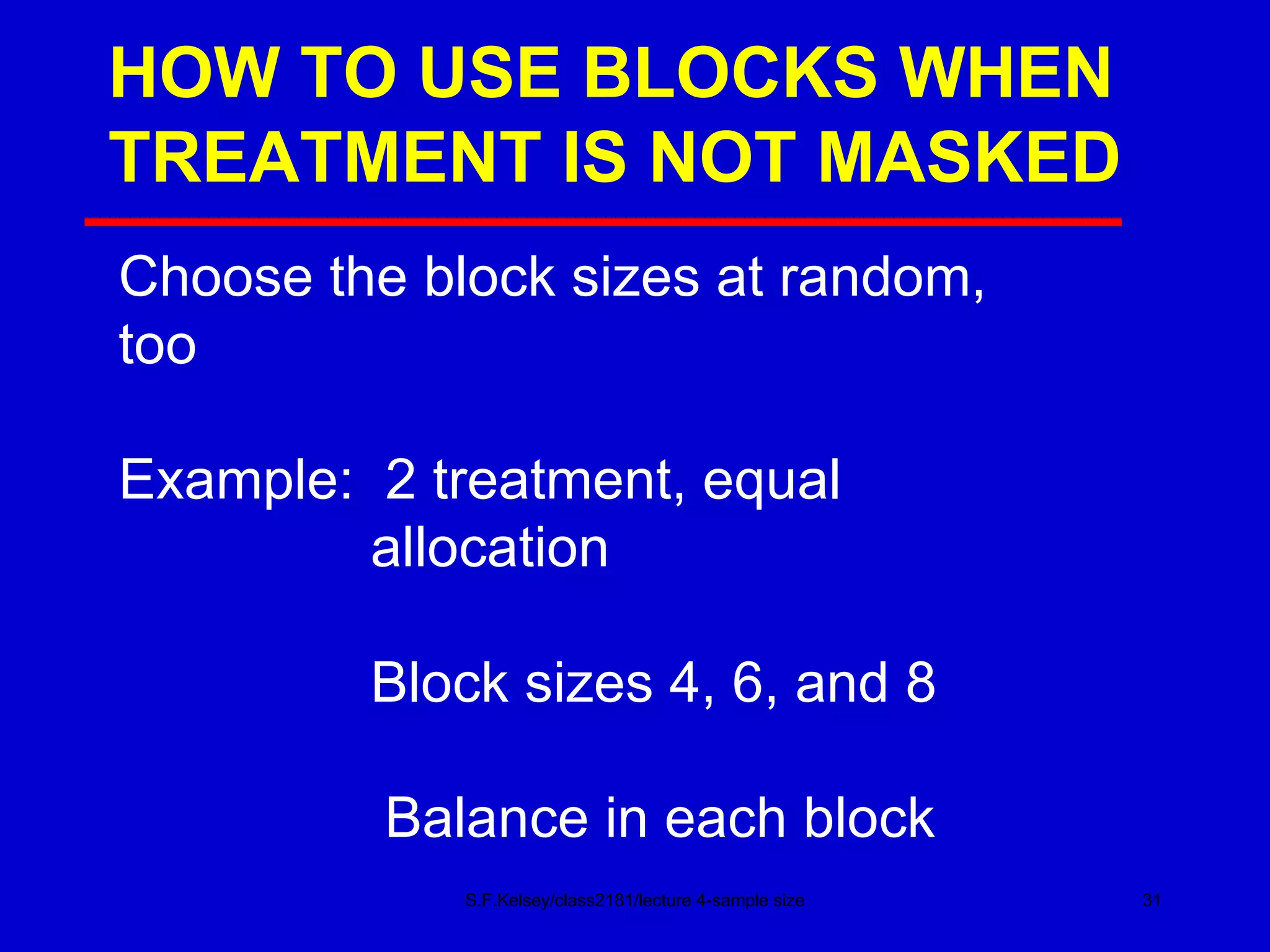
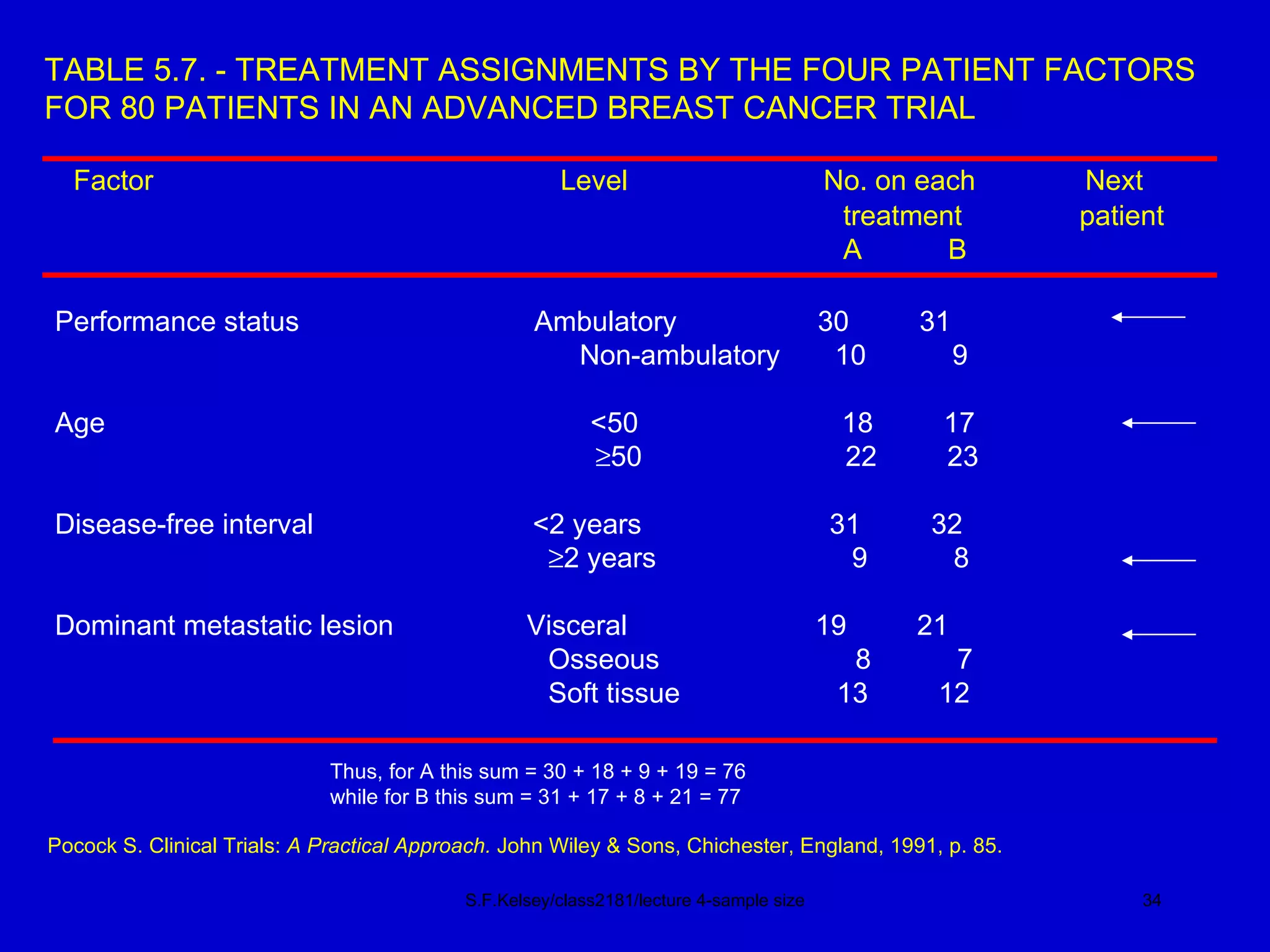
This document discusses key concepts in determining sample size and statistical power for clinical trials. It provides examples of calculating sample sizes for dichotomous and continuous outcomes. The importance of choosing an appropriate primary outcome and estimating event rates in control and intervention groups is emphasized. Methods for randomization in clinical trials like simple randomization and blocked randomization are also covered.