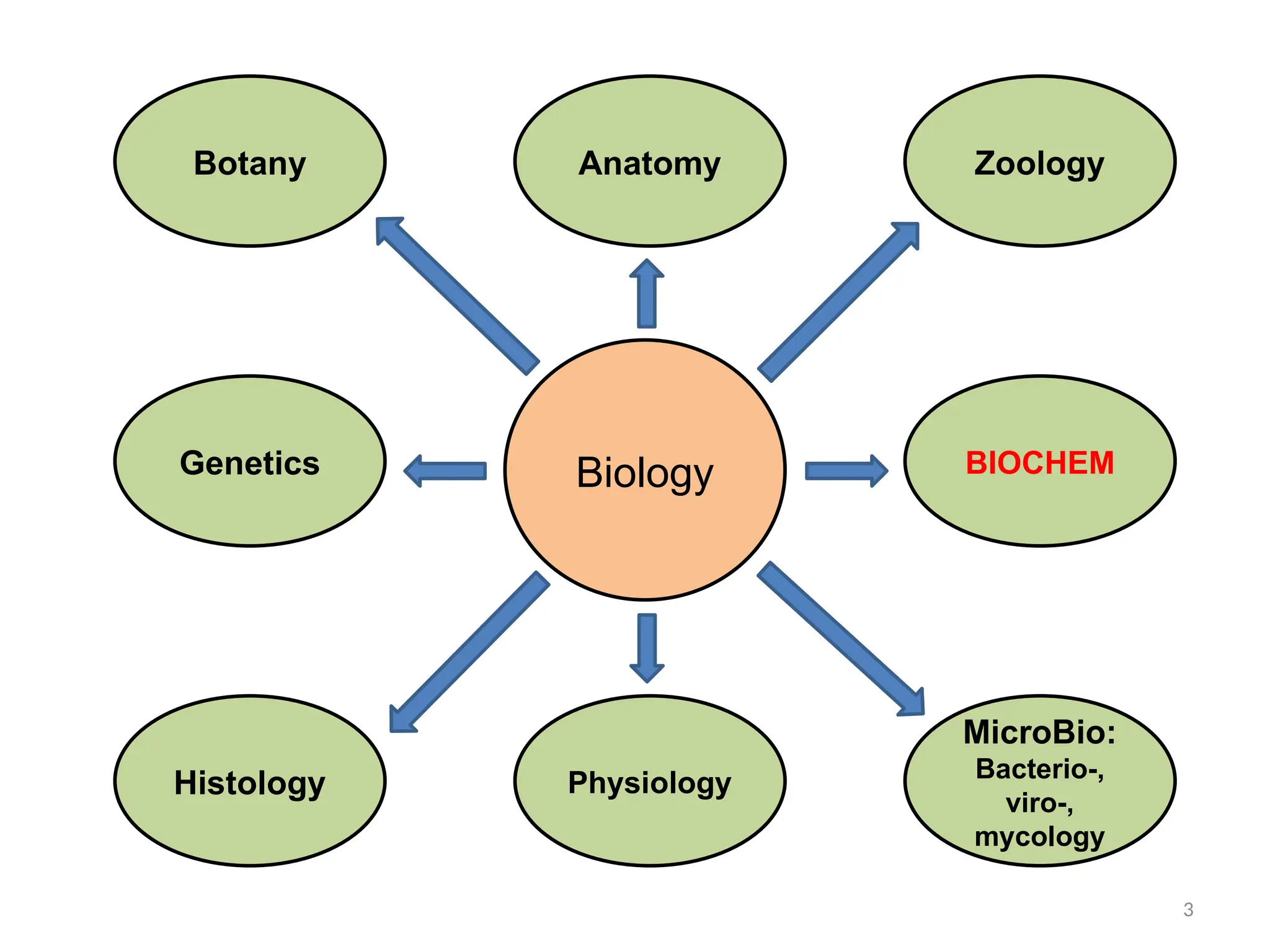
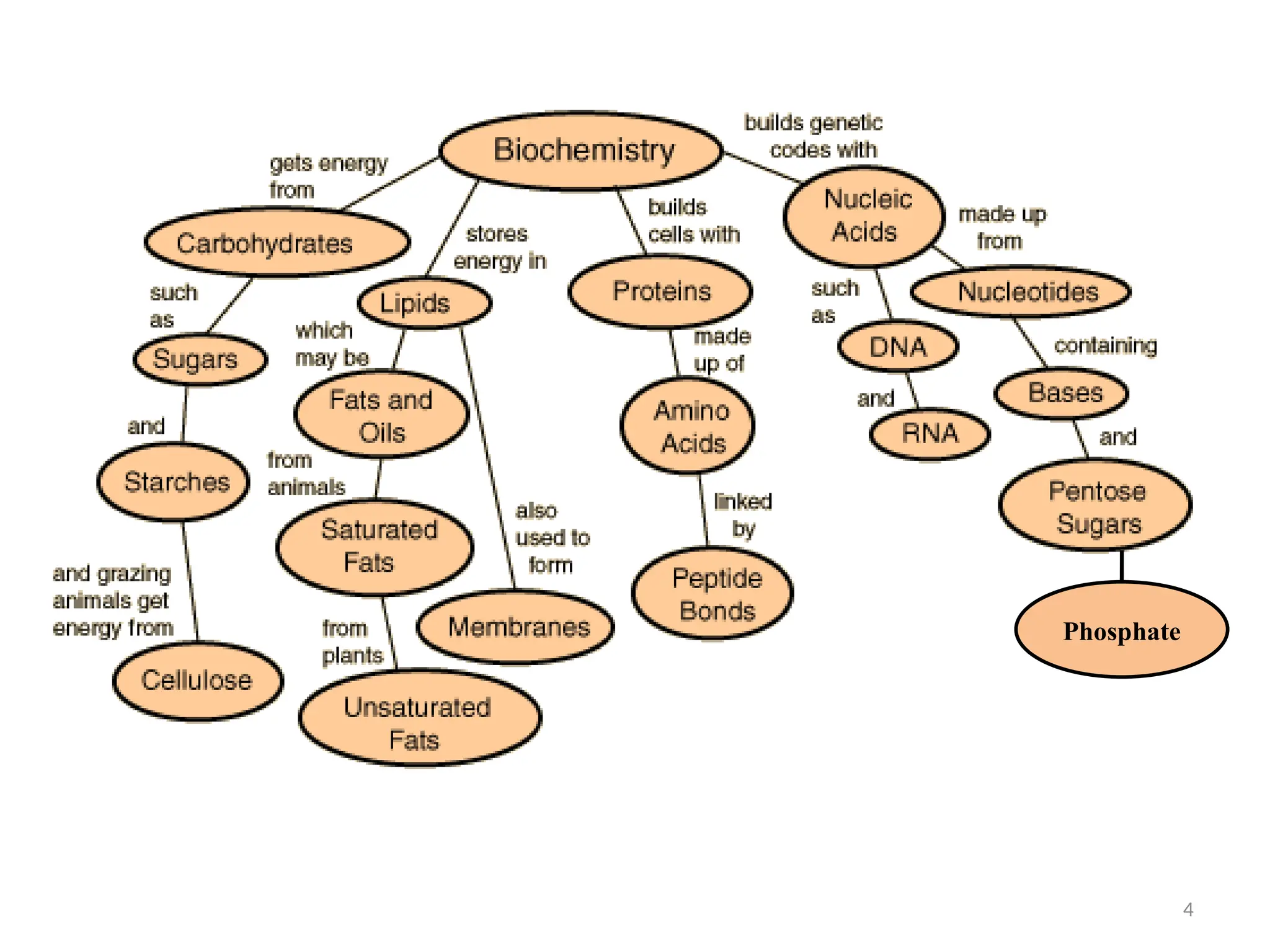
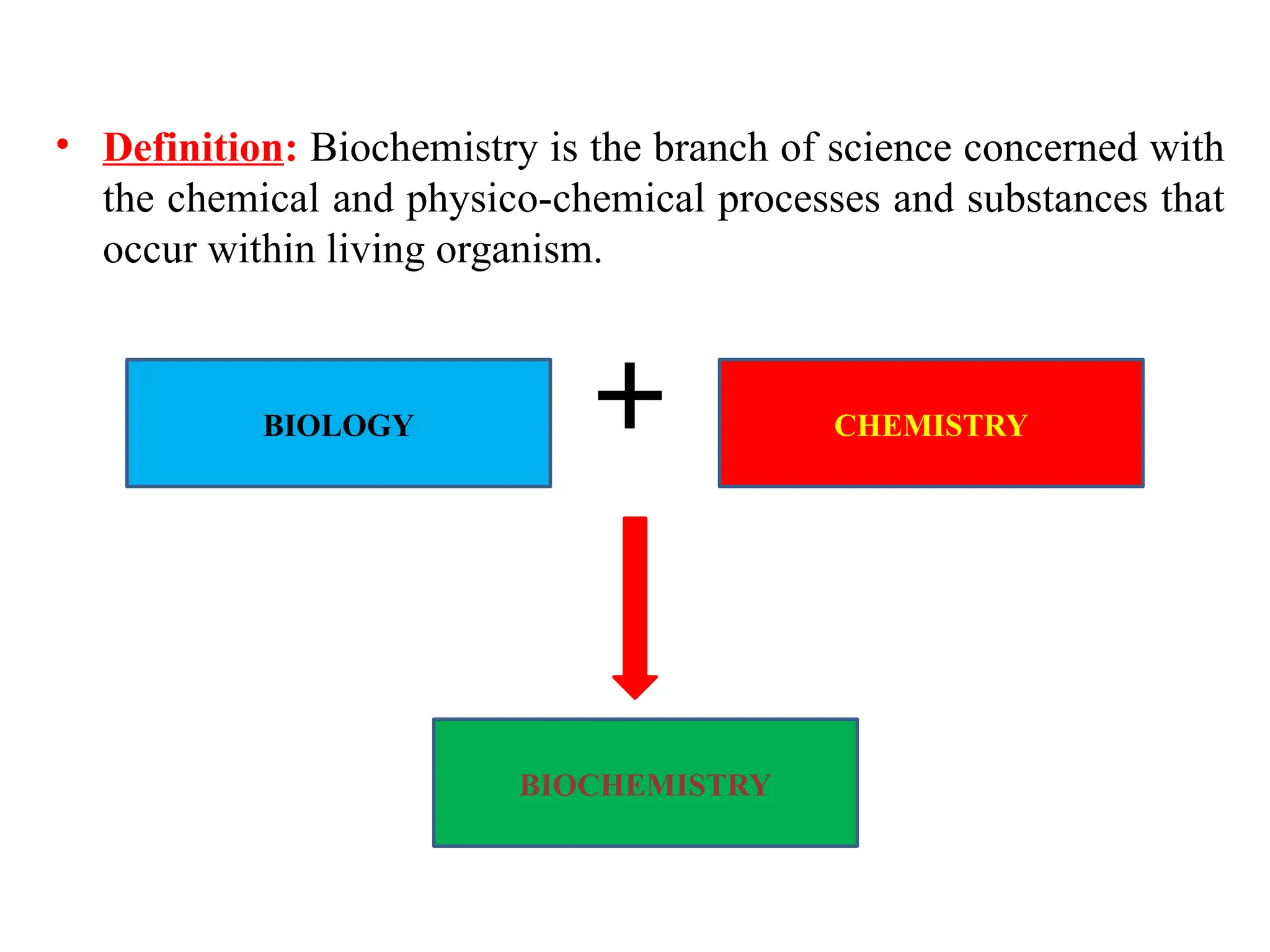
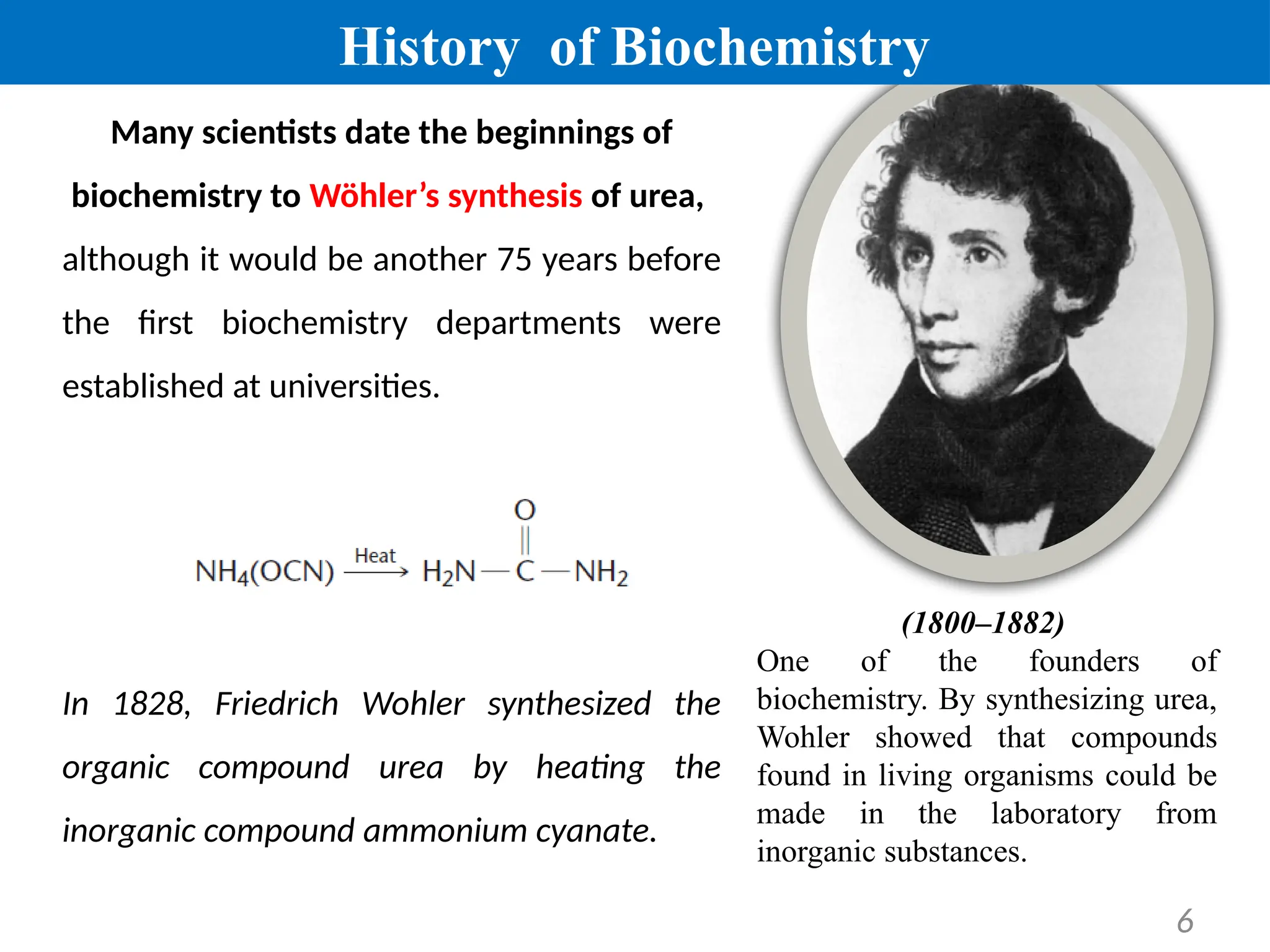
Biochemistry, first introduced by Carl Alexander Neuberg in 1903, studies chemical processes within living organisms, dating its origins to Friedrich Wöhler's synthesis of urea in 1828. Key milestones include discoveries by Nobel laureates like Eduard Buchner and James Sumner, contributing to understanding metabolic pathways and DNA structure, critical for advancements in various fields, including agriculture and medicine. Biochemistry plays a vital role in disease prevention, growth enhancement, food quality, and monitoring environmental factors in farming and fisheries.