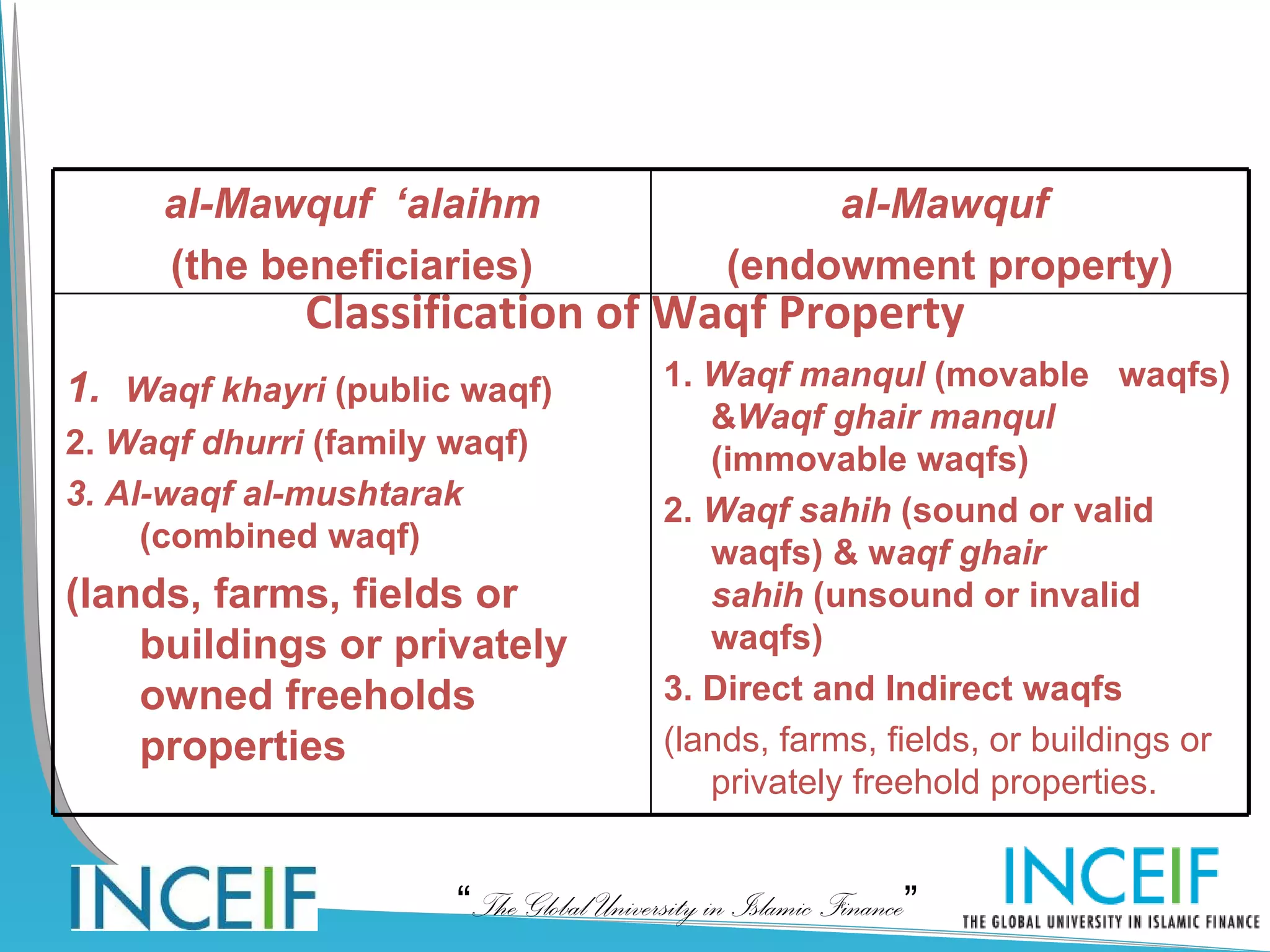
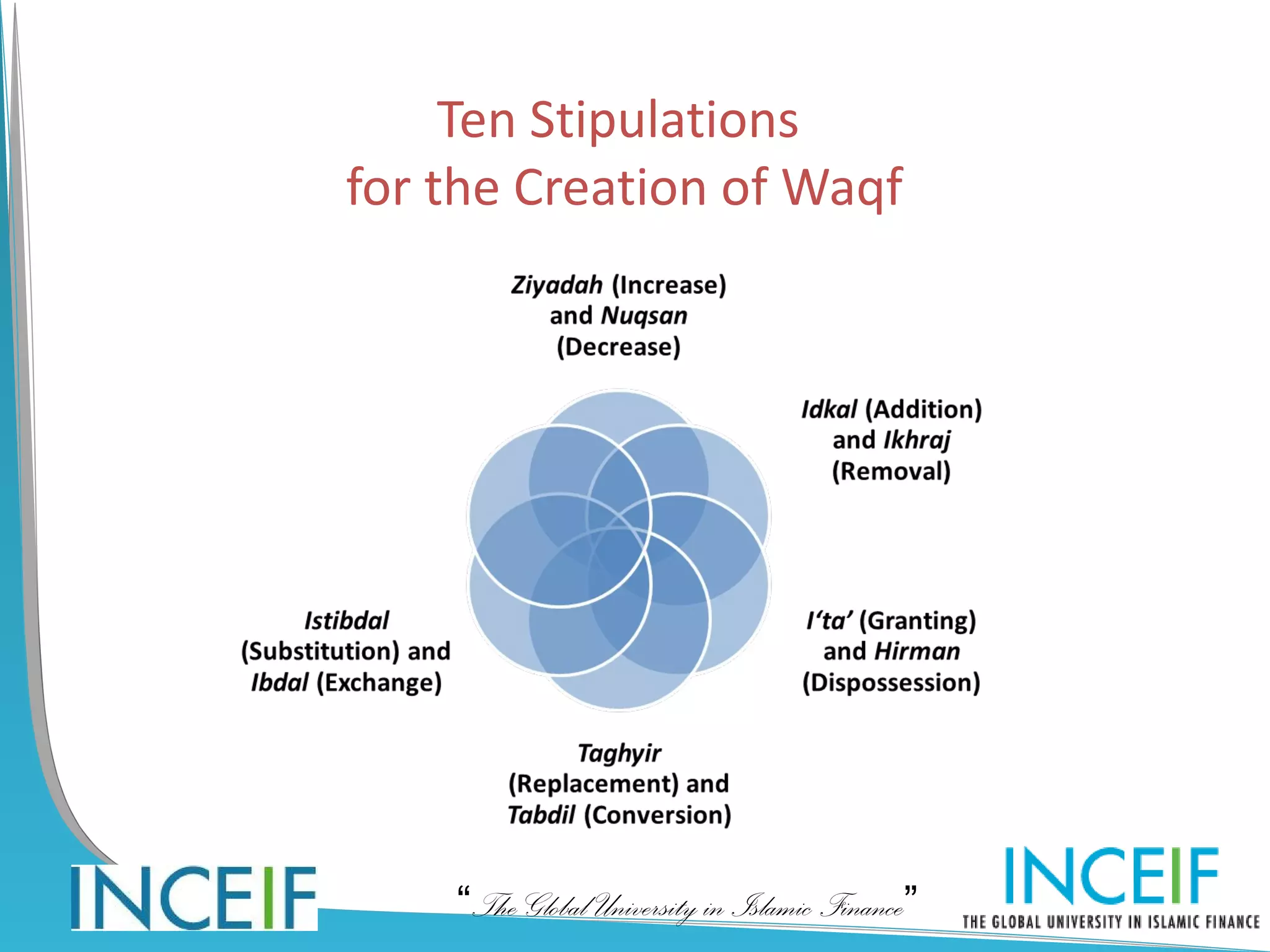
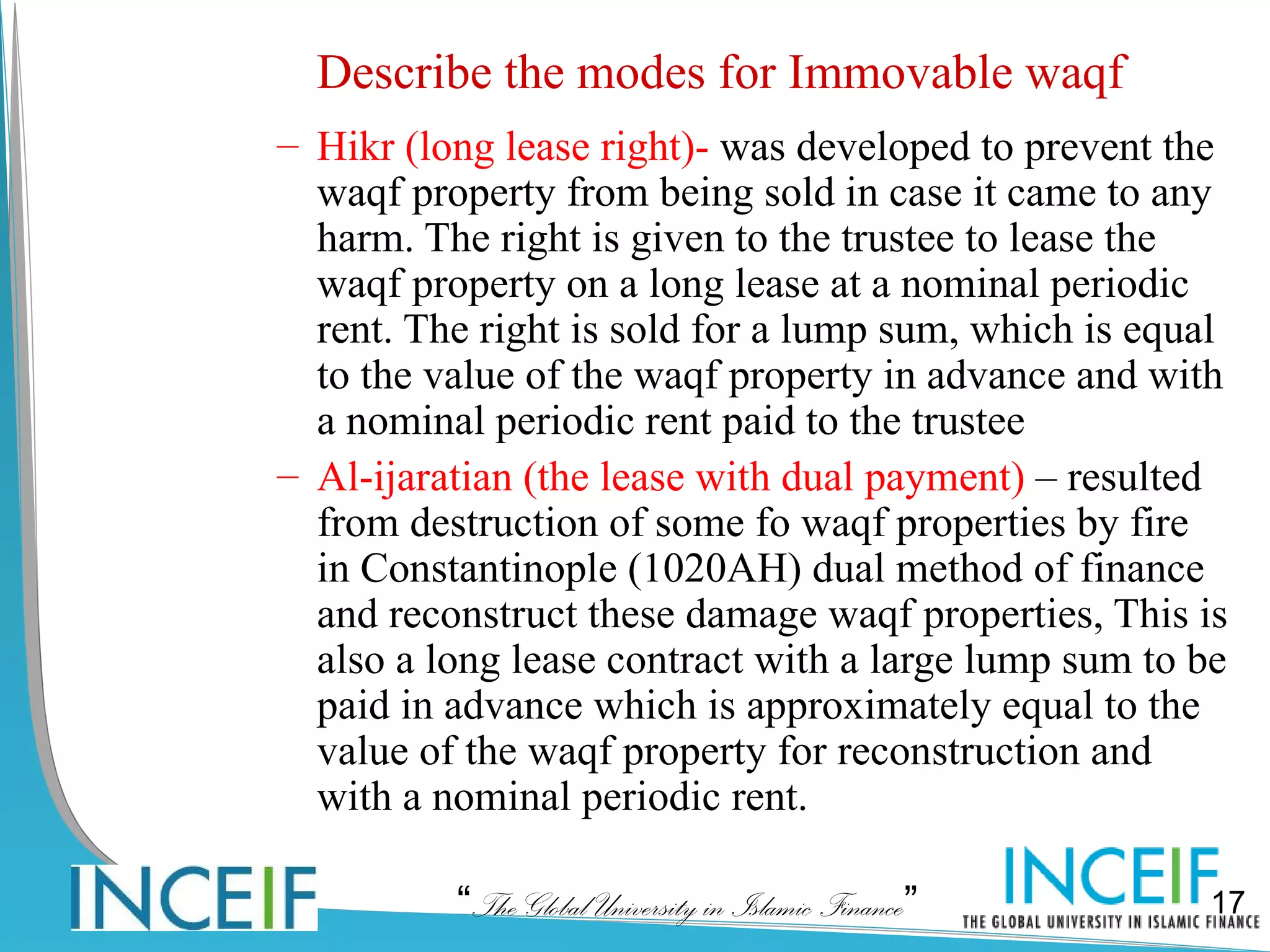
The document discusses wealth planning and management through the Islamic instrument of waqf (endowment). It begins by explaining the hadith about a person's good deeds continuing after death through recurring charity, beneficial knowledge, and righteous children. It then defines waqf and describes the three main types: public waqf, family waqf, and combined public-family waqf. The conditions for valid waqf creation and permissible waqf assets are also summarized.






























![ISLAMIC B A N K ( T R U S T E E )
ISLAMIC B A N K ( T R U S T E E )
CASH W AQF ( B A N K ) W I N D O W S
FUND A C C U M U L A T I O N INVESTMENT A N D P R O F IT
D IS T R IB U T IO N (C H A R IT Y ,
MNAGEMENT A N D C A P IT A L
ENDOW MENT OF SHARES ( I B AND OTHER E N H A N C E M E N T ) A N D
INSTITUTIONS) A S CASH W A Q F M A R K E T IN G .
CASH WAQF BY O T H E R S INSTITUTIONS FROM
THEIR P A R T S OF D I V I D E N D
WAQF LAND D E V E L O P M E N T S (MUDARABAH
AND M U S H A R A K A H )
WAQF CERTIFICATE (SPECIFIC OR G E N E R A L )
MICROFINANCE (GROUP B A S E D LENDING
OR S O C I A L COLLATERAL [E.G. P R A Y E R
WAQF INSURANE (SPECIFIC O R G E N E R A L ) LEADER], C O M P U L S O R Y SAVINGS AND
ASSETS INSURANCE FOR F A R M E R S
TEMPORARY W A Q F :
SME LOAN: M U S H A R A K A H (COLLATERRAL,
DEPOSIT W ITHOUT S H A R E O F P R O F I T
C O M P U L S O R Y SAVINGS, OPTIONAL
ASSETS I N S U R A N C E )
BUYING W AQF SHARES (50% O F DIVIDEND
POTFOLIO I N V E S T M E N T IN IFI’S
WILL BE D O N A T E D )
SECURI T I E S
E-WAQF (LUMP S U M A M O U N T ) EMERGENCY NEEDS F U L F I L L
OTHERS: SPECIFIC B Y DONOR AND
GENERAL (MOSQUE, MADRASH E T C . )
Figure 2. Cash WAQF model.
“The Global University in Islamic Finance”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture08finalupdated-120501001111-phpapp01/75/Lecture-08-final-updated-35-2048.jpg)
