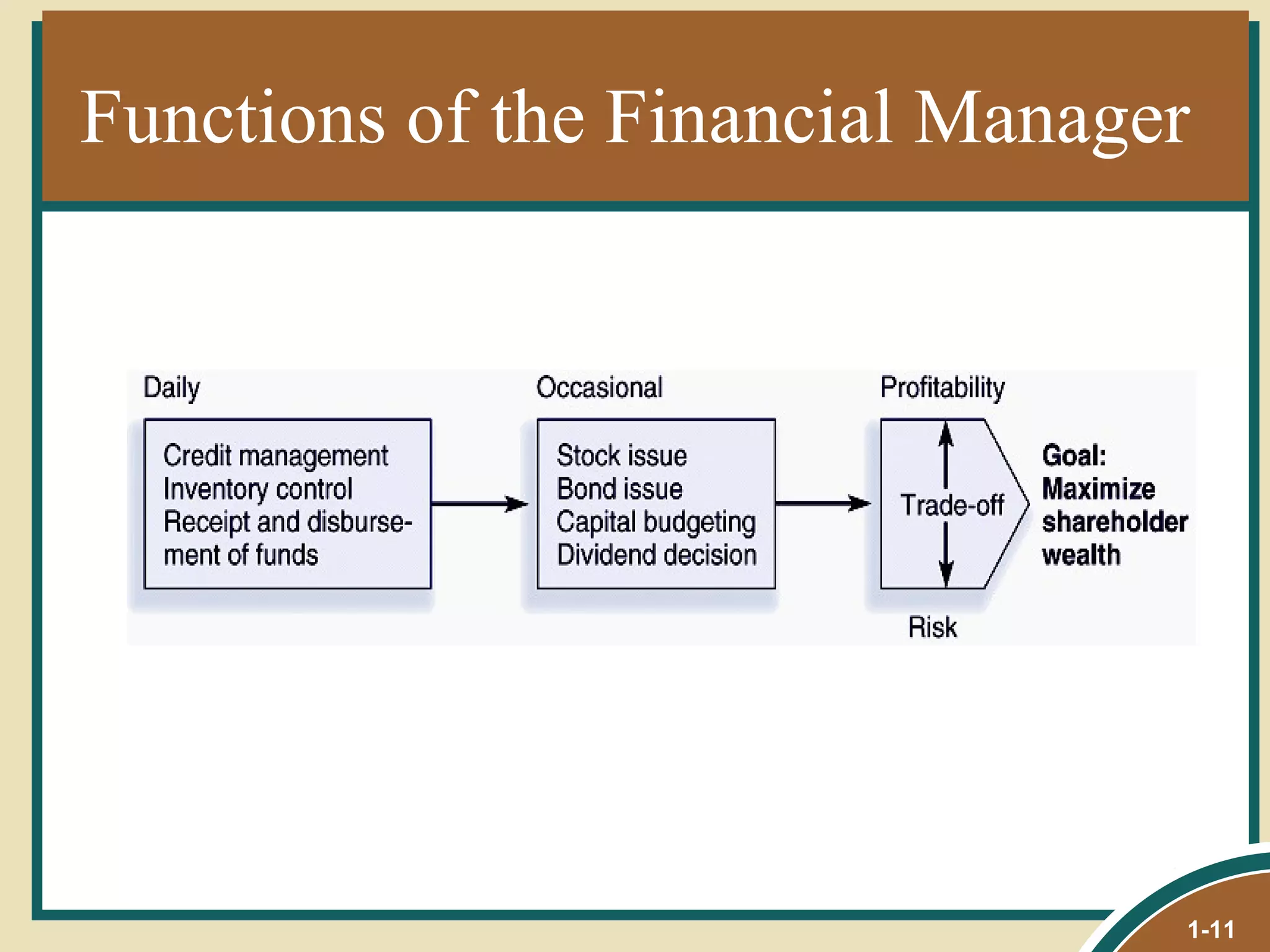
This document provides an overview of the goals and functions of financial management. It discusses how financial management links economic theory and accounting data. The primary goal of financial managers is to maximize shareholder wealth while balancing risk. Modern issues include risk-return analysis, capital structure, and the impact of inflation and technology. Financial markets help allocate capital and provide feedback to companies on performance.