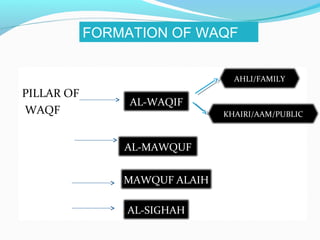
This document defines waqf and outlines its key principles and rules according to Islamic law. Waqf refers to holding an asset and preserving it to benefit certain philanthropic causes in line with the founder's wishes. There are several pillars to waqf: the founder, the endowed asset, the beneficiaries, and the establishment agreement. The endowed asset must meet certain conditions, be irrevocable, perpetual, and inalienable. There are also various methods for establishing and managing waqf assets and funds. The three main principles are that waqf assets cannot be sold, transferred as gifts, or inherited.