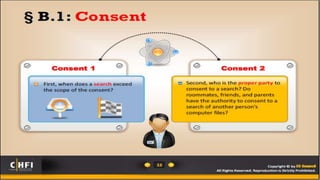
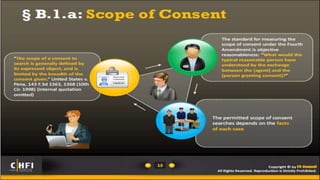
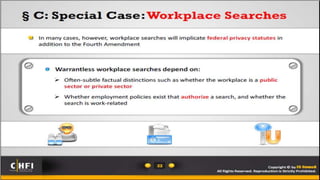
This document provides an introduction to searching and seizing computers for computer forensics. It discusses issues with digital evidence being volatile and massive in size. It explains that searching and seizing computers can be done with or without a warrant, depending on the country's constitution and exceptions like consent. Key aspects of searches include who conducted it, what was searched/seized, if it was a legal search/seizure, and if the search was reasonable with a warrant or under an exception. Probable cause and exceptions to warrants like emergencies, vehicles and borders are also outlined. Proper warrant preparation and seizing equipment on site are important parts of legally searching and seizing computer-related evidence.