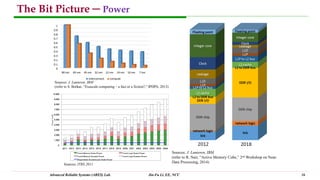
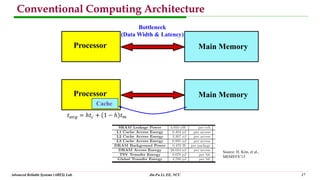
This document discusses trends in integrated circuit applications and technologies. It focuses on artificial intelligence, internet of things, and system-on-chip designs. The document presents diagrams of typical system-on-chip architectures that integrate processors, memory, and other components. It also discusses challenges related to the growing gap between computing power and data storage, and approaches to address this like near-memory computing and computing in memory. The overall trends are driving the development of more complex, specialized integrated circuits.