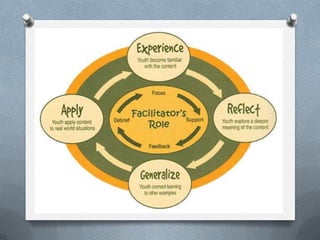
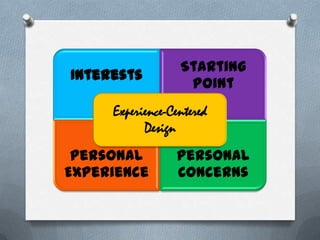
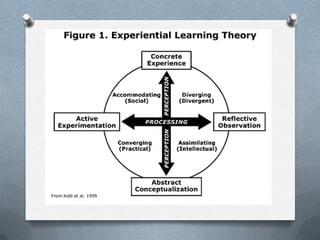
An experience-centered curriculum is based on students' interests and experiences rather than predefined knowledge. The teacher creates a stimulating learning environment for students to explore, make discoveries, and observe others. Students essentially design their own learning by constructing and revising knowledge through hands-on participation and observation. For Dewey, education should start with students' existing experiences and interests, which are personal and constantly changing. The teacher analyzes students' experiences to continually adapt the curriculum to their needs.