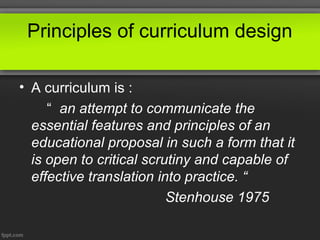
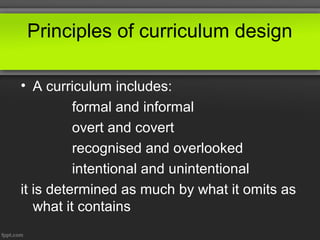
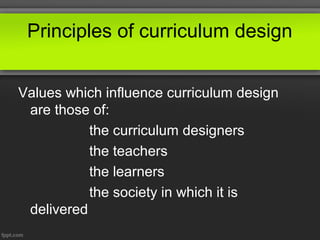
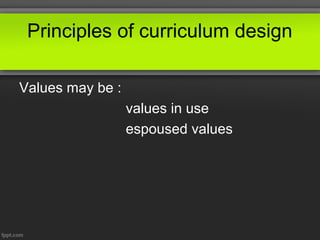
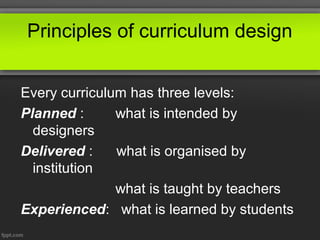
This document discusses principles of curriculum design. It states that a curriculum communicates essential educational proposals for critical review and practical application. A curriculum reflects a profession's best thinking and includes both overt and covert elements determined by what is included and omitted. Values of designers, teachers, learners, and society influence curriculum design. There are three levels to every curriculum: what is planned, what is delivered, and what is experienced by students. The document also outlines different curriculum approaches like subject-centered, child-centered, problem-centered, and behavioral as well as the roles of curriculum supervisors and stakeholders involved in the process.