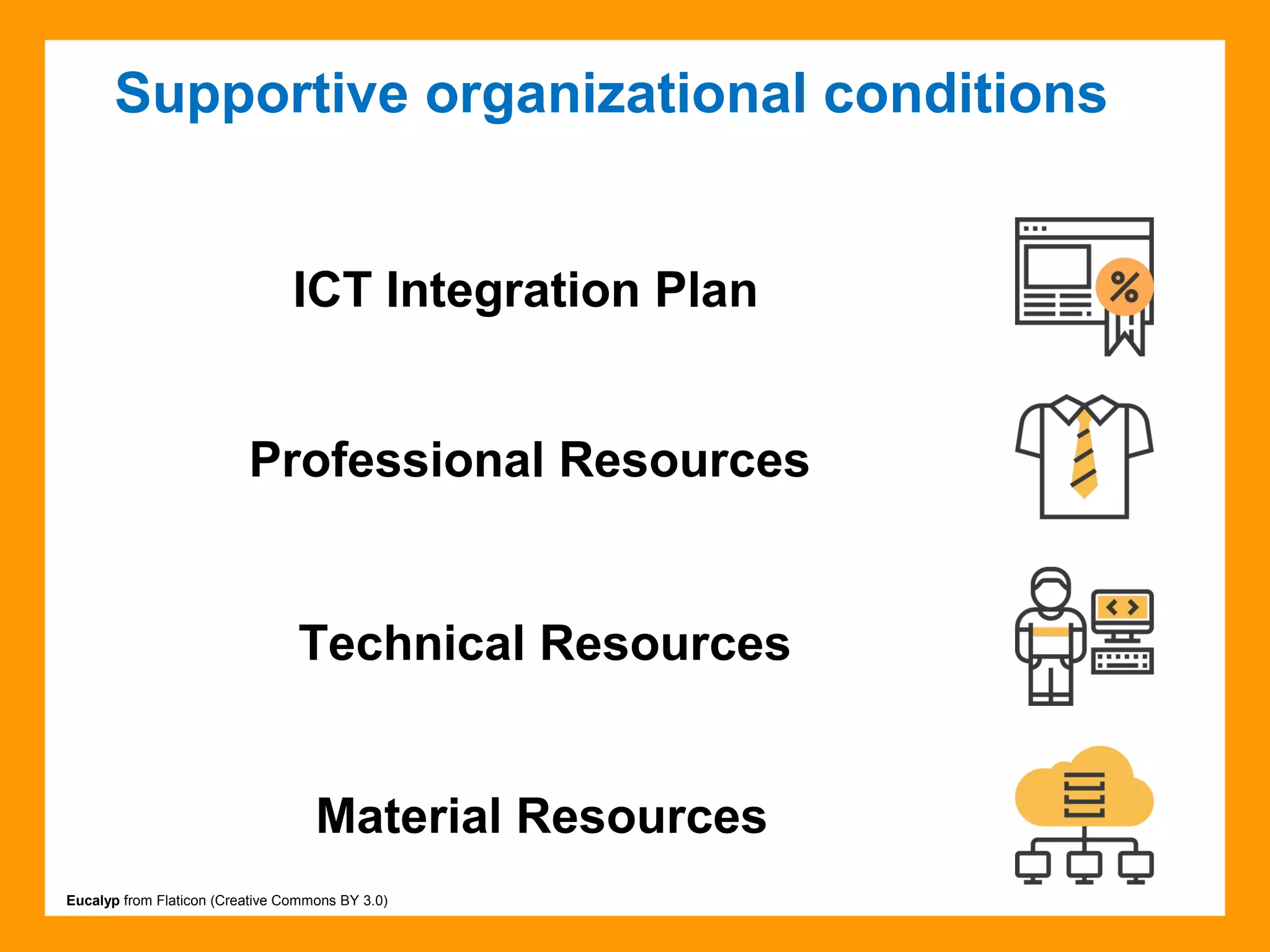
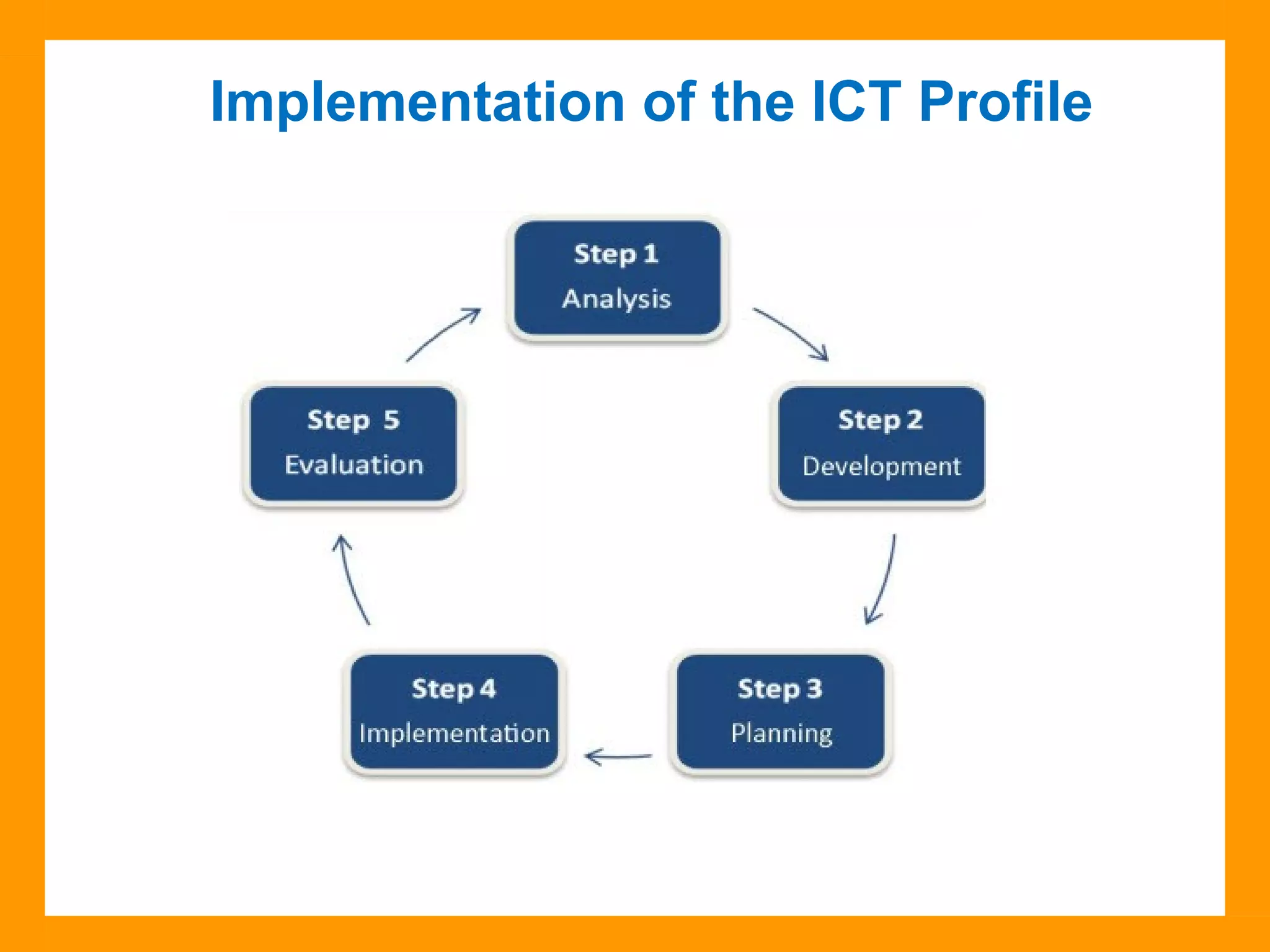
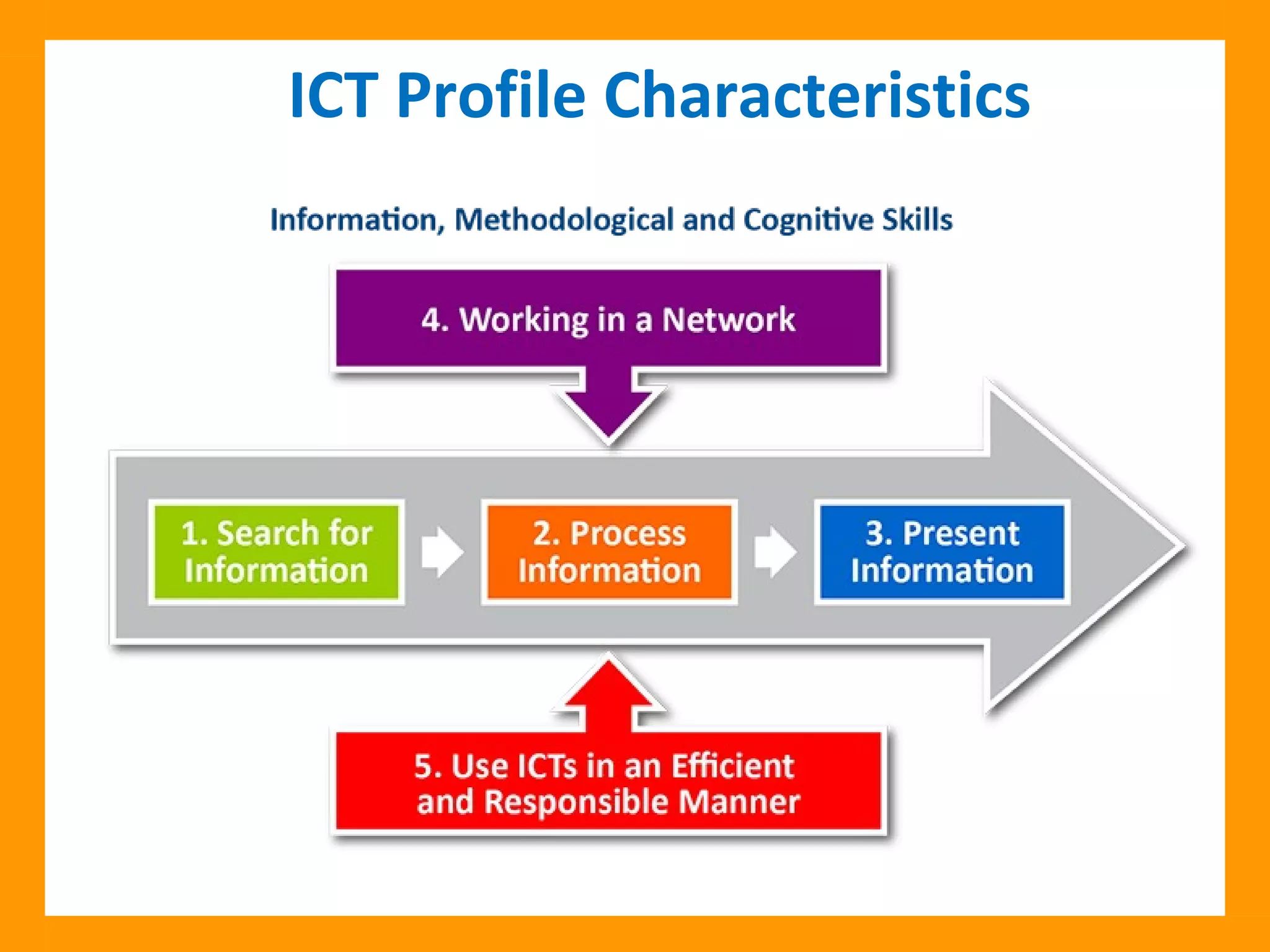
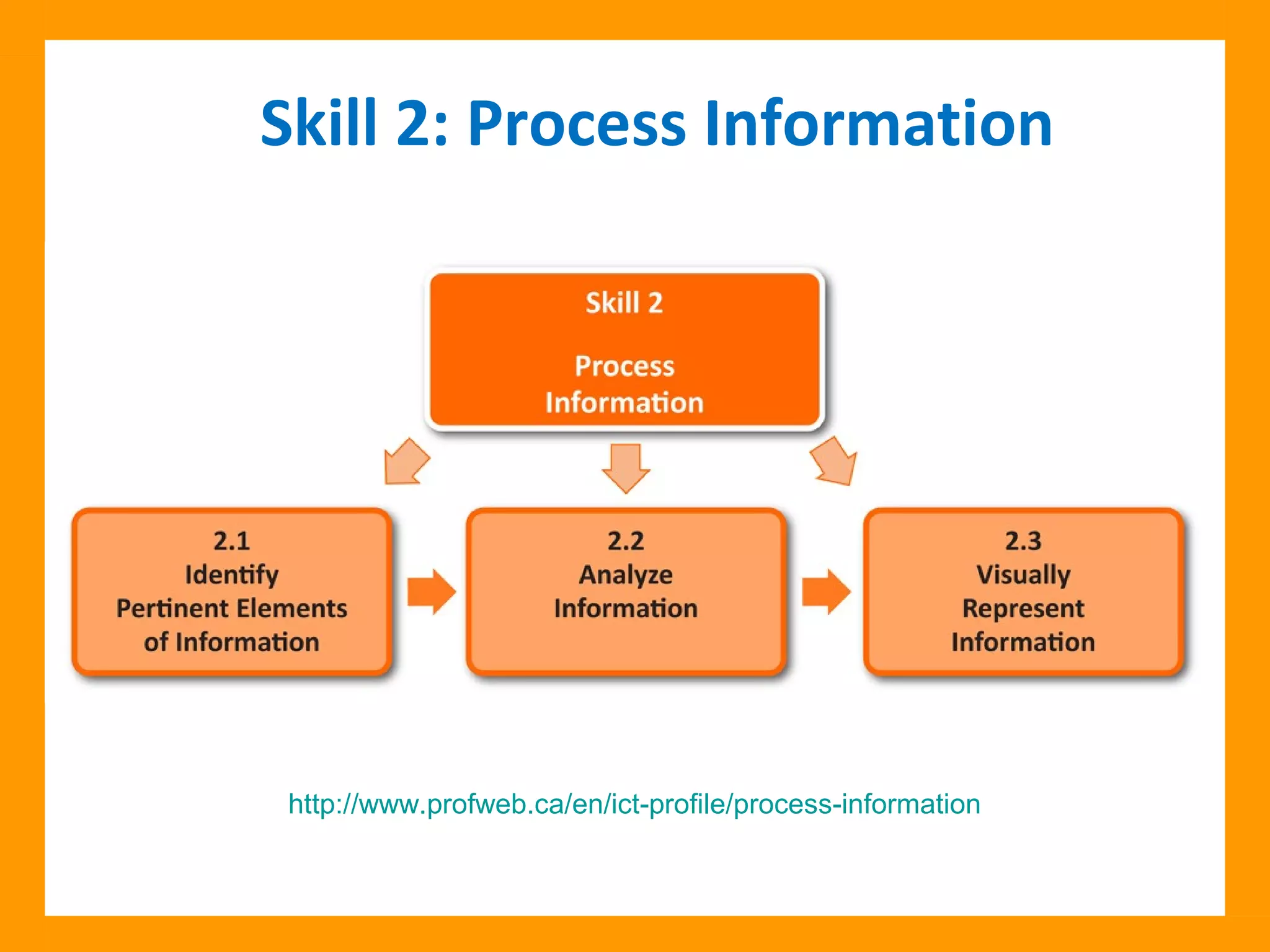
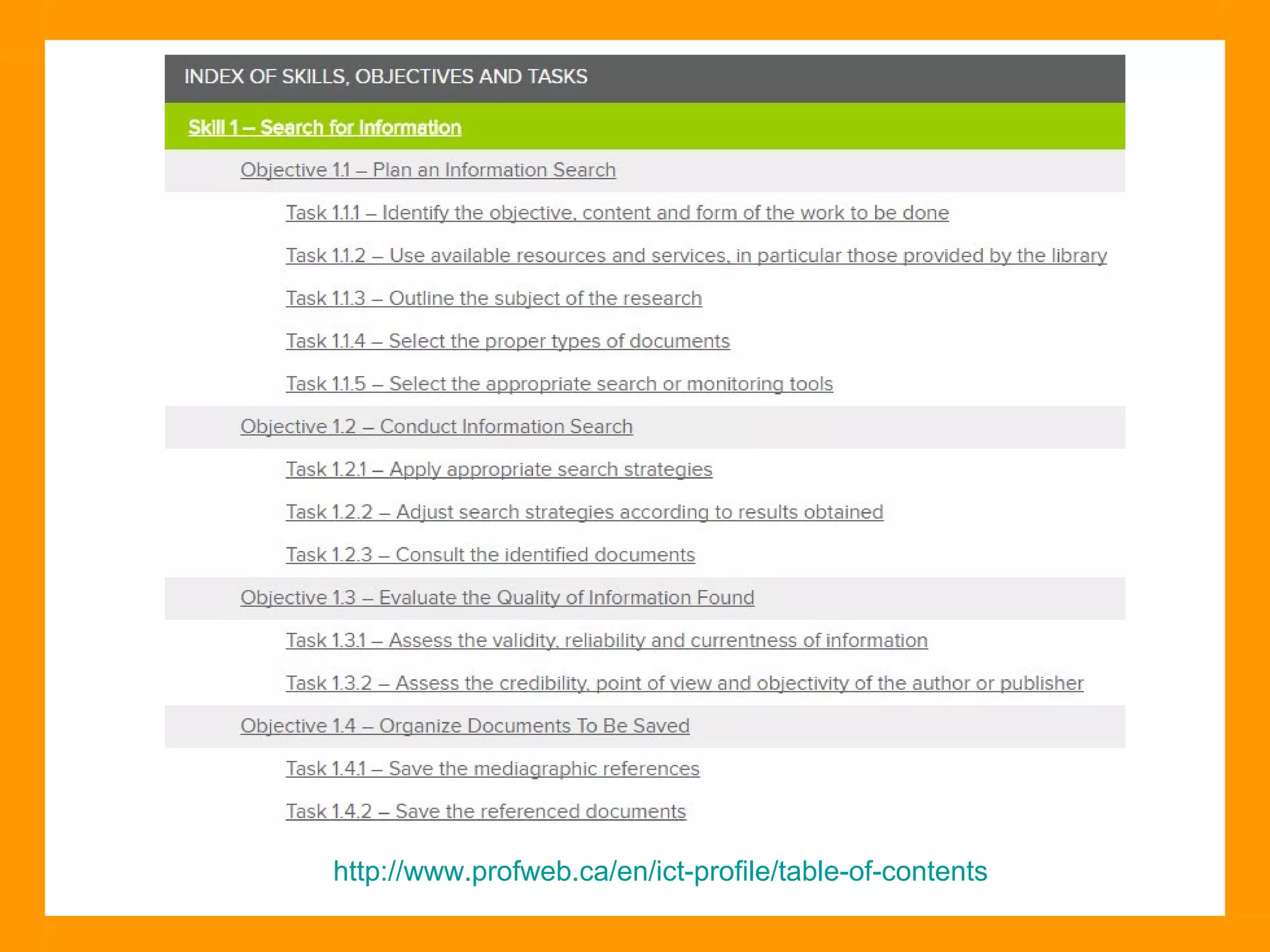
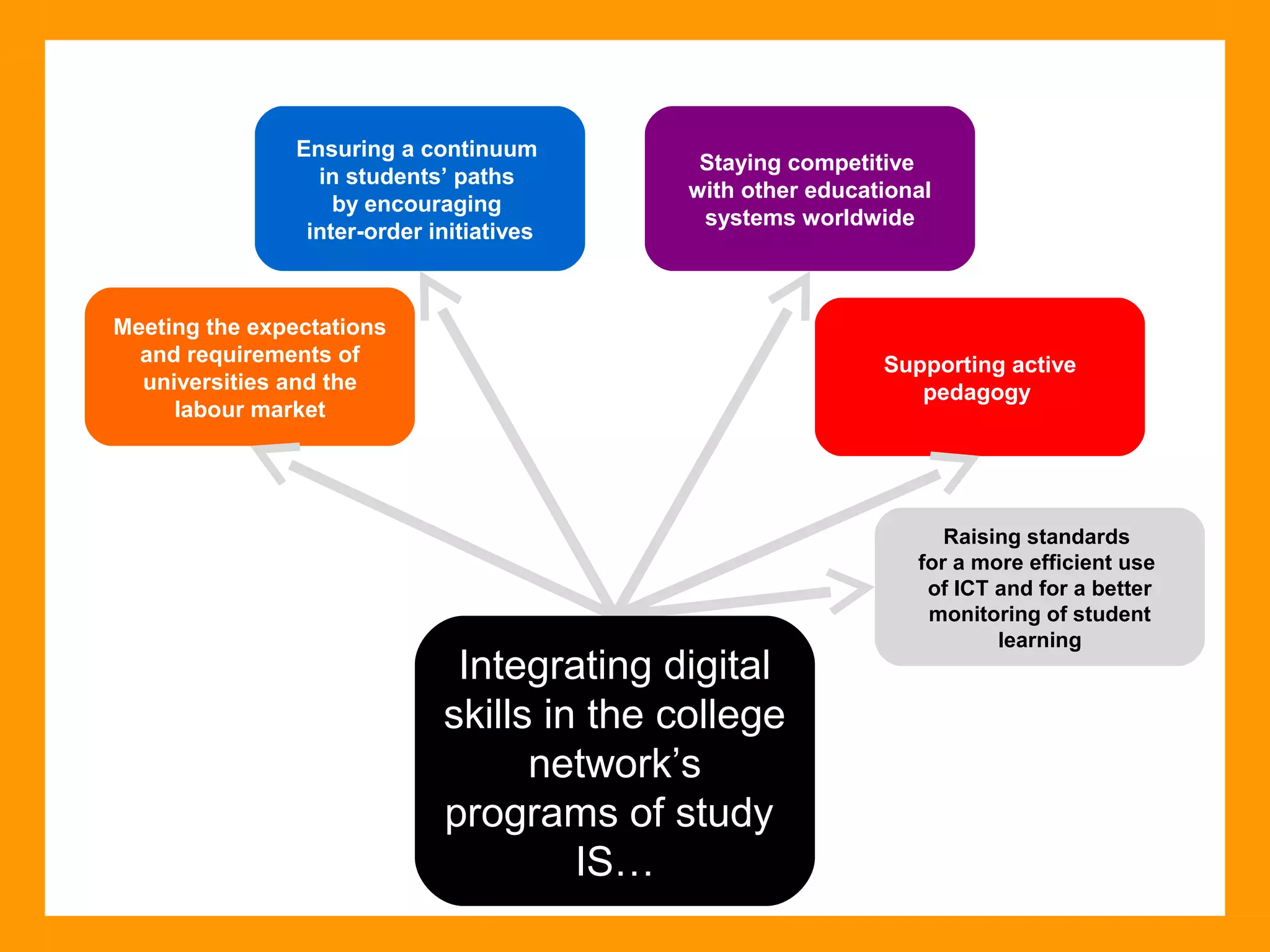
The document discusses the ICT Profile, which is a framework that colleges can use to help students develop information, methodological, and technological skills. The ICT Profile consists of 5 skills: searching for information, processing information, presenting information, working in a network, and using ICTs efficiently and responsibly. It is a universal framework that can be adapted to any college program. Implementing the ICT Profile involves teachers integrating it into the curriculum with help from an ICT pedagogical advisor and ICT subcommittee.



























![Supporting the Mastering of Digital Skills
ICTProfile.ca [En]
ProfilTIC.ca [Fr]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictprofileintrov1-180219154014/75/The-ICT-Profile-33-2048.jpg)