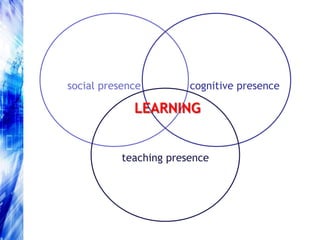
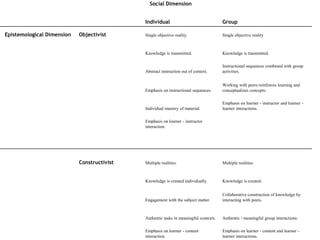
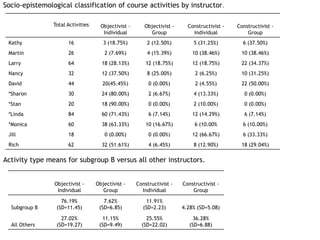
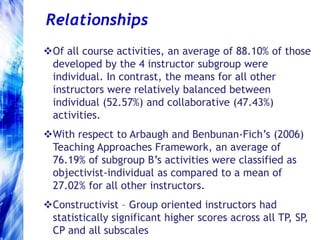
This document explores factors influencing instructor success in online courses using the Community of Inquiry framework, which emphasizes social, cognitive, and teaching presence. The findings reveal that commonly accepted factors such as previous experience and training do not significantly impact instructor effectiveness, while gender and collaborative learning approaches show more relevance. The study suggests that socio-epistemological orientations may affect instructors' capacities to create effective online learning experiences, calling for further research and potential screening for instructor selection.