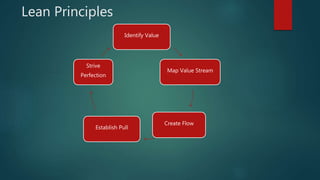
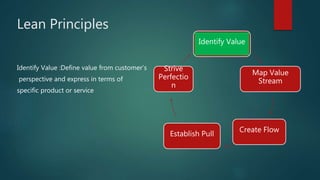
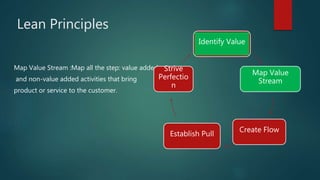
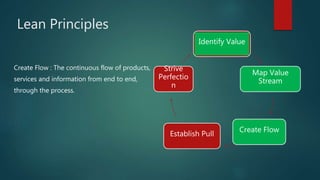
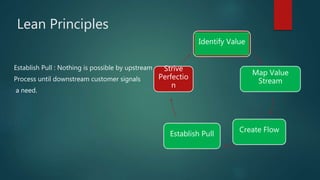
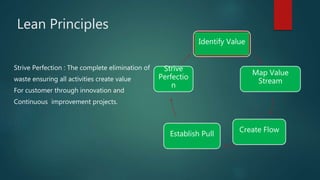
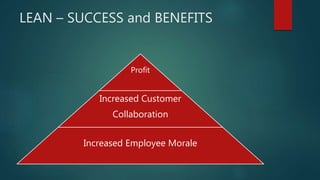
The document discusses Lean principles and concepts. It defines Lean as focusing on reducing waste to increase customer value. The roots of Lean come from the Toyota Production System after World War 2. The document outlines the five Lean principles: identify value, map the value stream, create flow, establish pull, and strive for perfection. It defines the seven types of waste in Lean: overproduction, waiting, transportation, overprocessing, inventory, motion, and defects. Benefits of Lean include increased profits, customer collaboration, and employee morale. Challenges can include disruptions during implementation and the need to rethink process flows with changes.