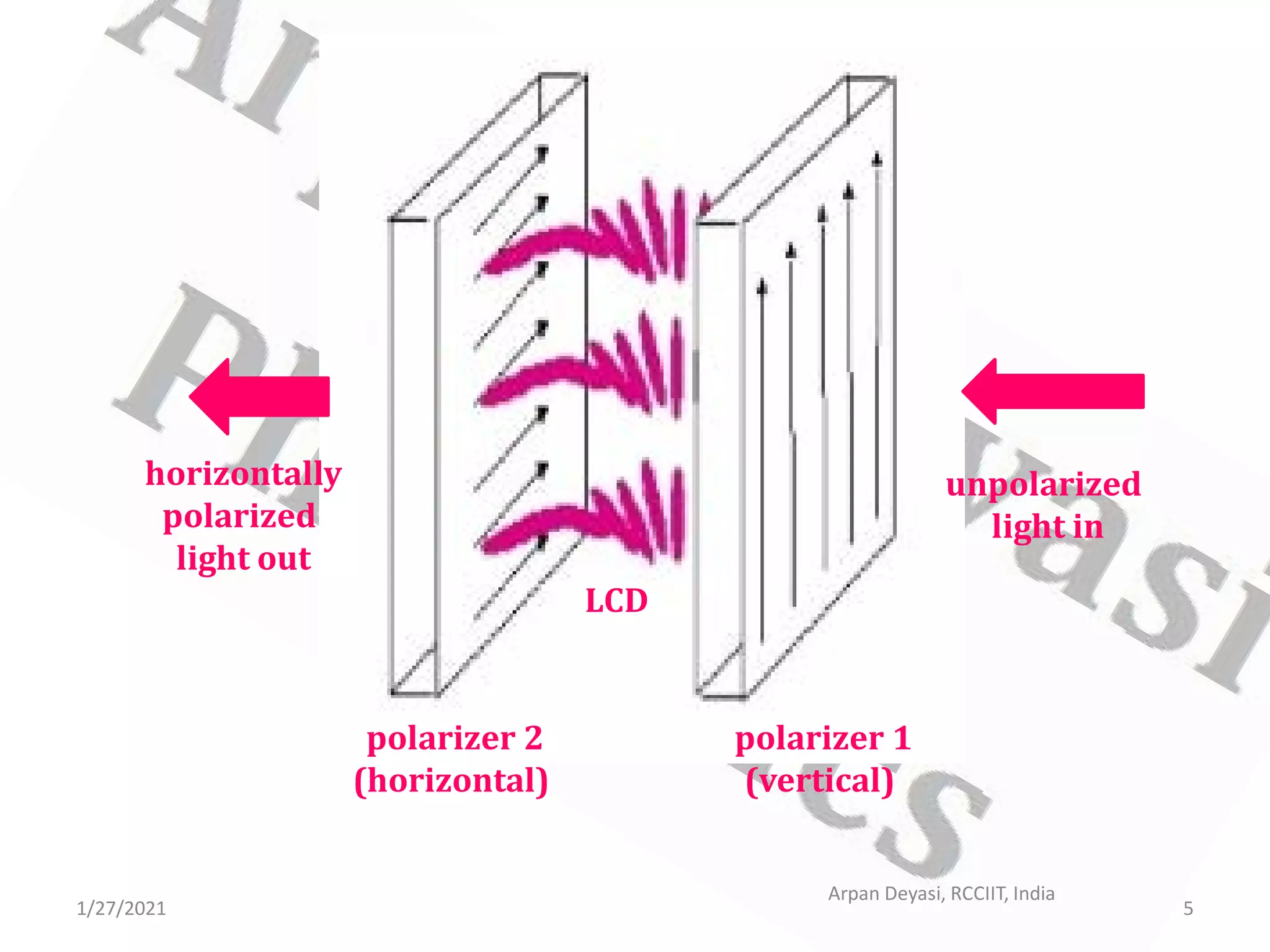
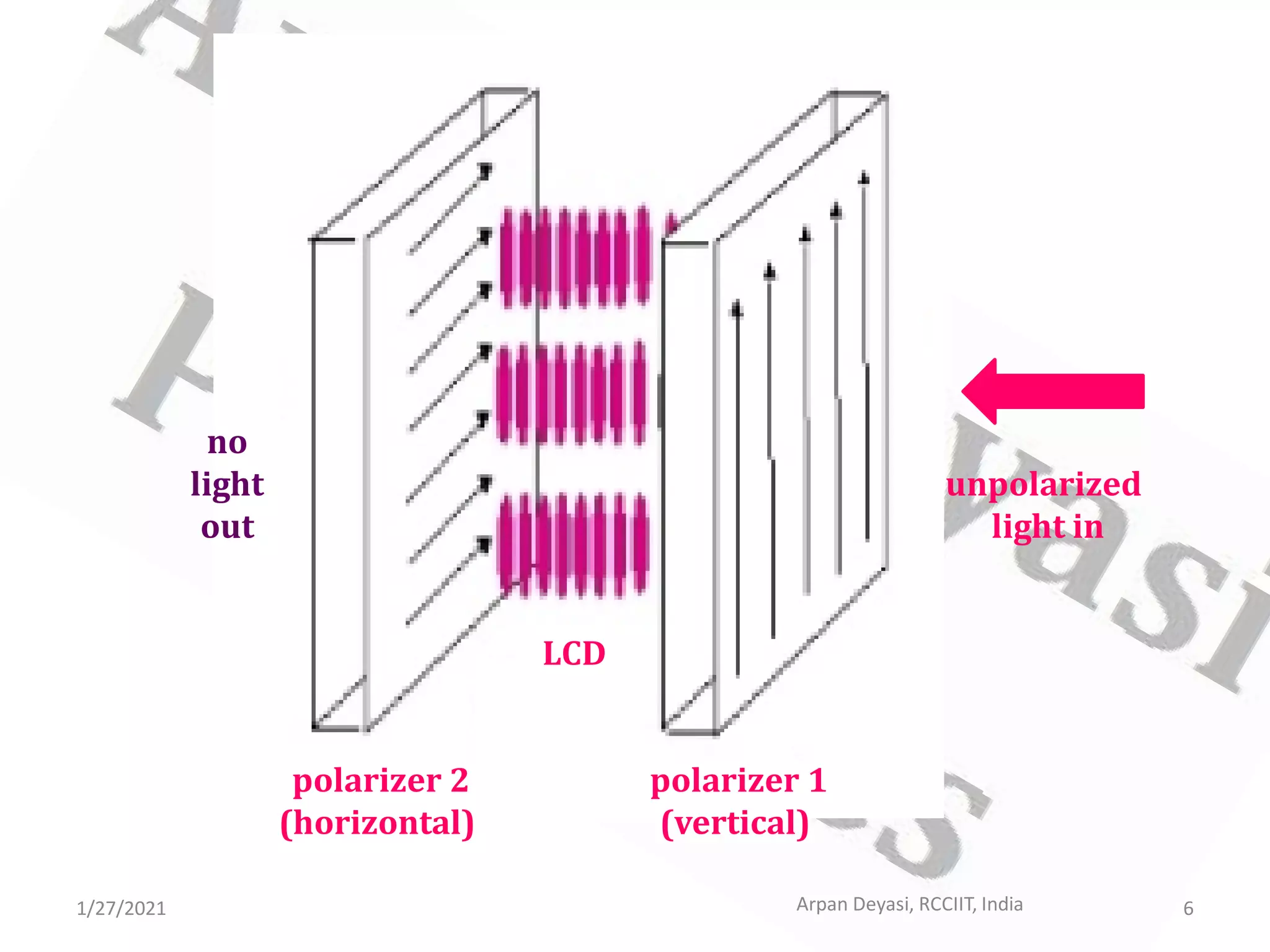
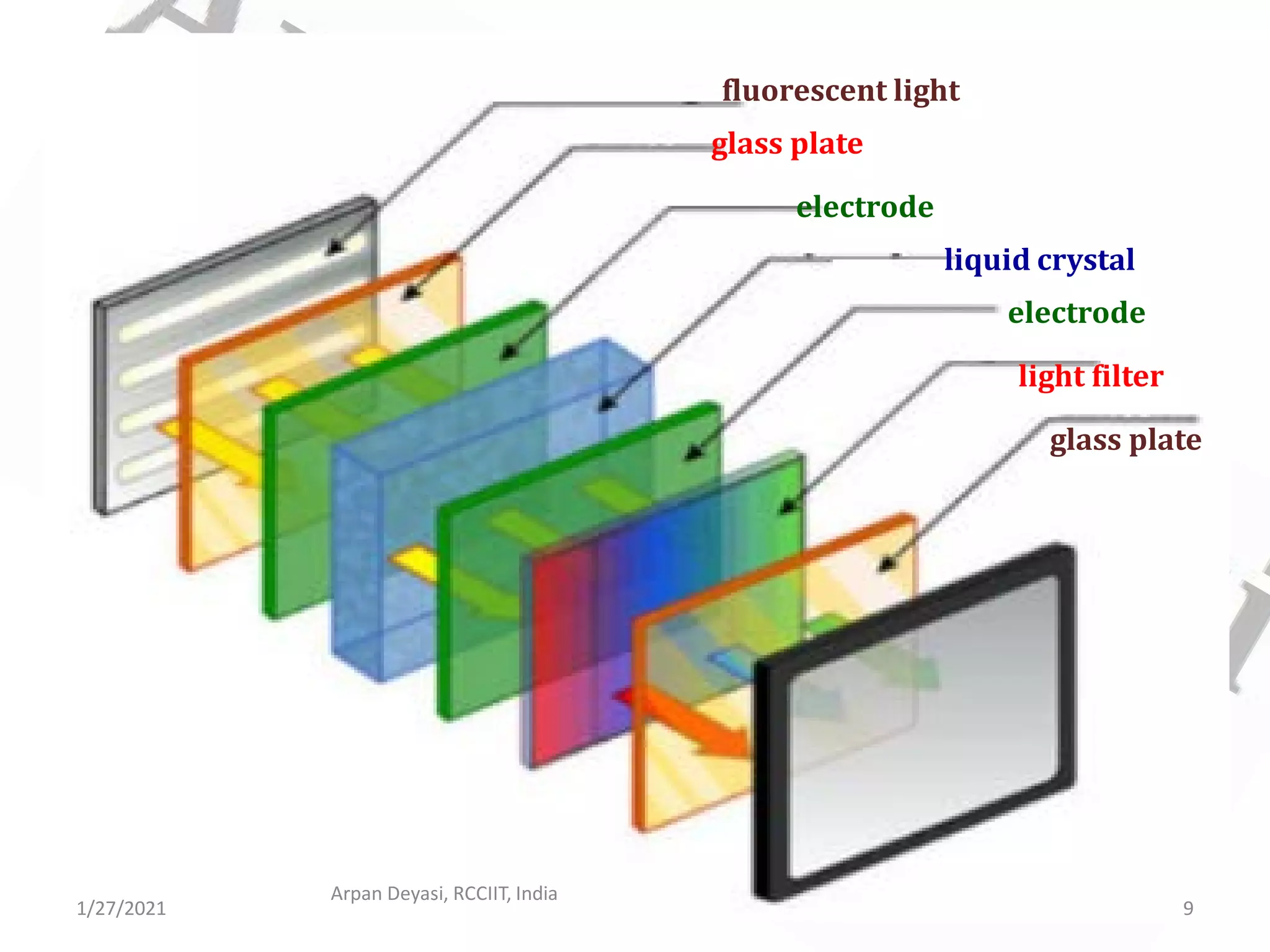
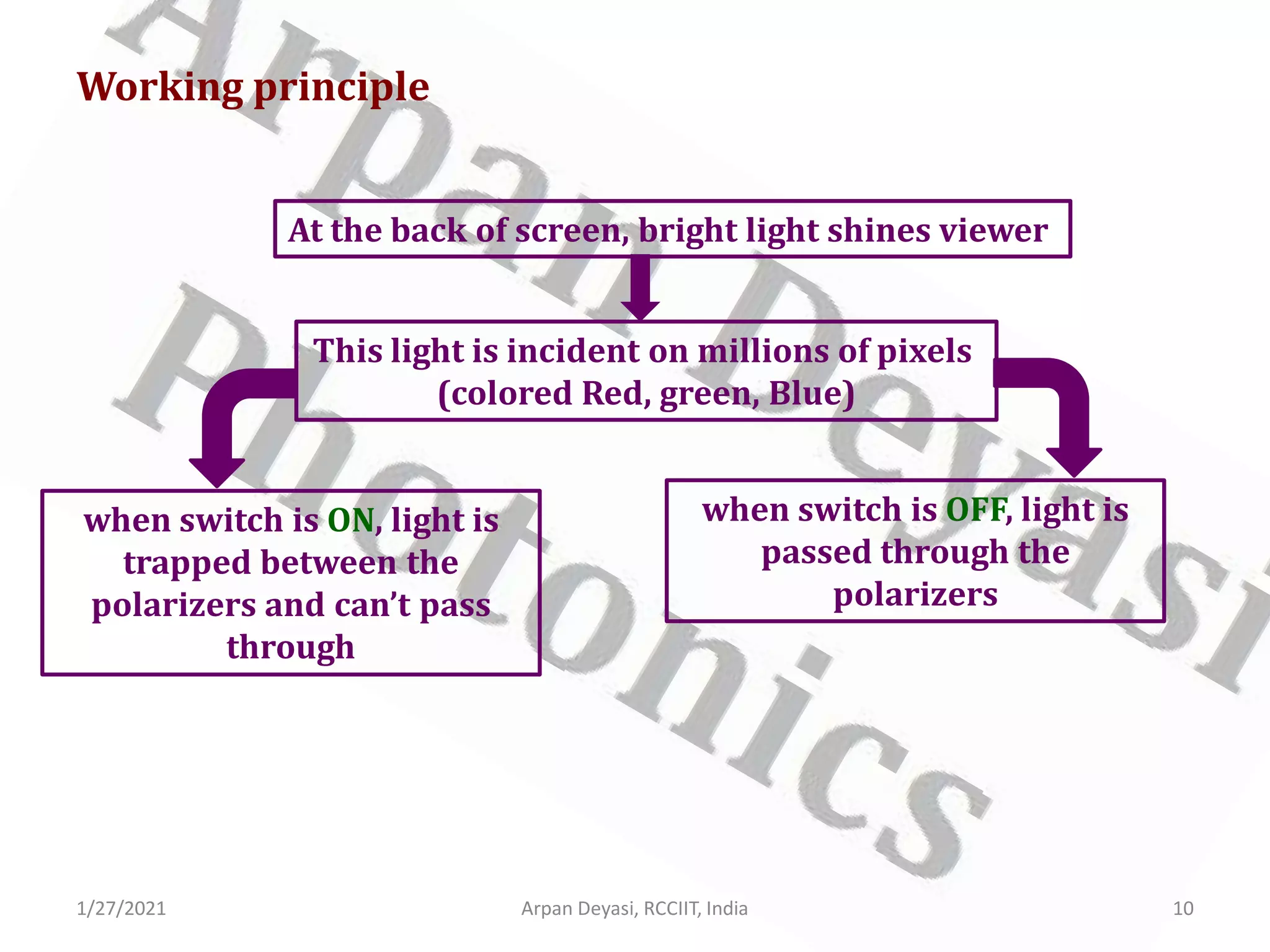
This document provides an overview of liquid crystal displays (LCDs). It discusses that LCDs are thin, flat panel displays that use polarized light and the polarization properties of liquid crystals to display electronic information like text, audio, and video. LCDs are preferred over older cathode ray tube (CRT) displays because they are smaller, use less power, weigh less, and have no electromagnetic radiation emission. The document explains the material properties and phases of liquid crystals, as well as how LCDs work using polarized light and pixels to switch areas of the display between opaque and transparent. It also covers different types of LCDs and some disadvantages compared to CRTs.