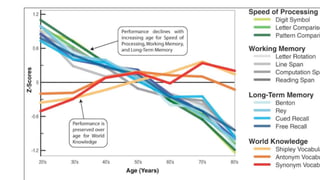
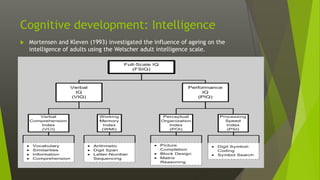
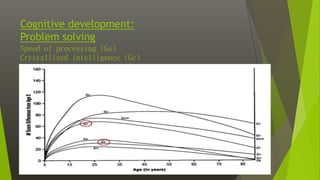
This document discusses various aspects of late adulthood, including physical, cognitive, and social development. Physically, aging affects the skin, hair, senses, brain, and other organs. Cognitive abilities like processing speed and fluid intelligence decline with age, while crystallized intelligence remains intact or increases. Socially, retirement adjustment and changes in relationships are developmental tasks. Death and dying also become more salient concerns in late life. Overall, late adulthood involves navigating physical, mental, and social changes that come with aging.