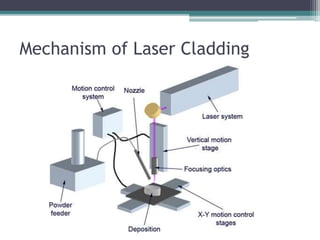
Laser cladding is a process that uses a laser to melt and consolidate powdered material in order to coat a substrate. The powder is injected into the melt pool created by the interaction of the laser with the substrate. As the substrate moves, the melt pool solidifies, building up a track of solid metal. Different materials can be used for the powder depending on the desired properties, such as corrosion or wear resistance. Laser cladding is useful for repairing worn parts and coating components to improve properties. It provides benefits like a strong metallurgical bond between the coating and substrate.