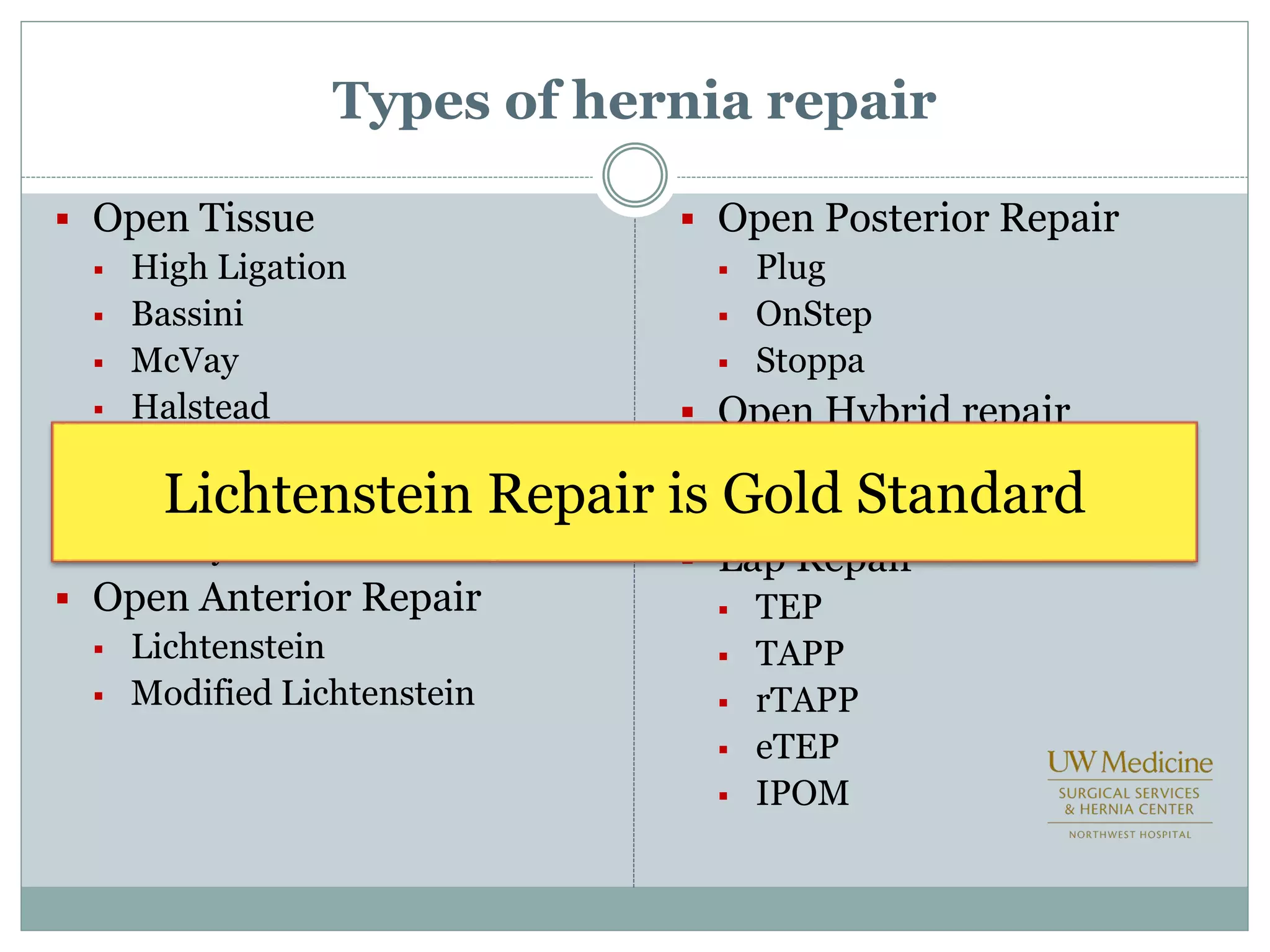
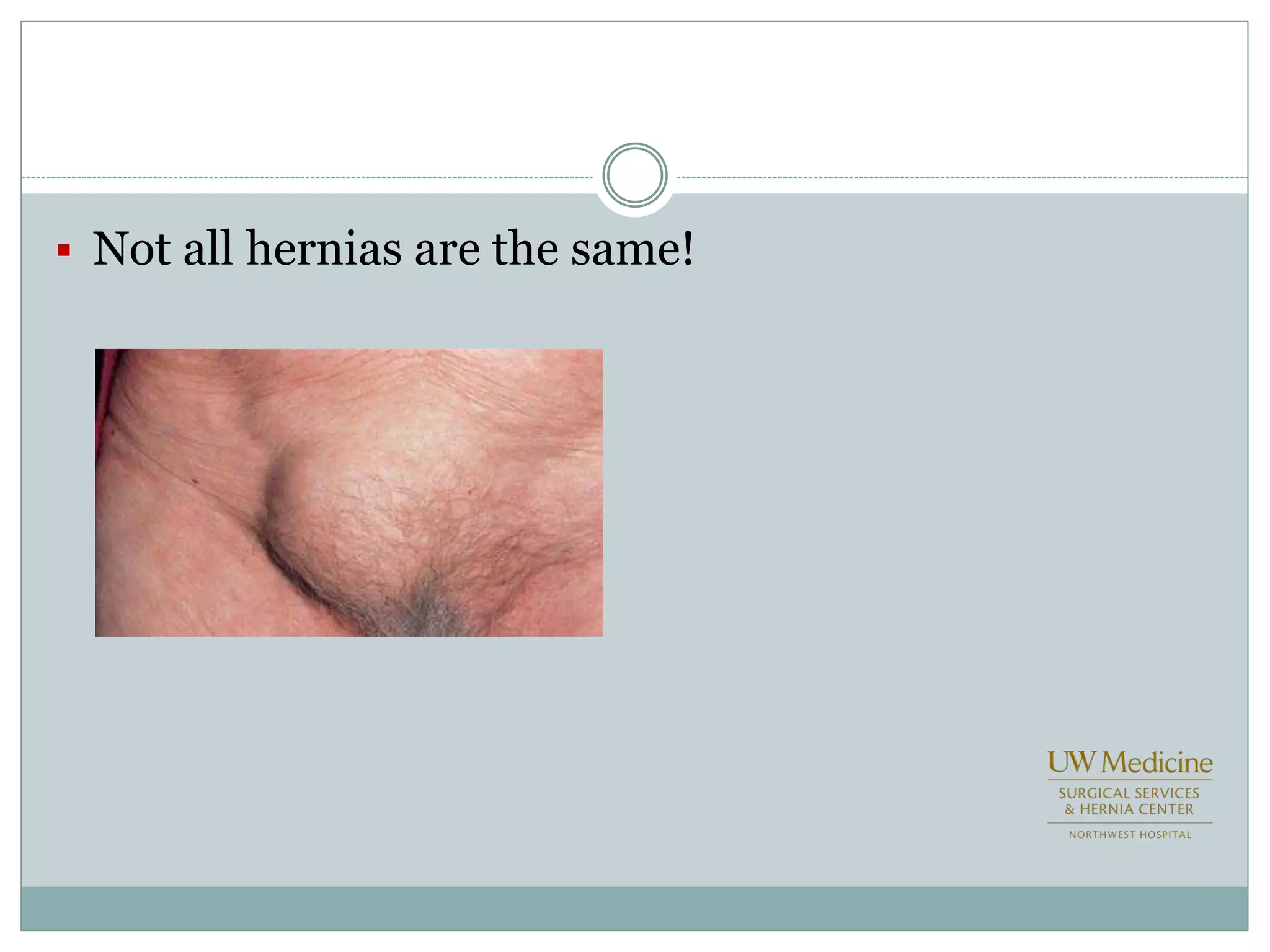
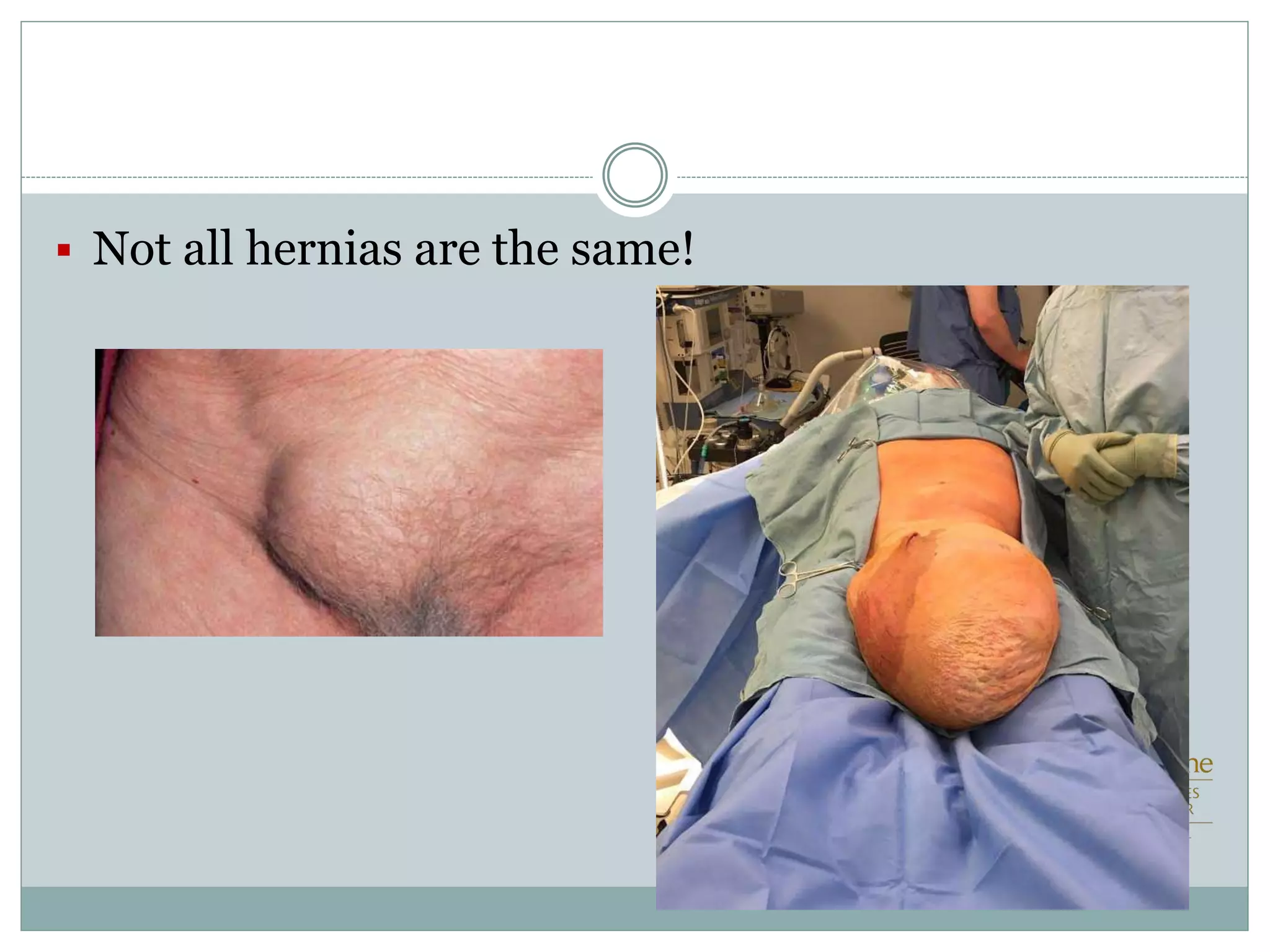
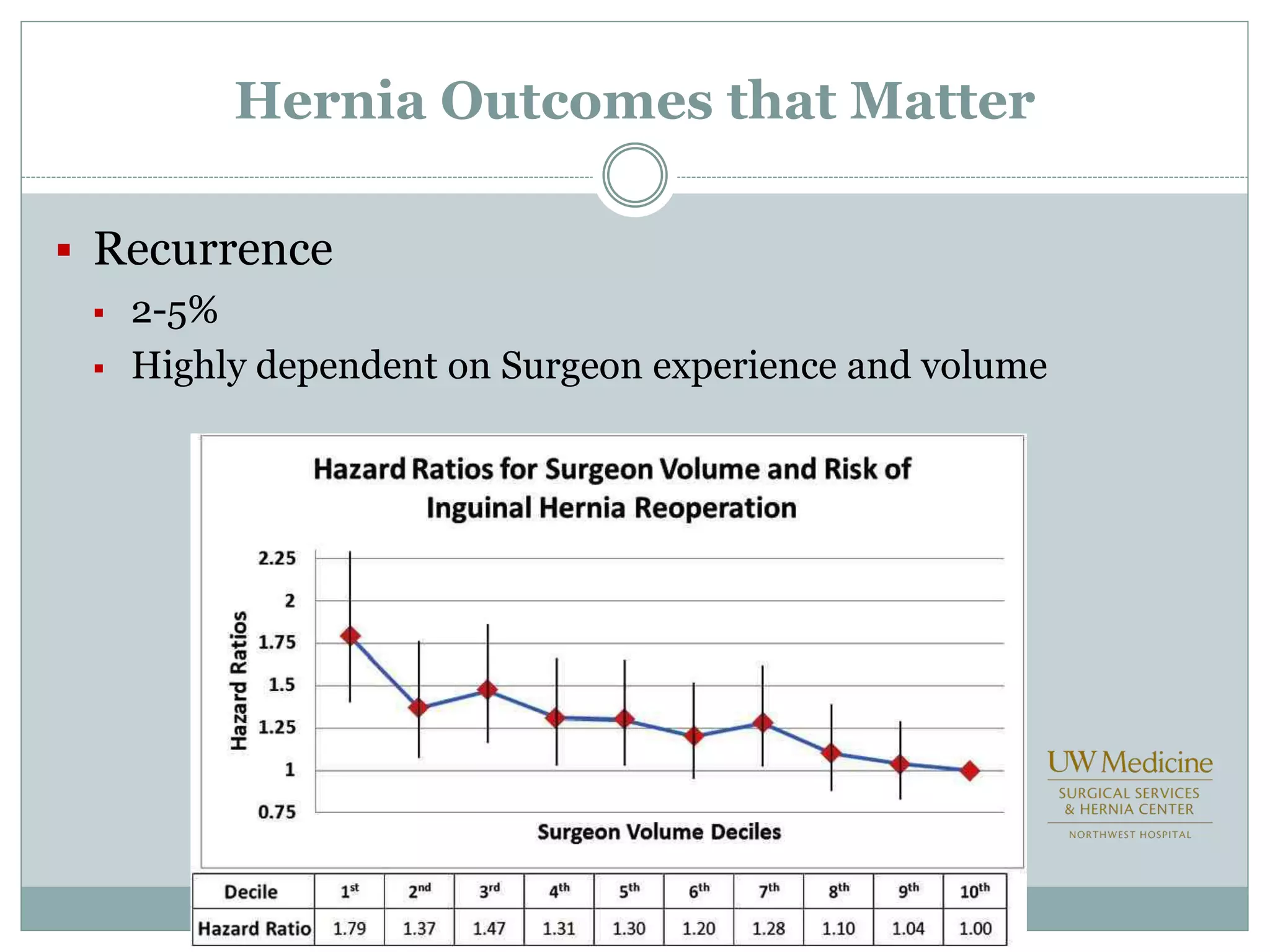
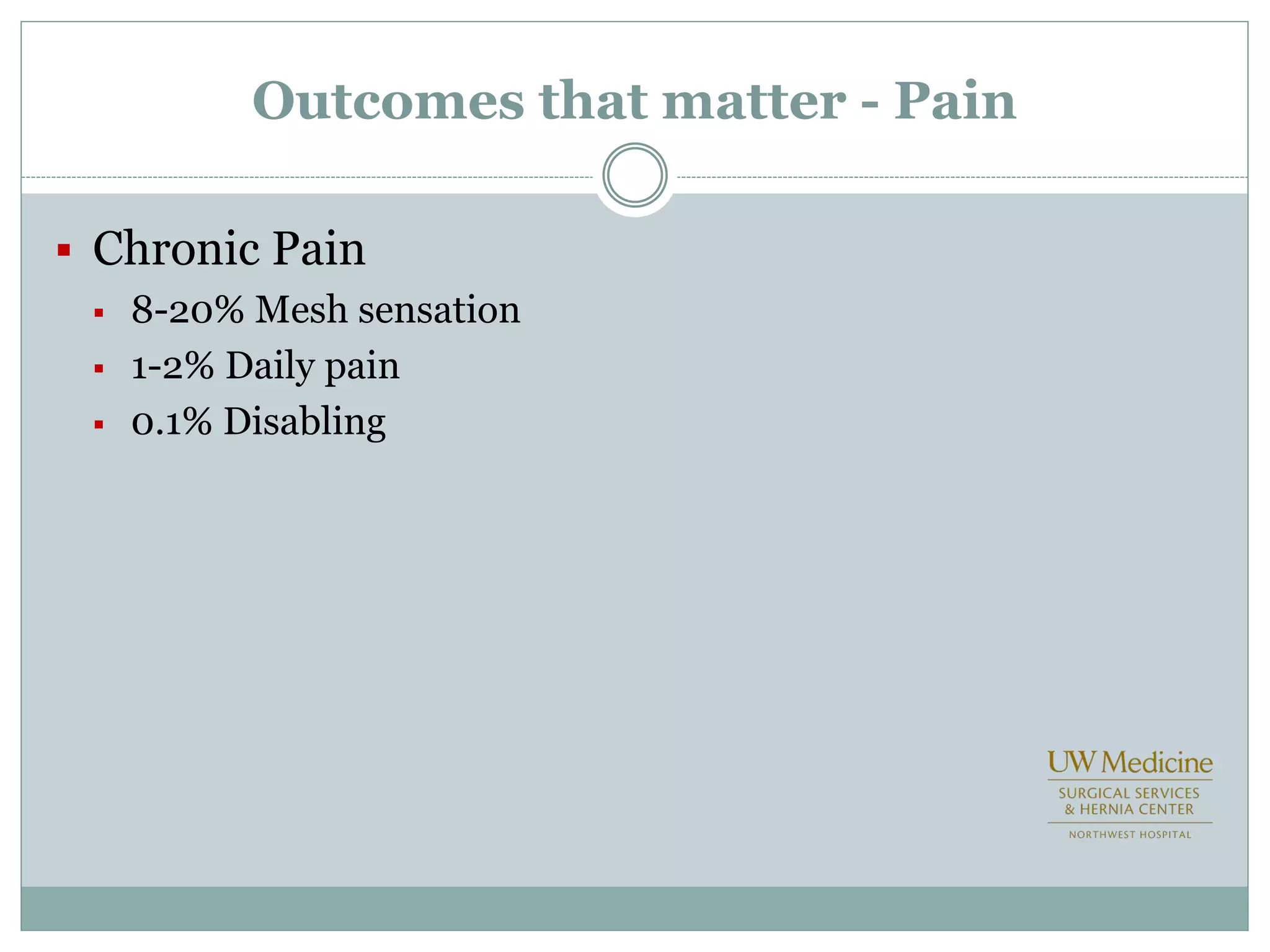
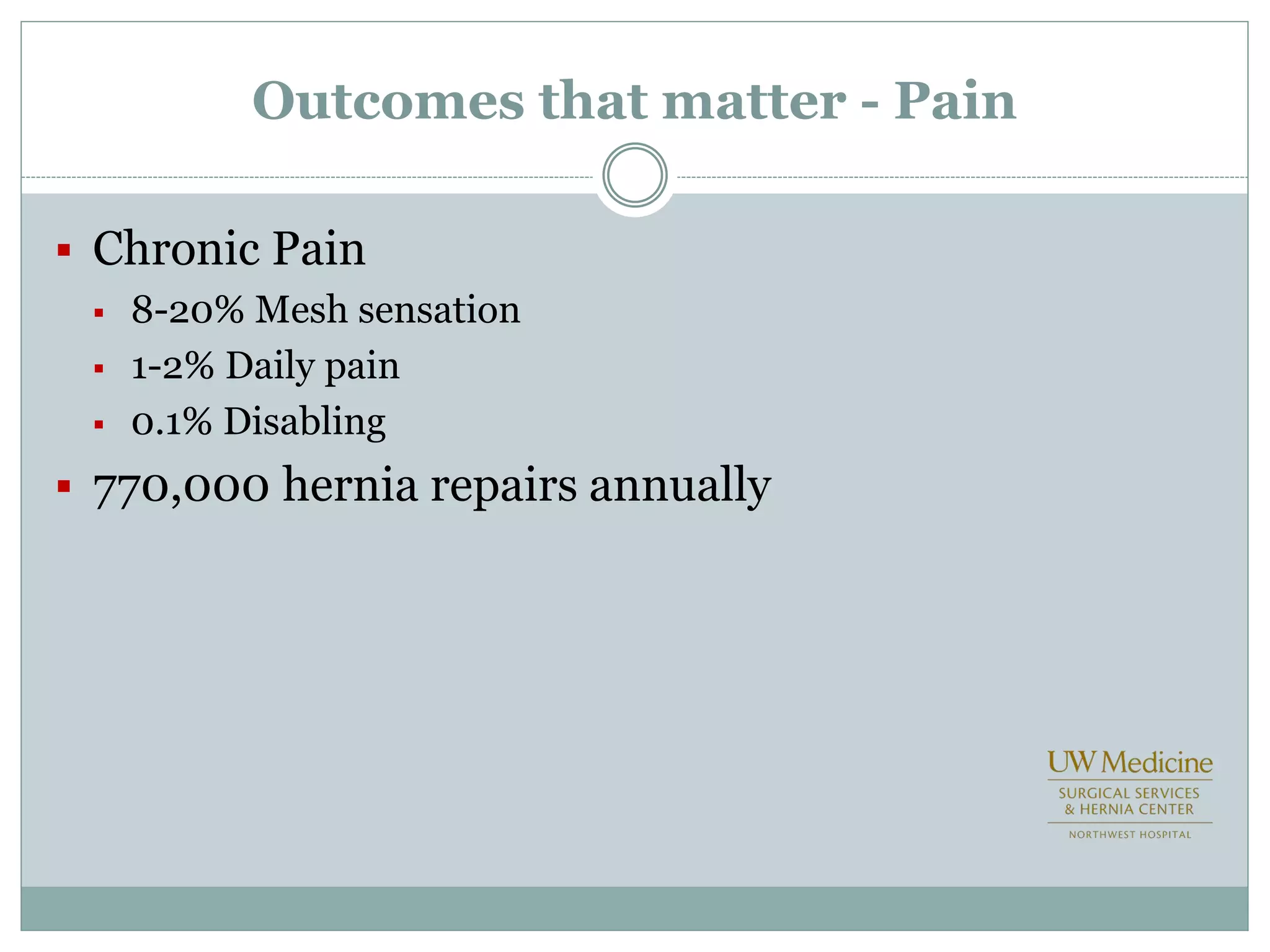
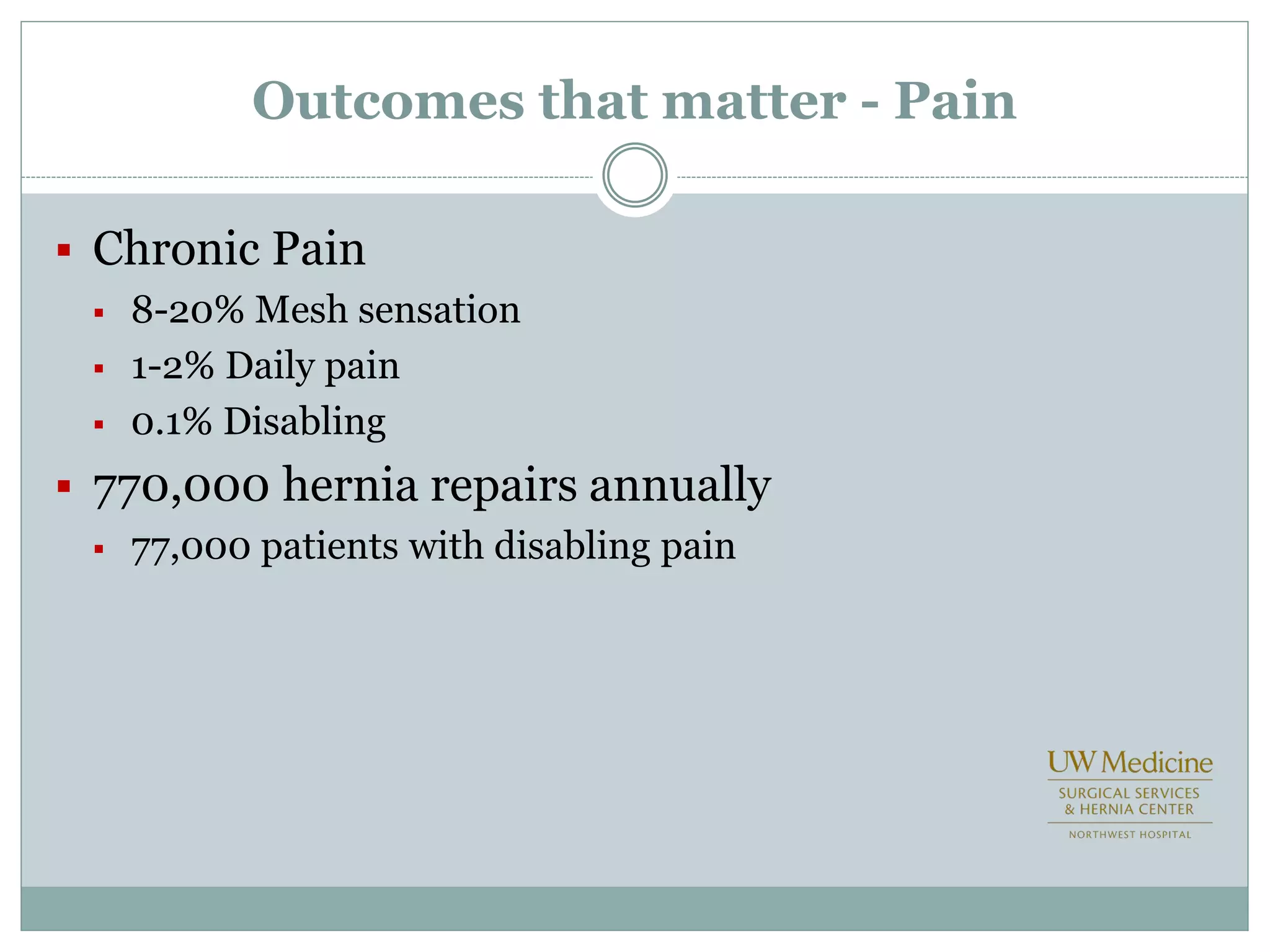
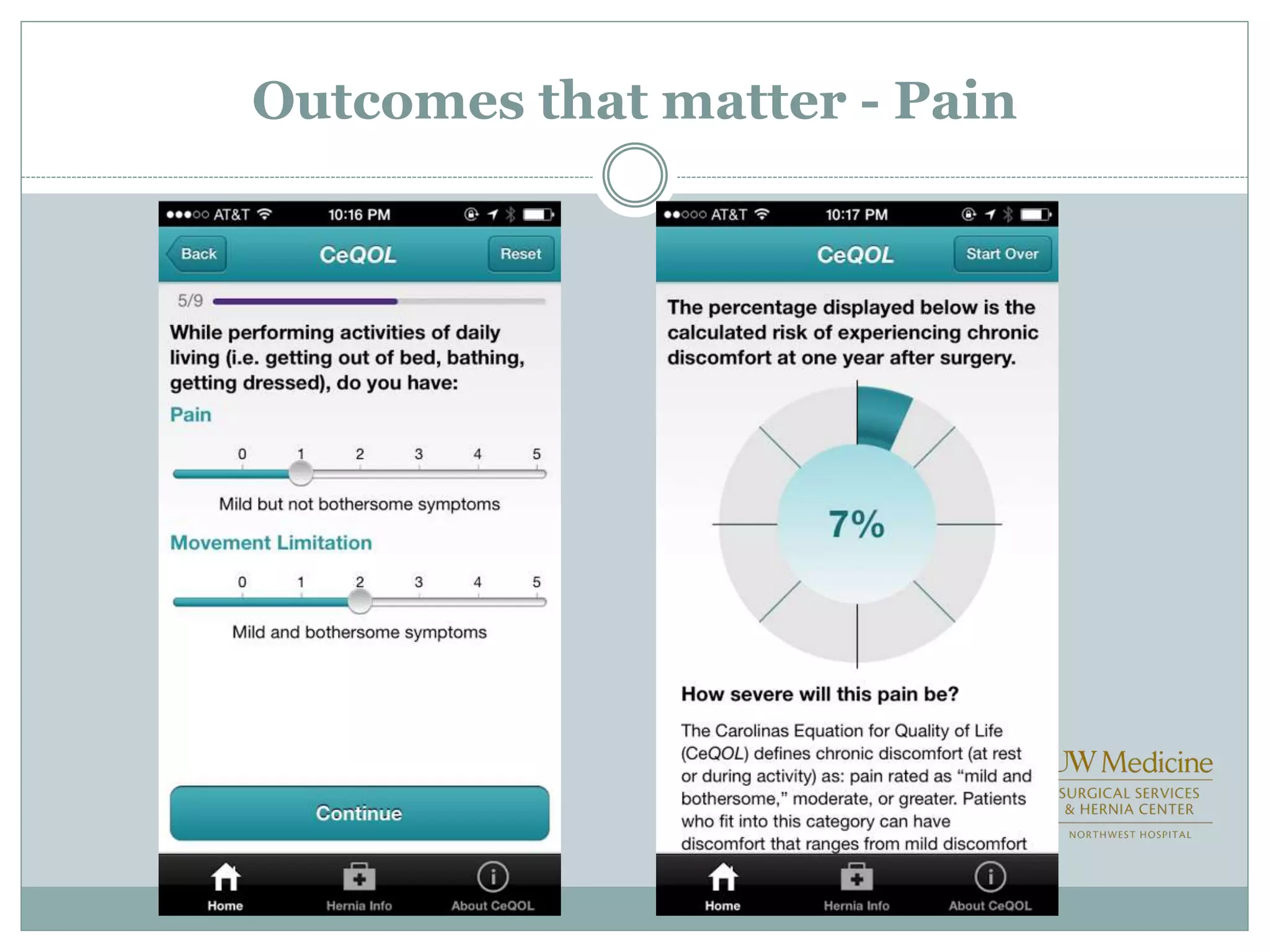
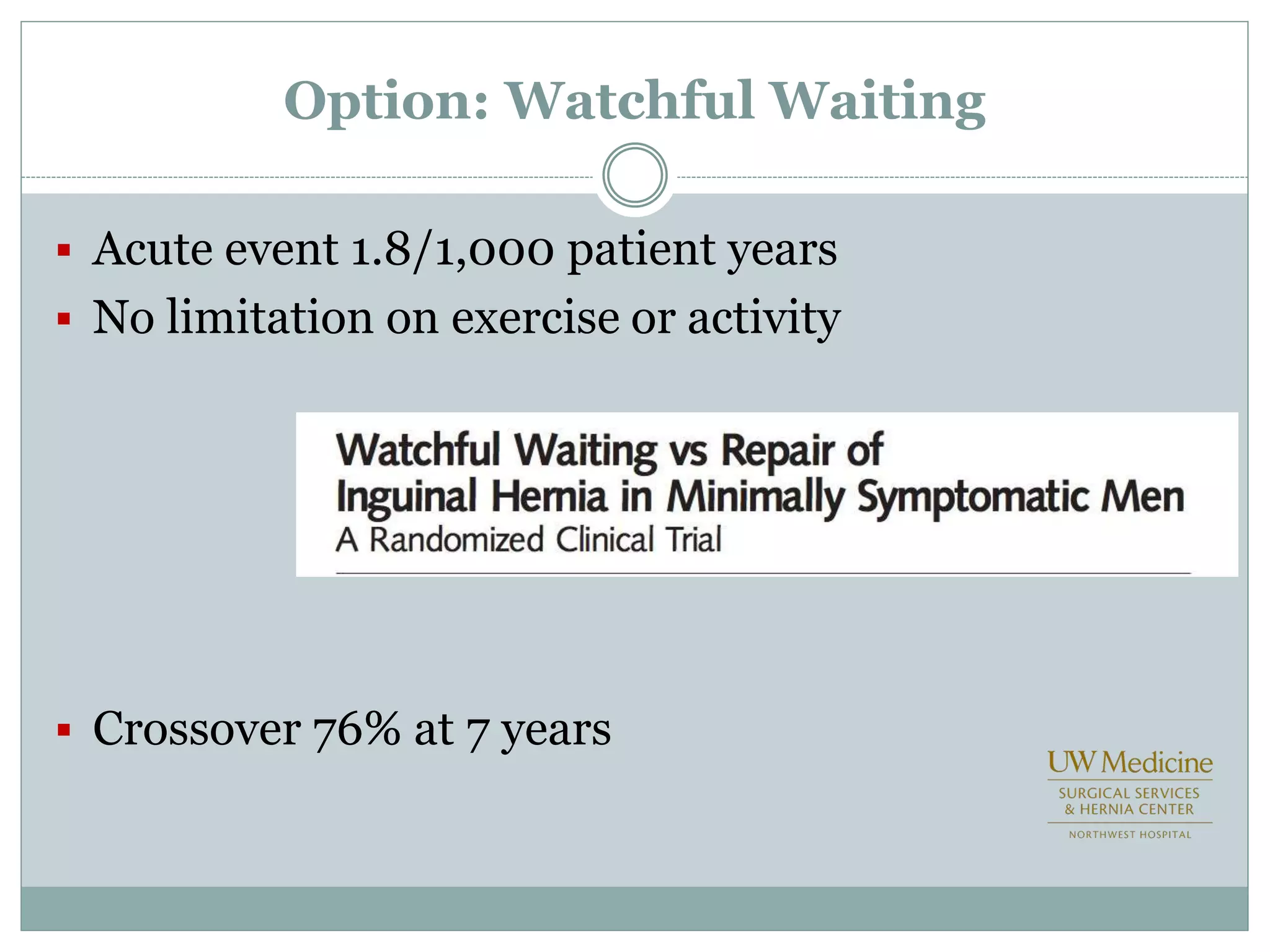
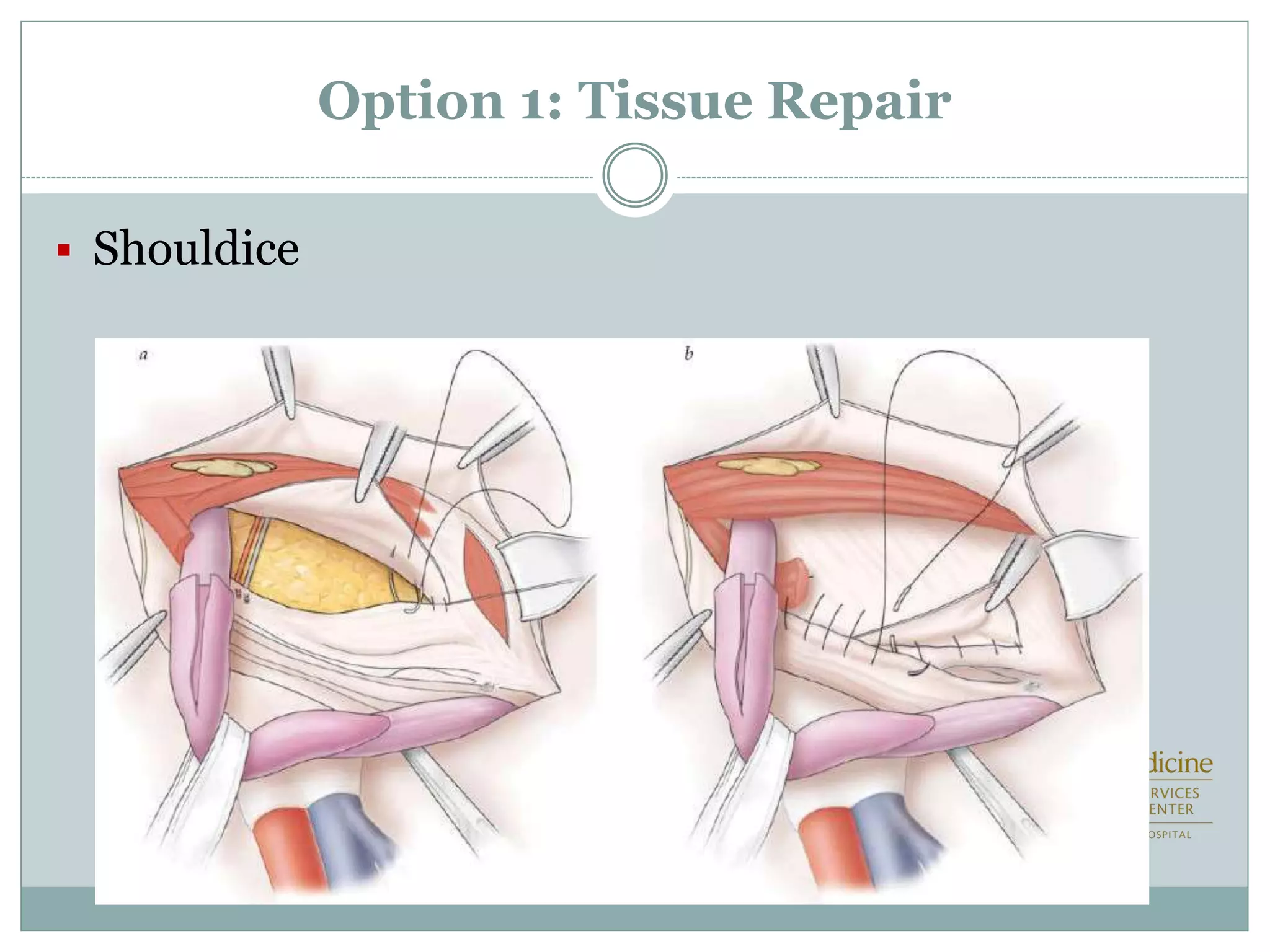
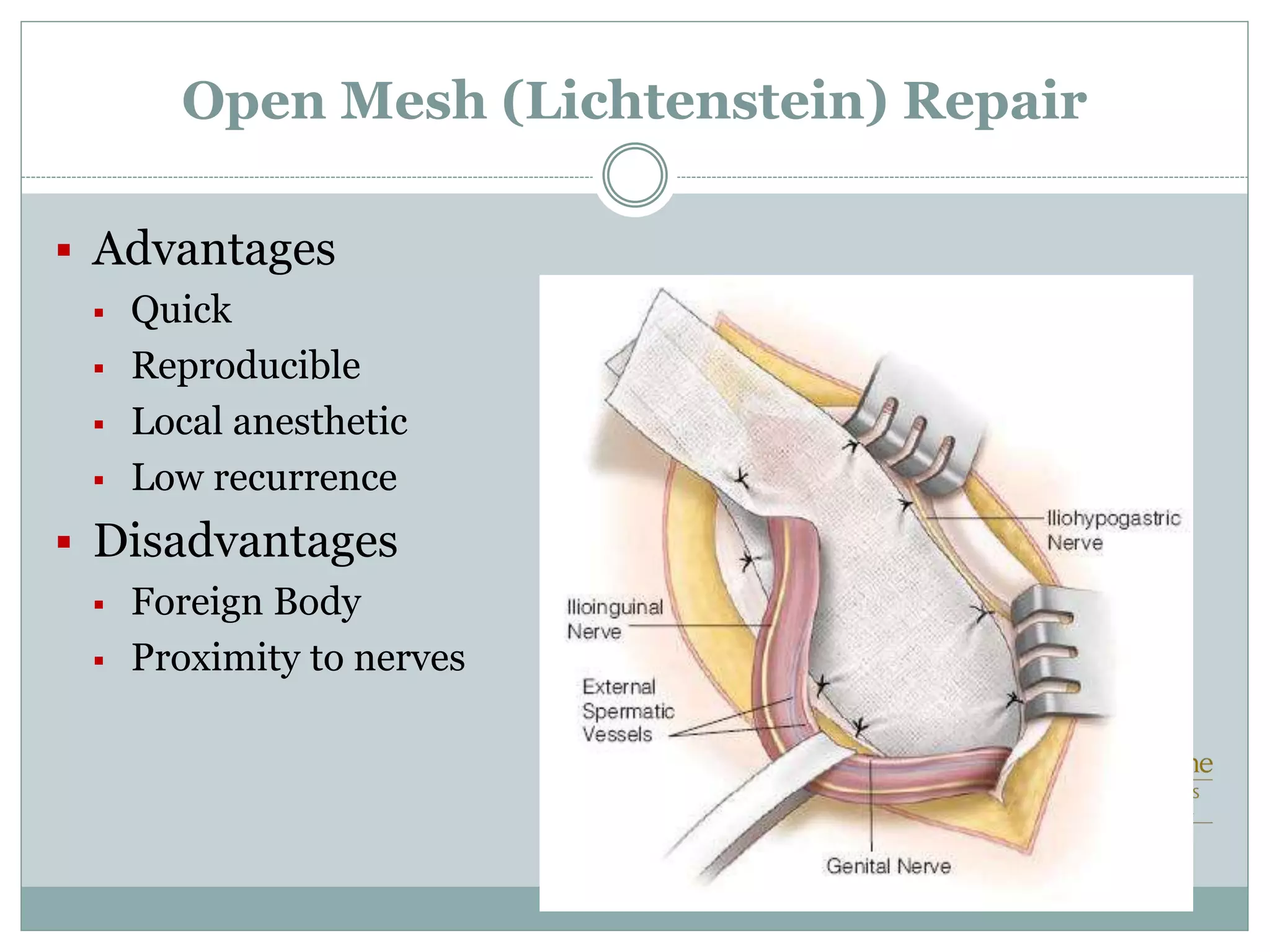
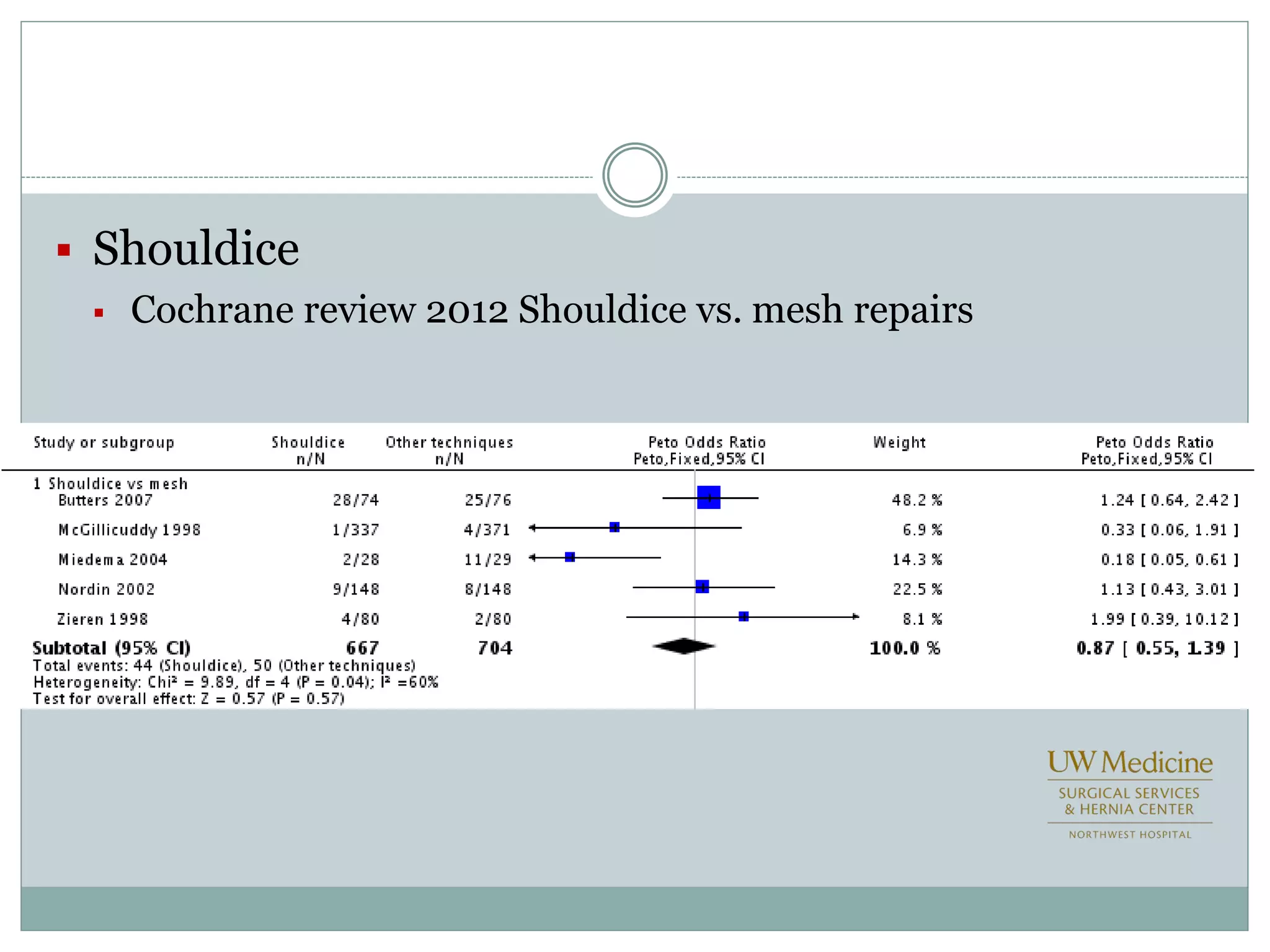
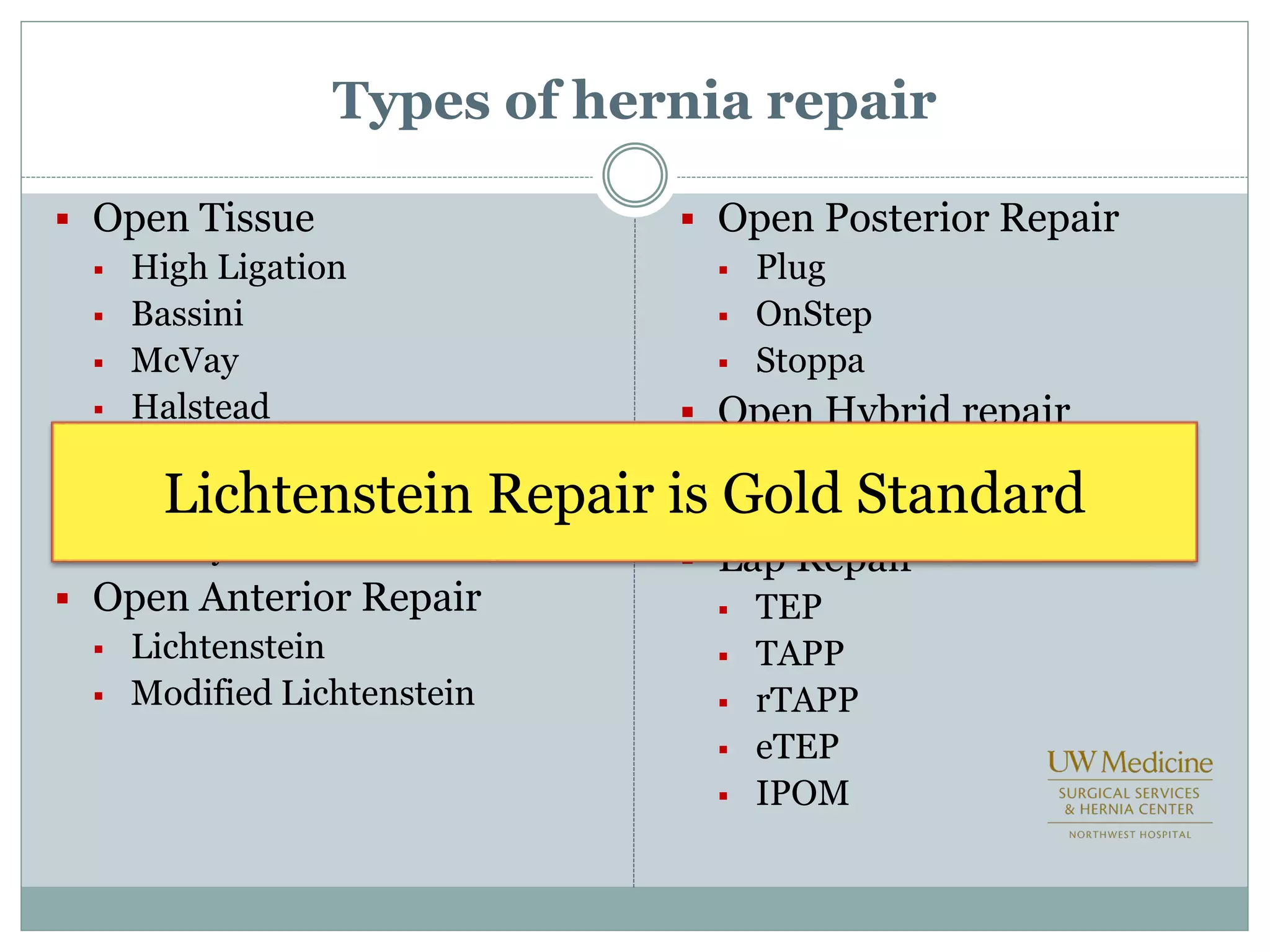
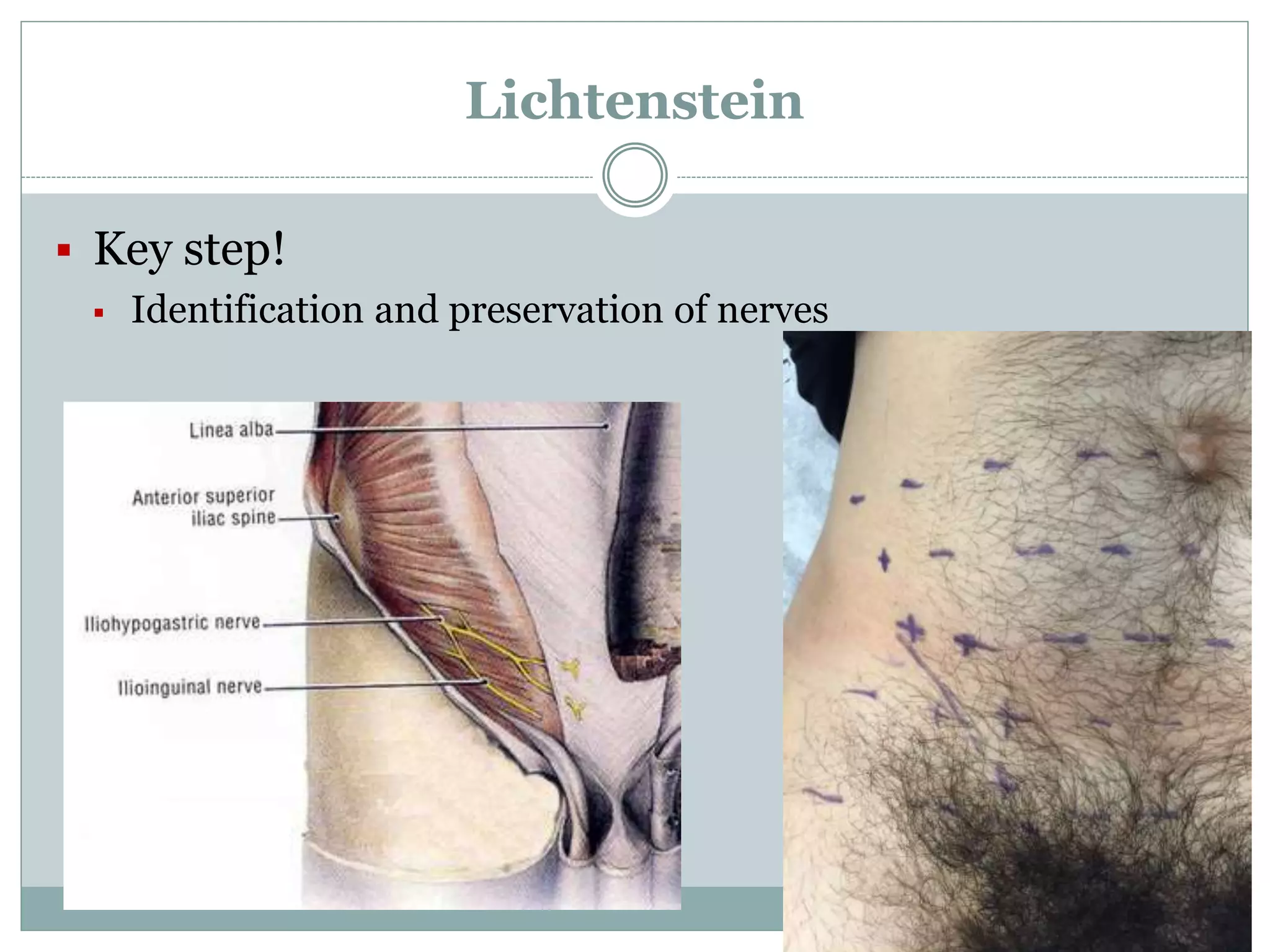
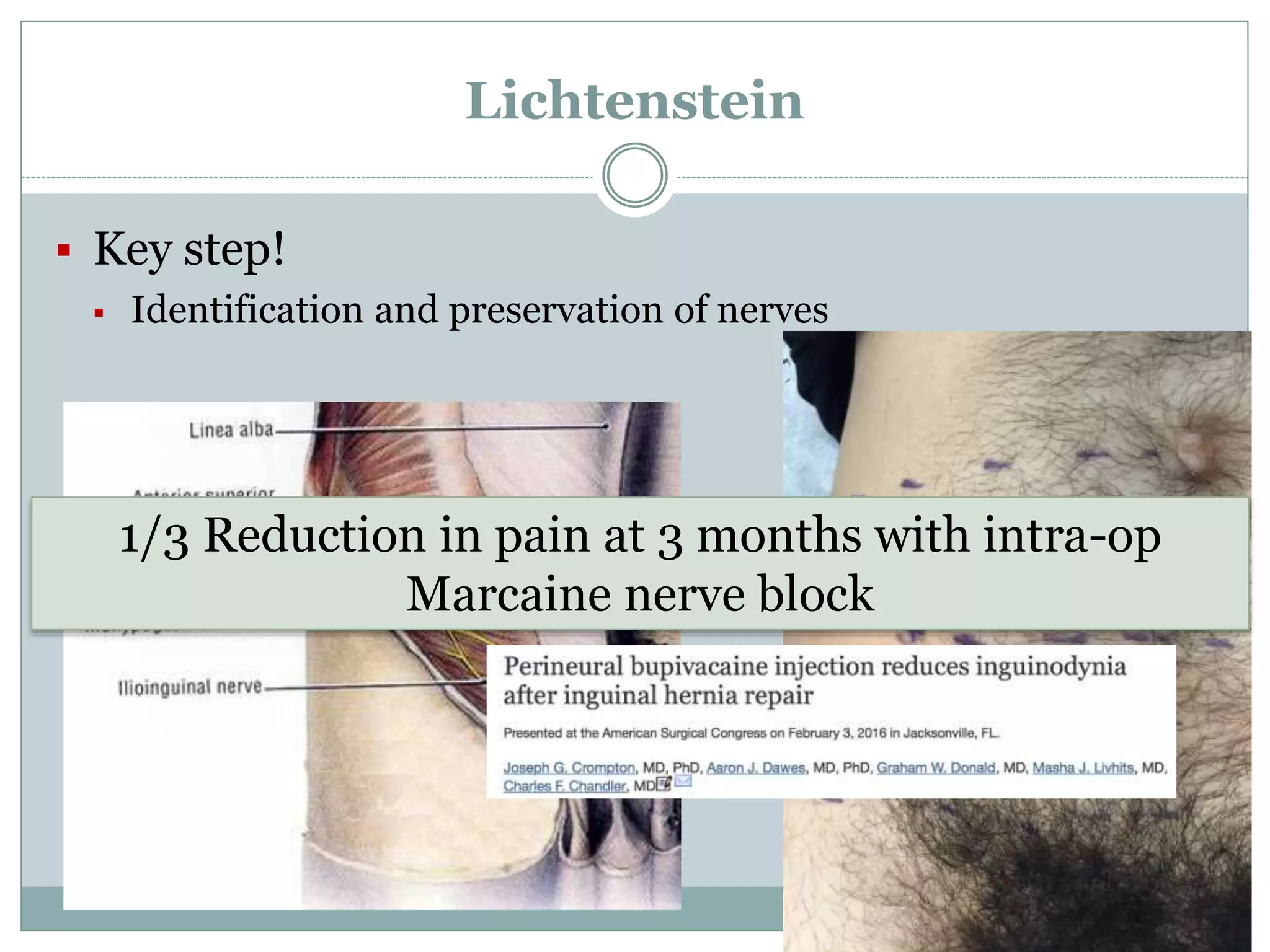
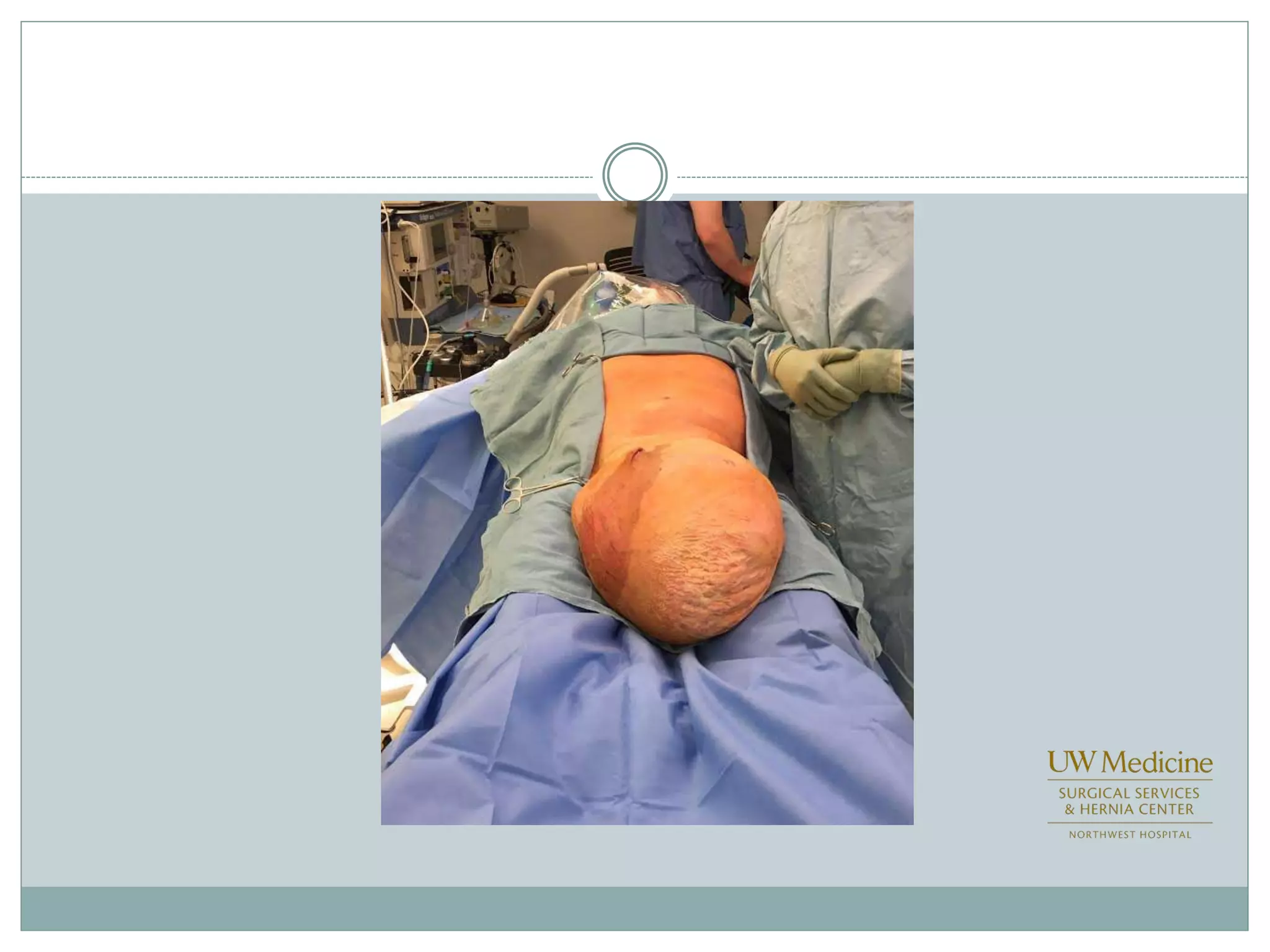
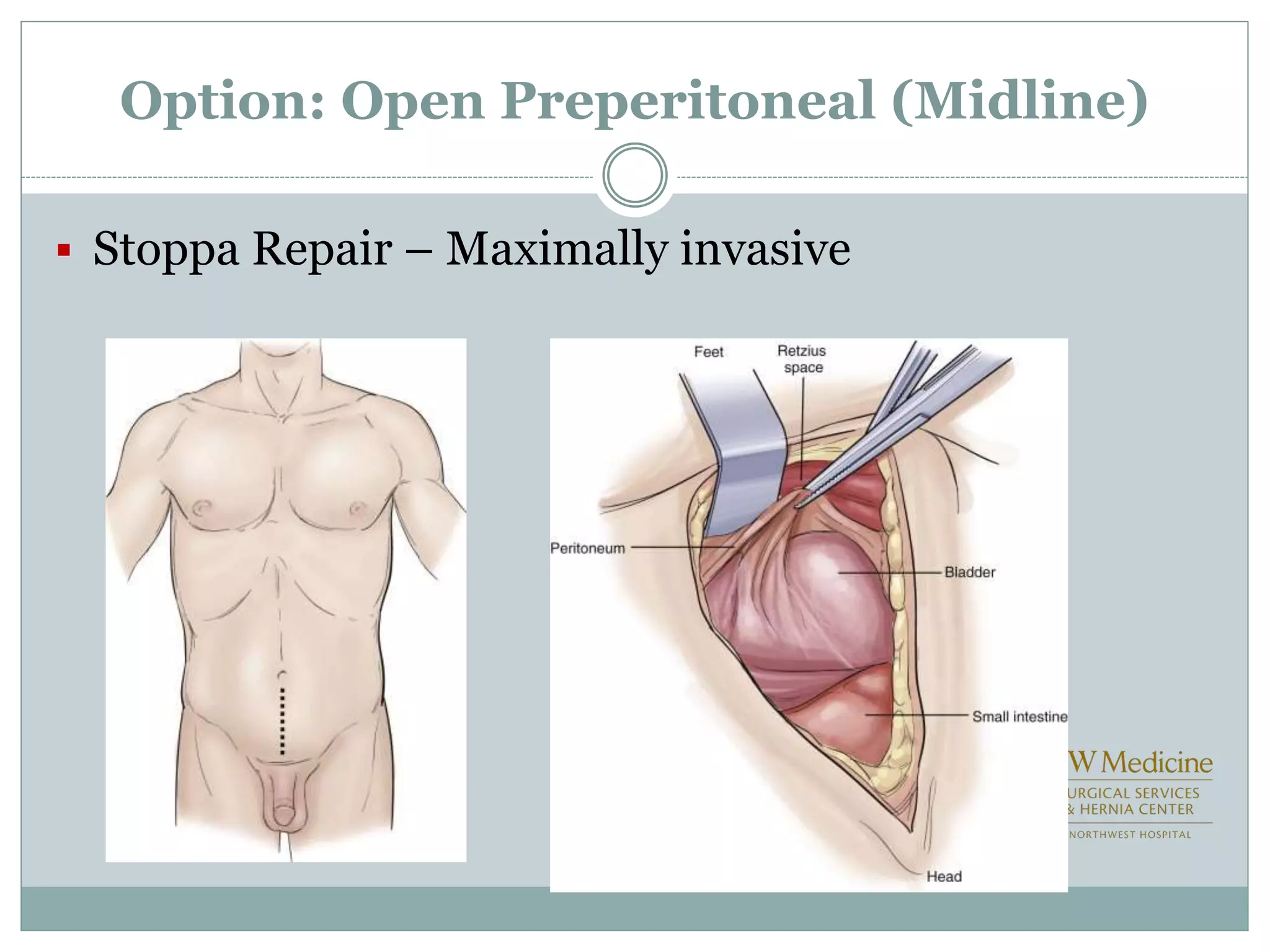
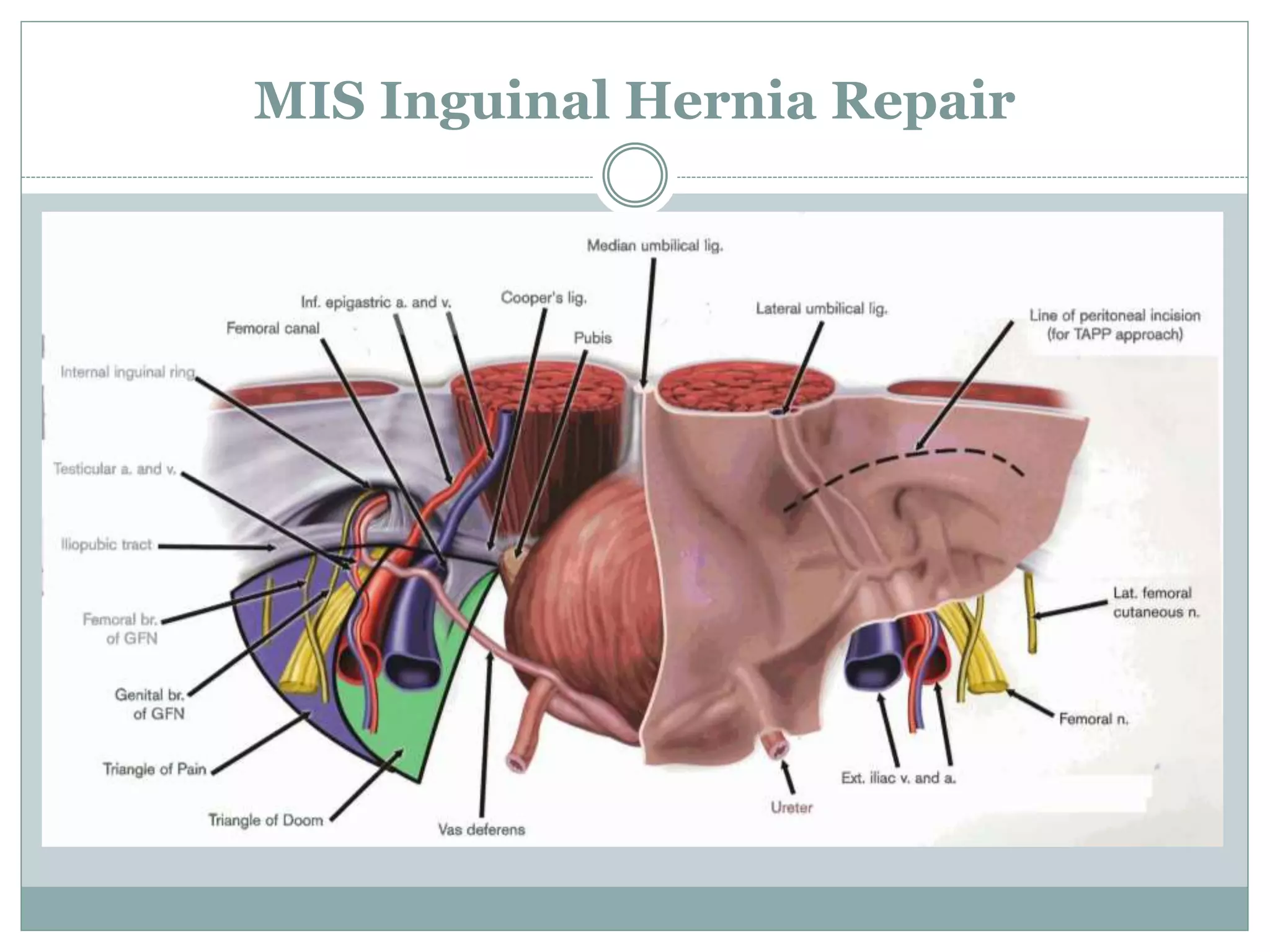
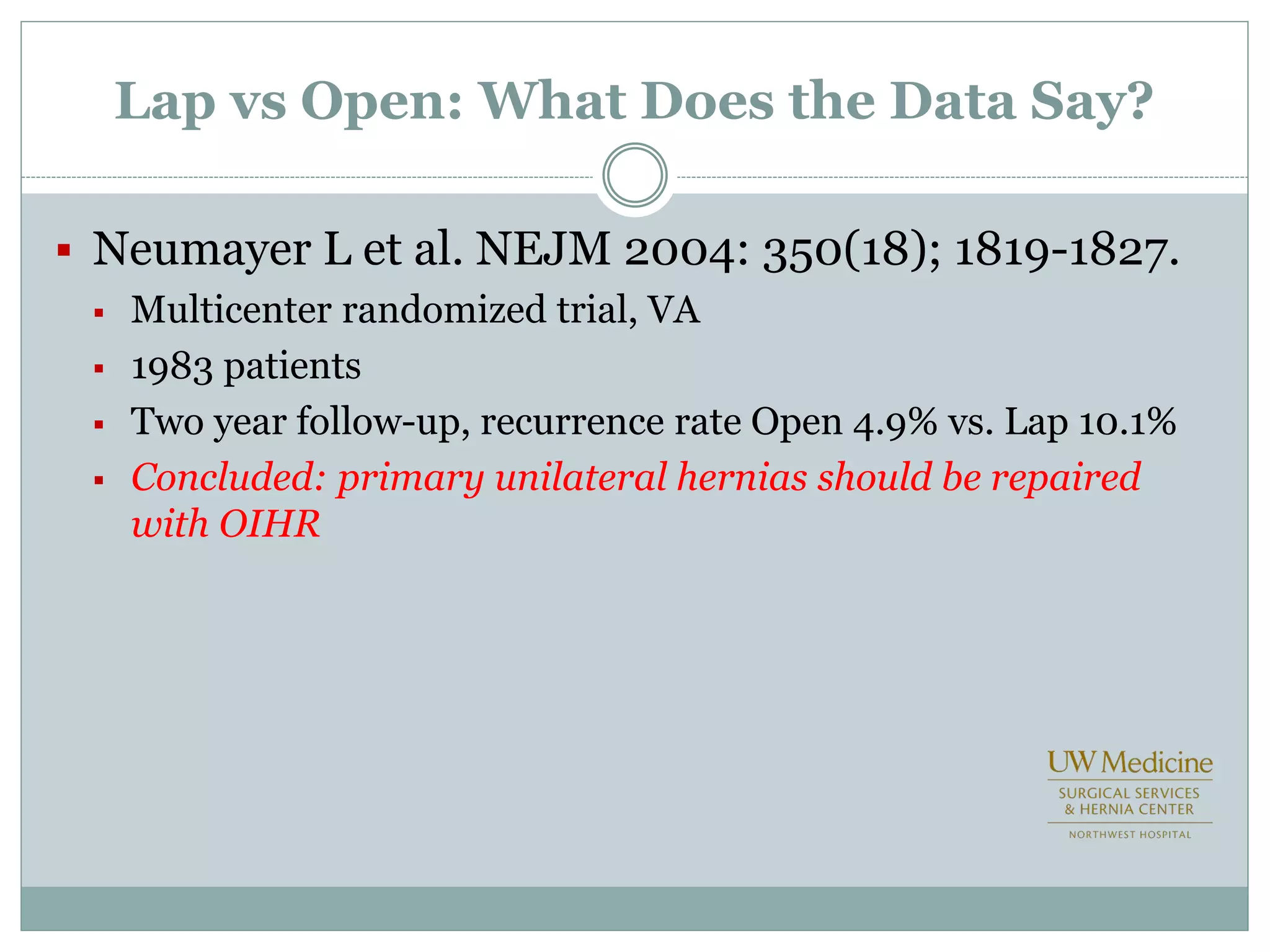
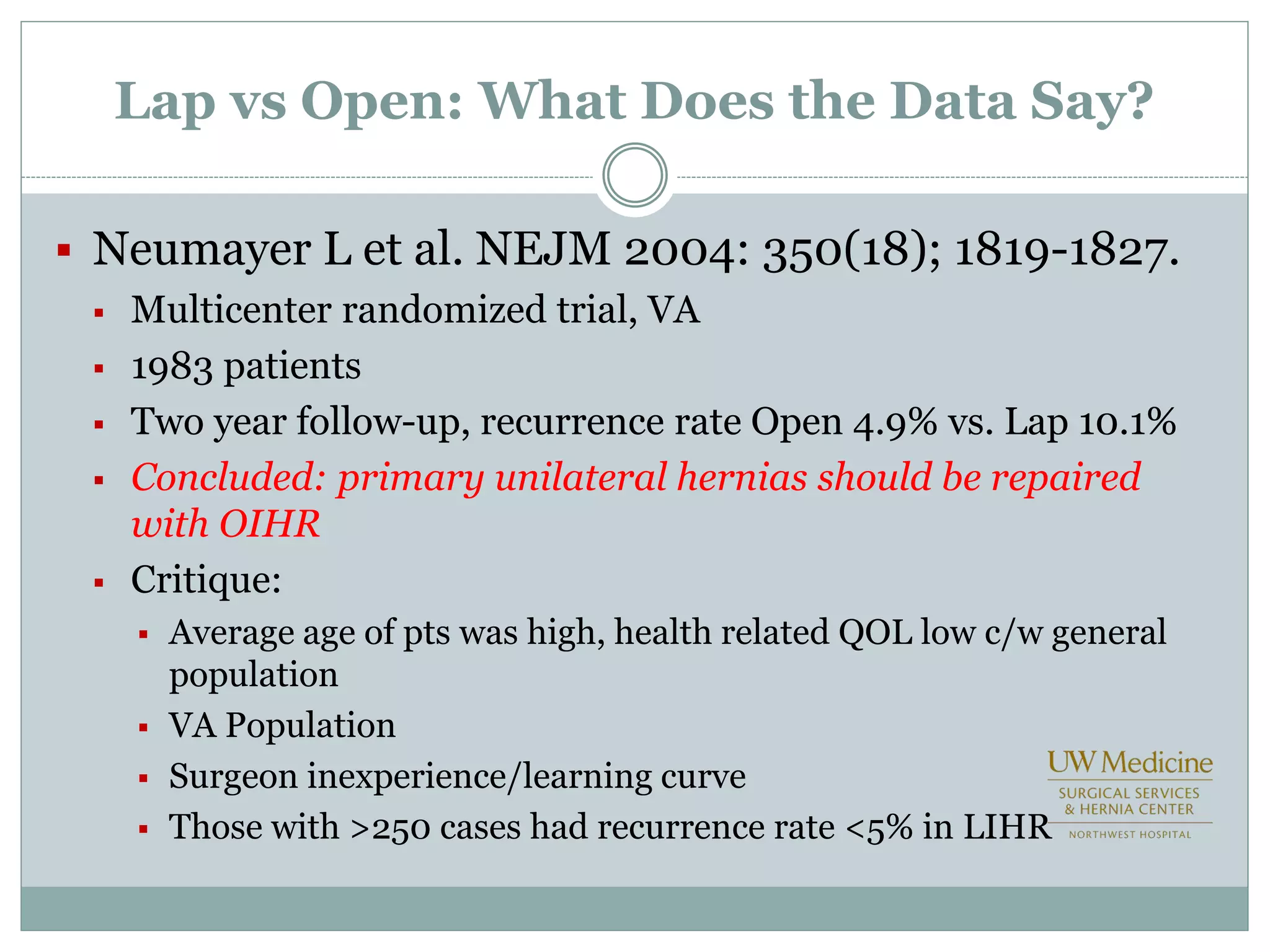
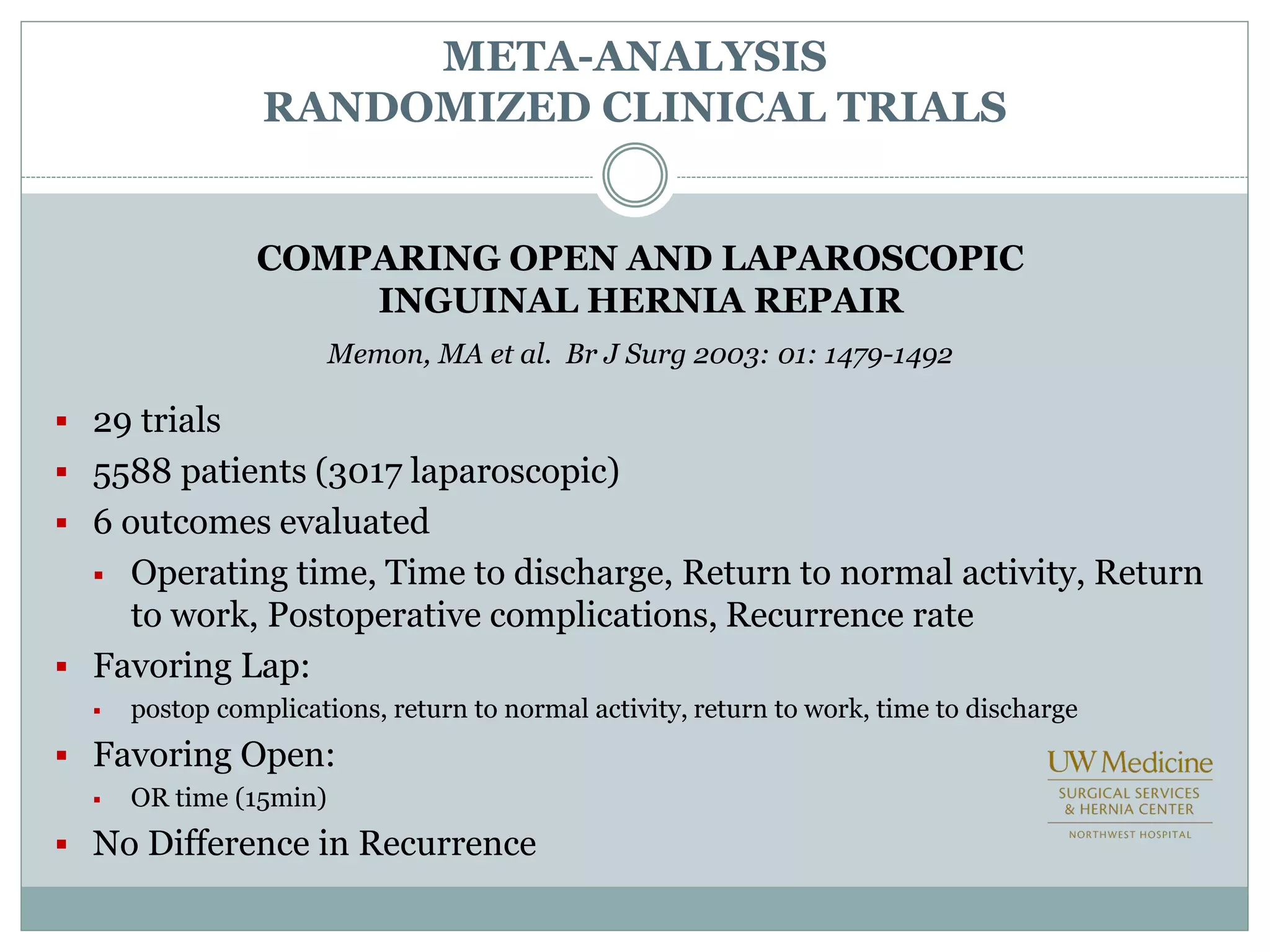
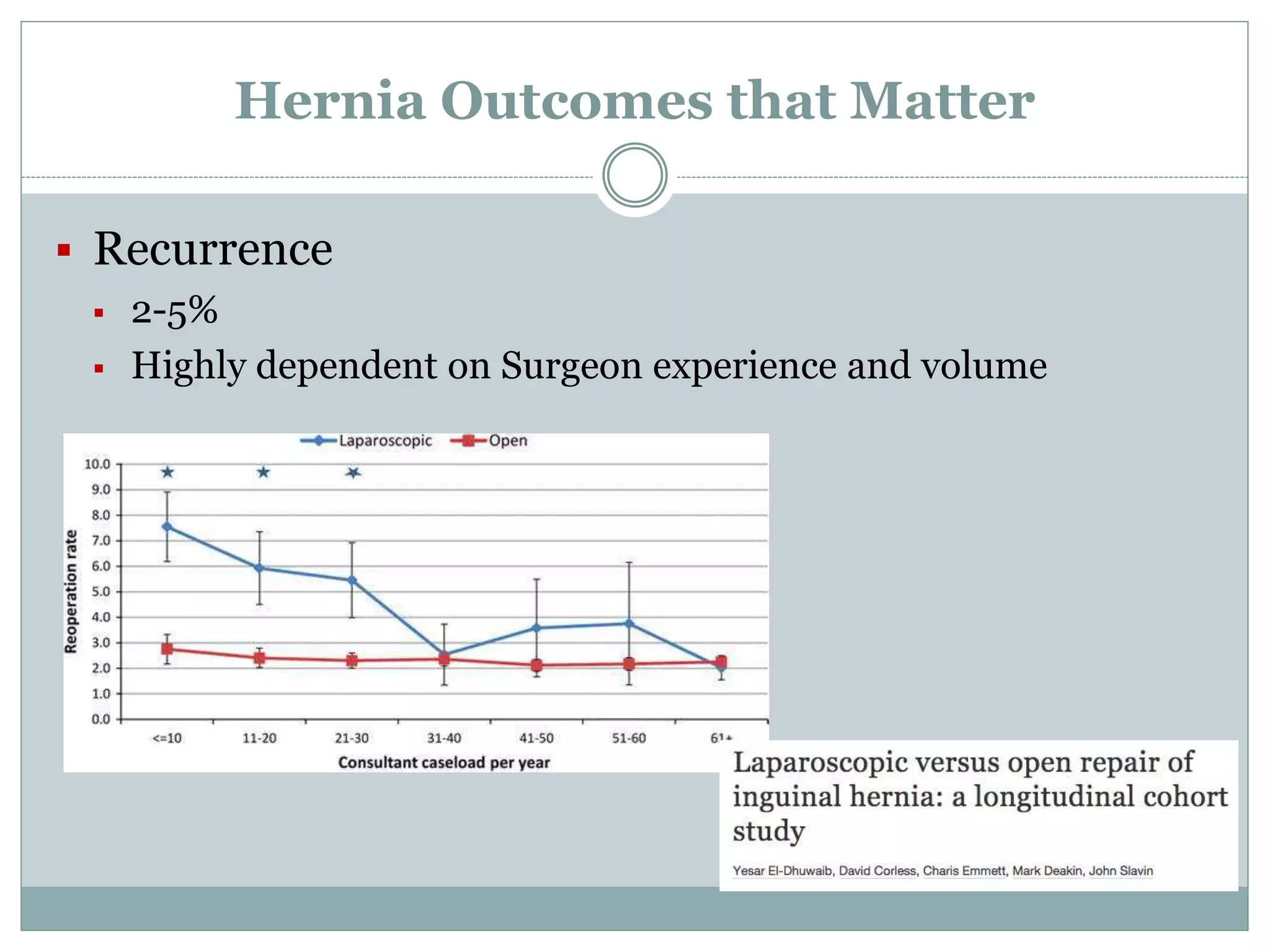
This document discusses different types of hernia repair techniques including open and laparoscopic approaches. It provides details on various open tissue repair techniques as well as open mesh repairs like Lichtenstein repair. Laparoscopic repairs like TEP and TAPP are discussed along with their advantages of less pain and faster recovery compared to open repairs. However, laparoscopic repairs are noted to be more technically challenging. Several studies comparing open and laparoscopic outcomes are summarized, finding laparoscopic repairs result in less short-term pain and faster recovery but higher recurrence rates, especially among low-volume surgeons. The document emphasizes the importance of not reserving laparoscopic repairs only for more complex cases in order to overcome the learning curve.