Embed presentation
Downloaded 184 times







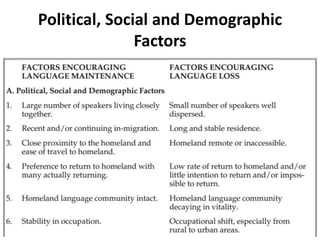





This document discusses language maintenance and shift that can occur when speakers are exposed to a second language. There are three main outcomes: 1) language maintenance, where speakers maintain their mother tongue, 2) language shift, where speakers shift to the new second language as their main or only language, or 3) bilingualism. Typically, a full language shift takes around three generations, though it can be slower or faster depending on factors like the use of a standardized written language or arranged marriages keeping the original language alive. Studies have found language shift can occur through five stages from monolingualism in the minority language to monolingualism in the majority language over multiple generations.











