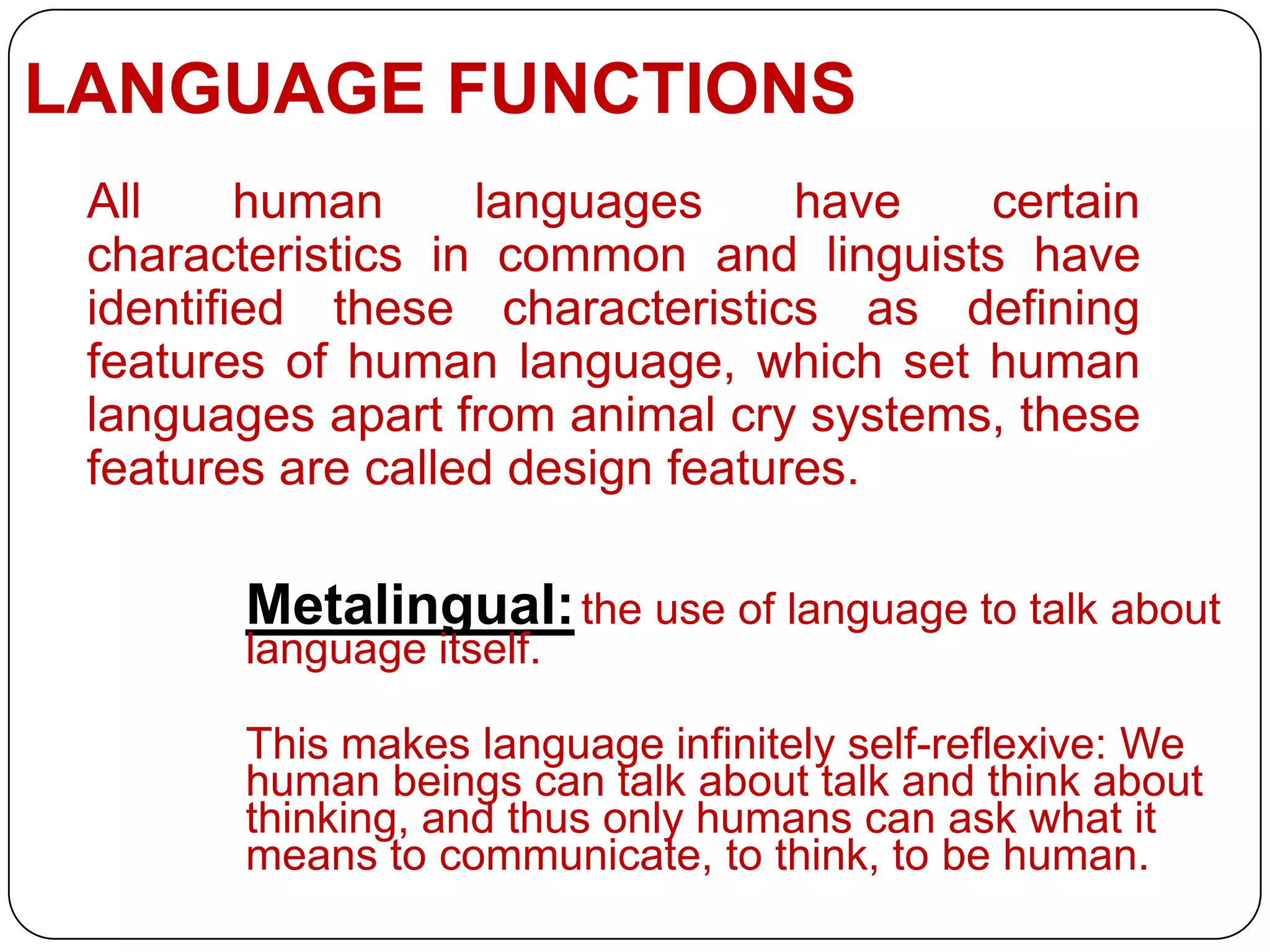
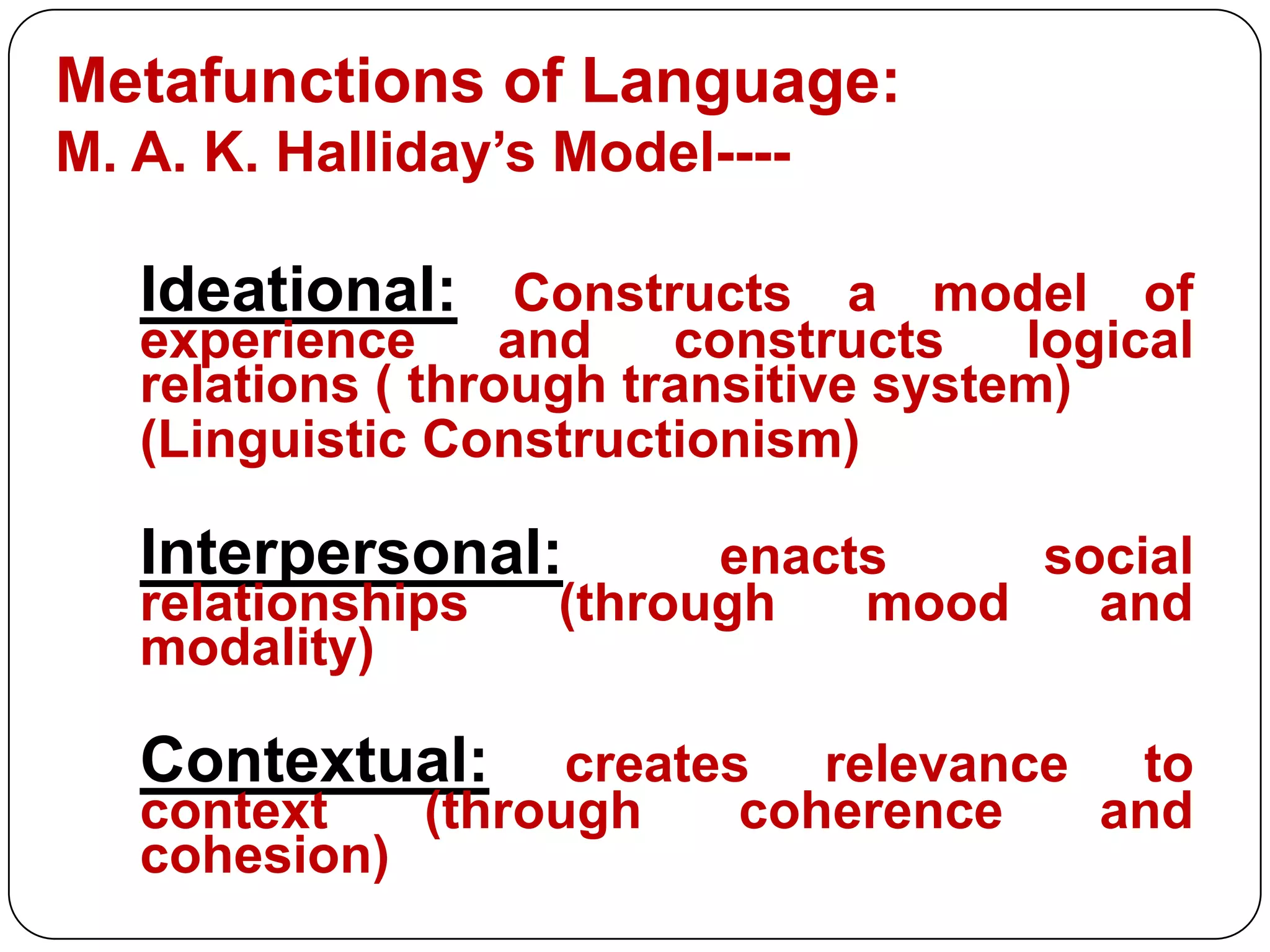
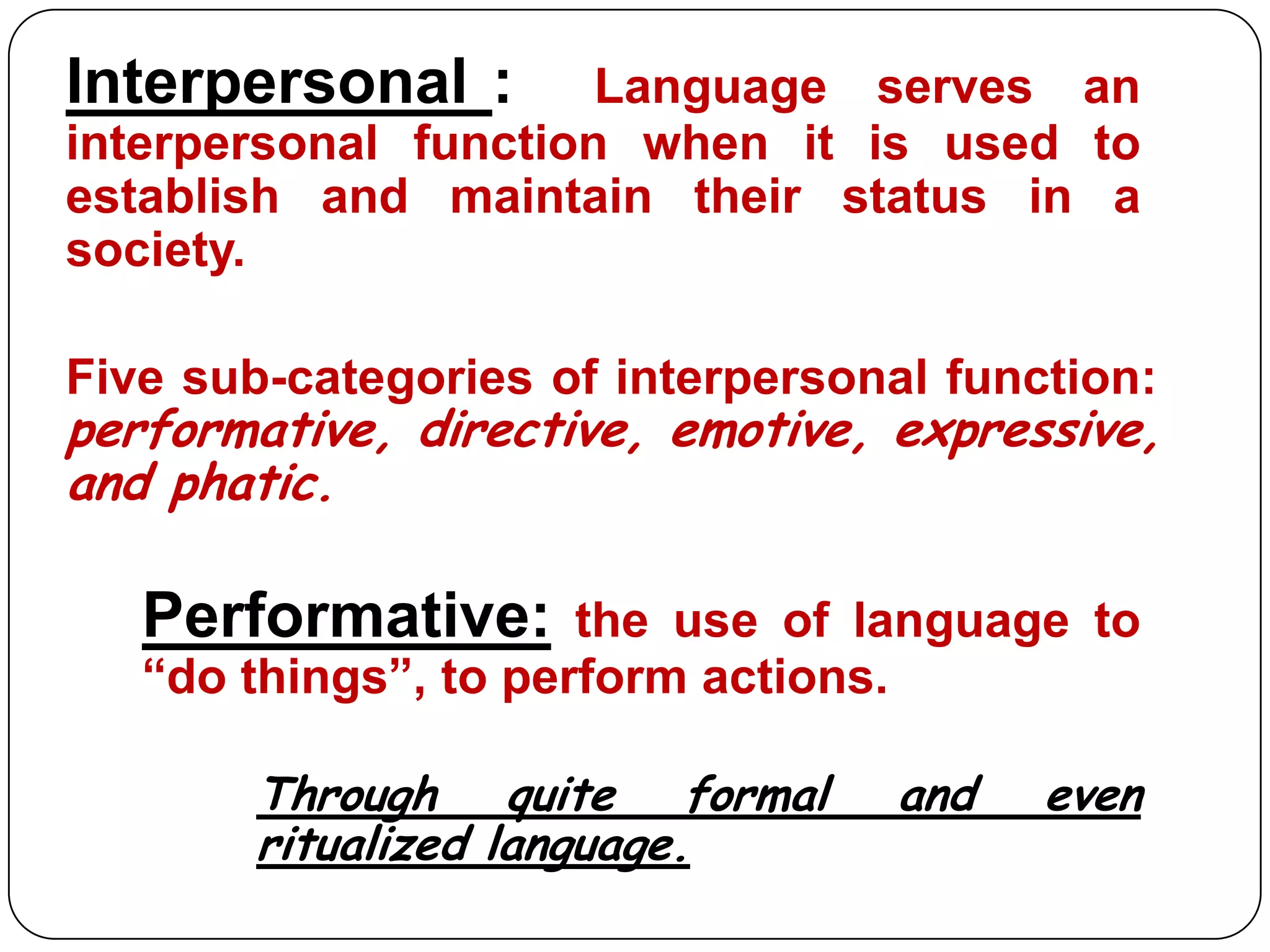
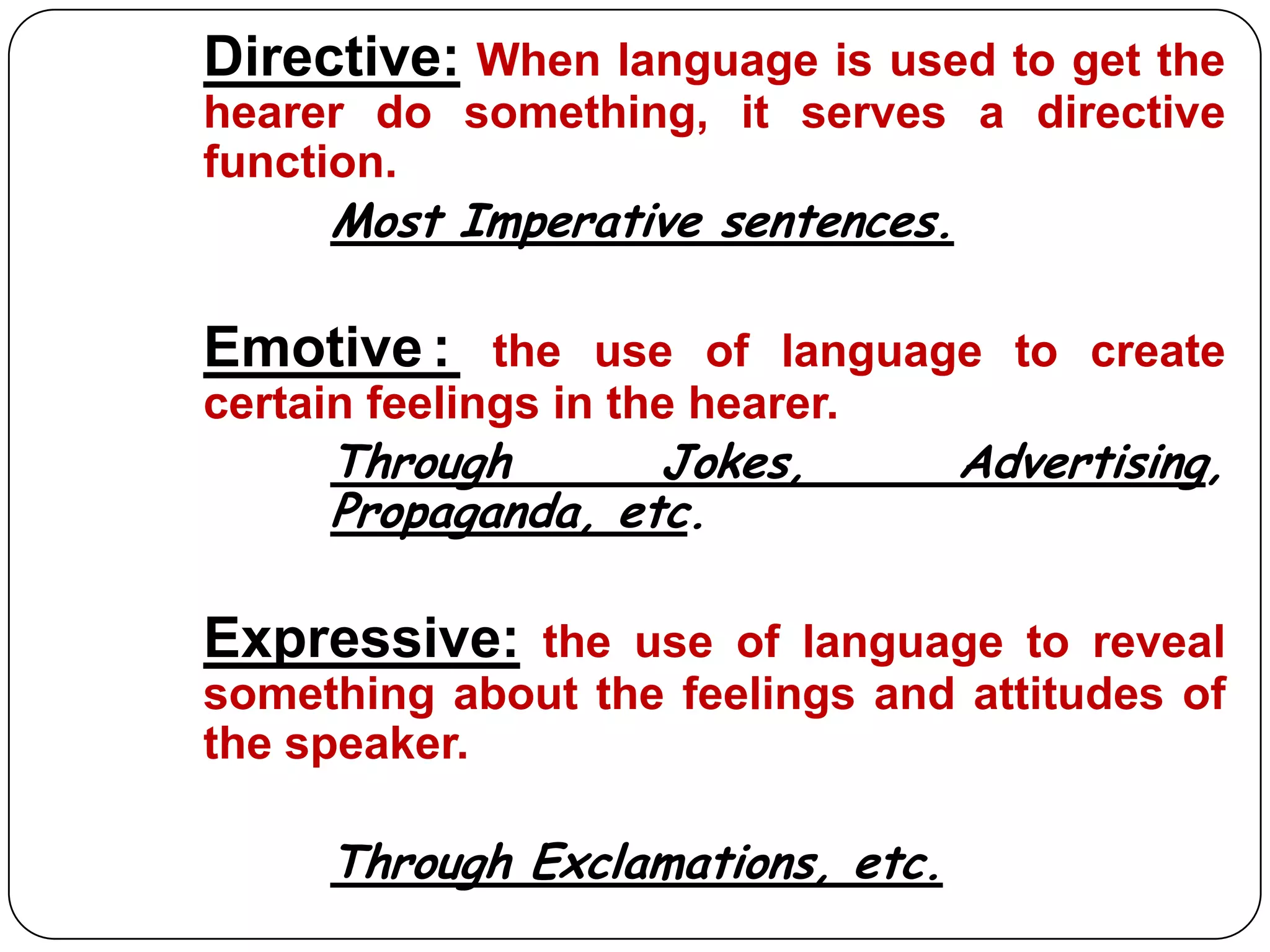
This document discusses language functions and notions. It identifies several key characteristics of human language including that language can be used to talk about language itself (metalinguistic). It also outlines M.A.K. Halliday's model of language which describes three metafunctions: ideational, interpersonal, and contextual. Several common language functions are defined such as informative, interrogative, interpersonal, and recreational. Finally, it lists and describes several common language notions including existential, spatial, temporal, and relational notions.