Embed presentation
Downloaded 74 times






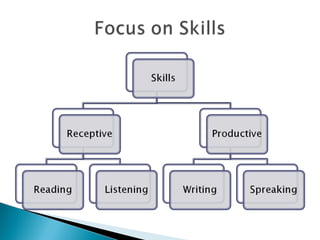




The document discusses the goals of an English lecturer training program, which are to increase awareness of the English language and provide background knowledge to make informed lesson planning choices. It also discusses psychological differences between students, study habits, personality, and motivation as factors in language learning. Key language learning concepts like interlanguage, grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, context, and functions are defined. Productive and receptive language skills and the typical ratio of language to skills practice in lessons are also mentioned.









