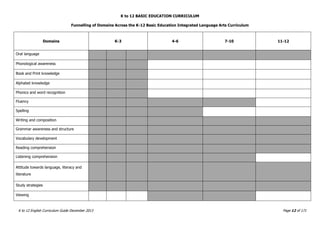
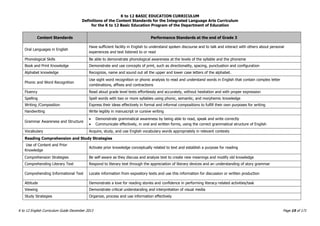
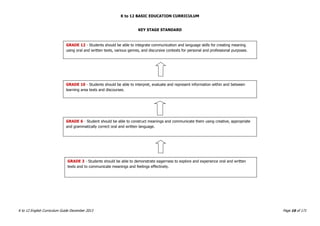
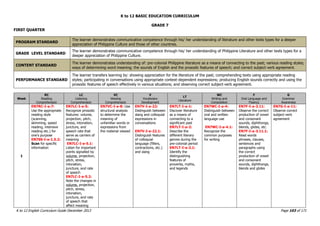
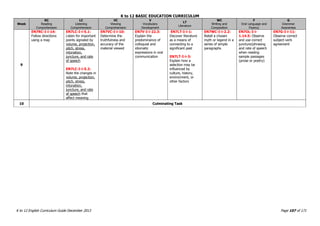
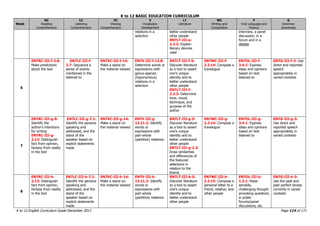
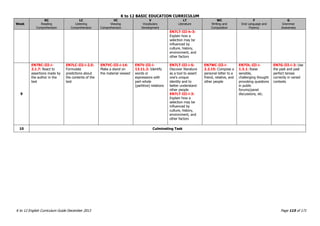
This document provides a summary of the K to 12 English curriculum in the Philippines. It discusses the philosophy, guiding principles, outcomes and conceptual framework of the curriculum. The curriculum aims to develop students' communicative competence and multiliteracy skills. It is designed based on principles such as spiral progression, interaction, integration and contextualization. The curriculum teaches students to understand language, cultures and apply language skills and strategies to interpret and construct meaning. It prepares students for a globalized world through enhancing their critical thinking, literacy and ability to communicate in English.