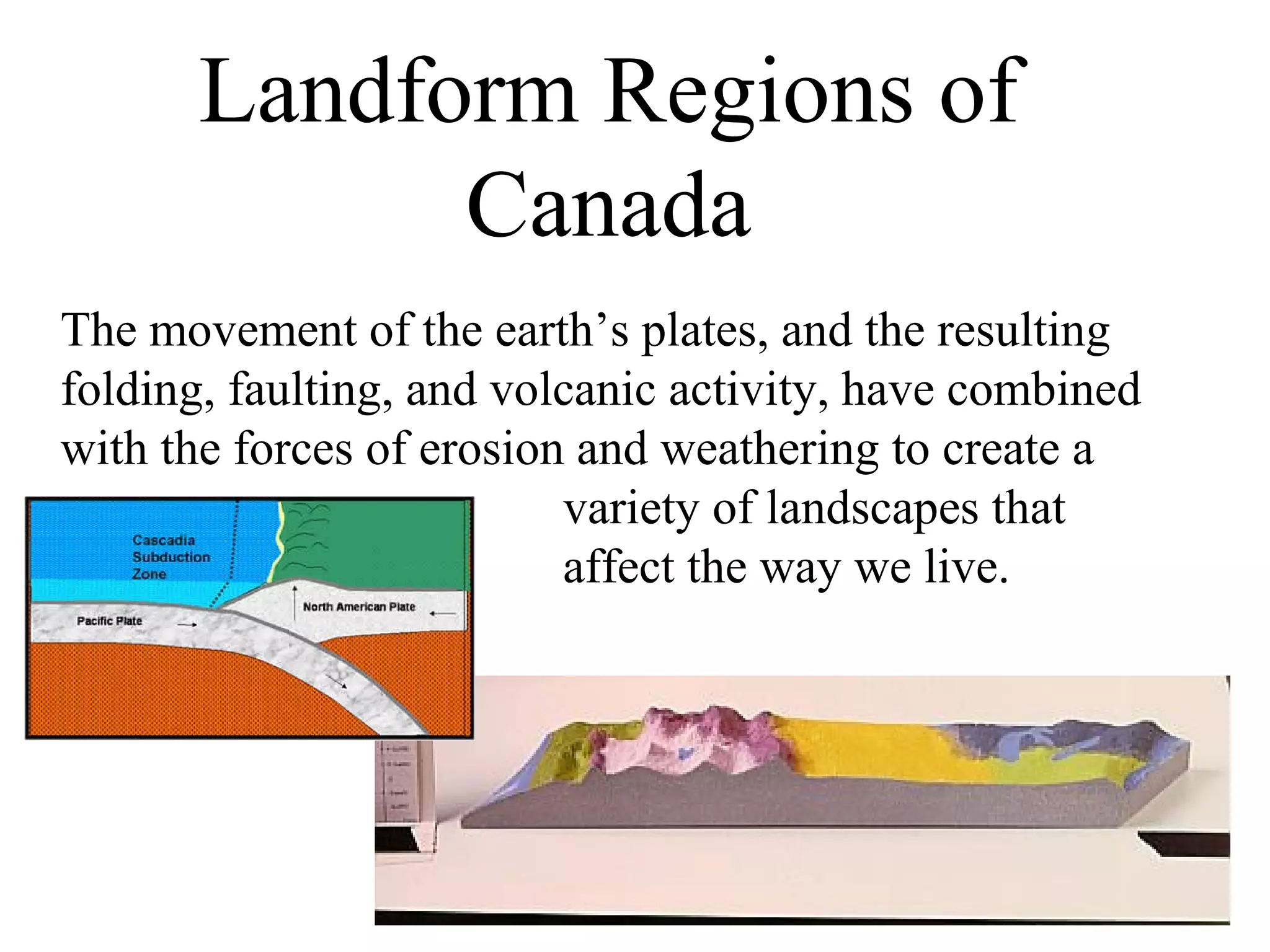
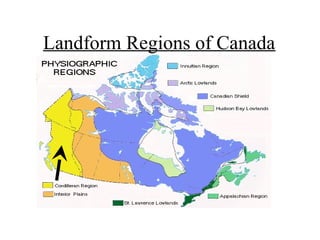
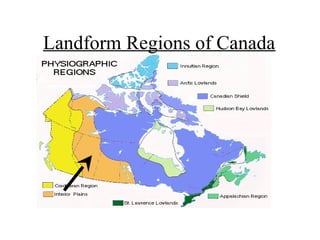
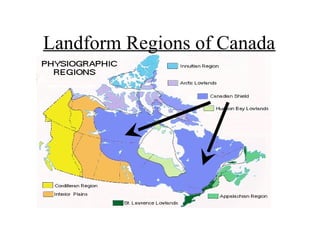
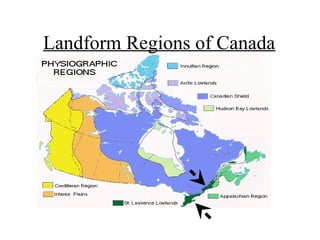
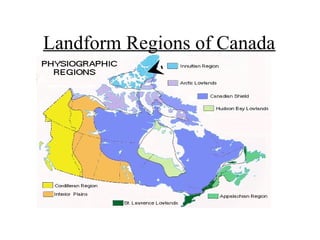
Canada can be divided into 8 distinct landform regions defined by their unique physical features and climates. These regions include the Western Cordillera characterized by high mountains, the Interior Plains known as the "bread basket" for its fertile soil and farming, the Canadian Shield with its lakes and mineral resources, and the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands containing 50% of Canada's population. The other regions are the Appalachian Mountains, Hudson Bay Lowlands, Arctic Lowlands, and Innuitian Mountains. Each region supports different plant and animal life and has varying potential for human settlement and resource extraction.