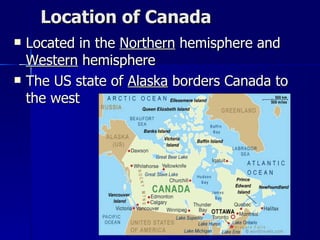
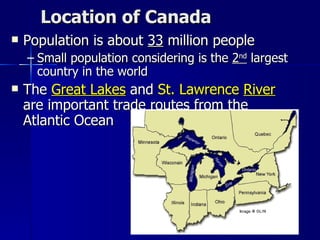
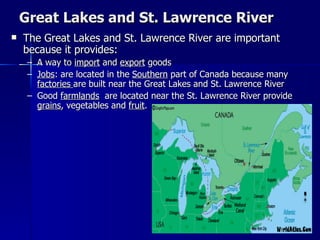
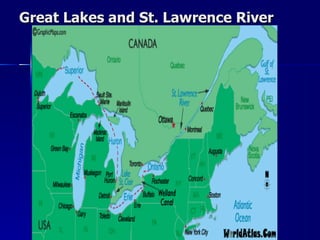
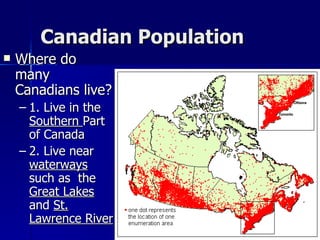
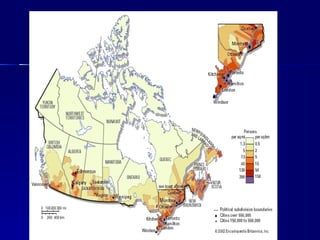
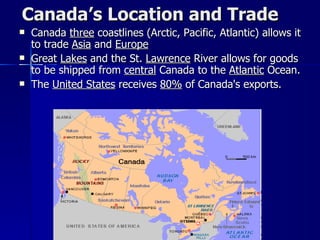
Canada's location provides access to three coastlines and several important waterways like the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence River, which influence where Canadians live and the country's trade. The southern part of Canada has a climate suitable for agriculture and most of the population lives near the Great Lakes or St. Lawrence River. Canada's natural resources like forests, minerals, and hydroelectric power from rivers are major exports, though extracting them has caused environmental issues.