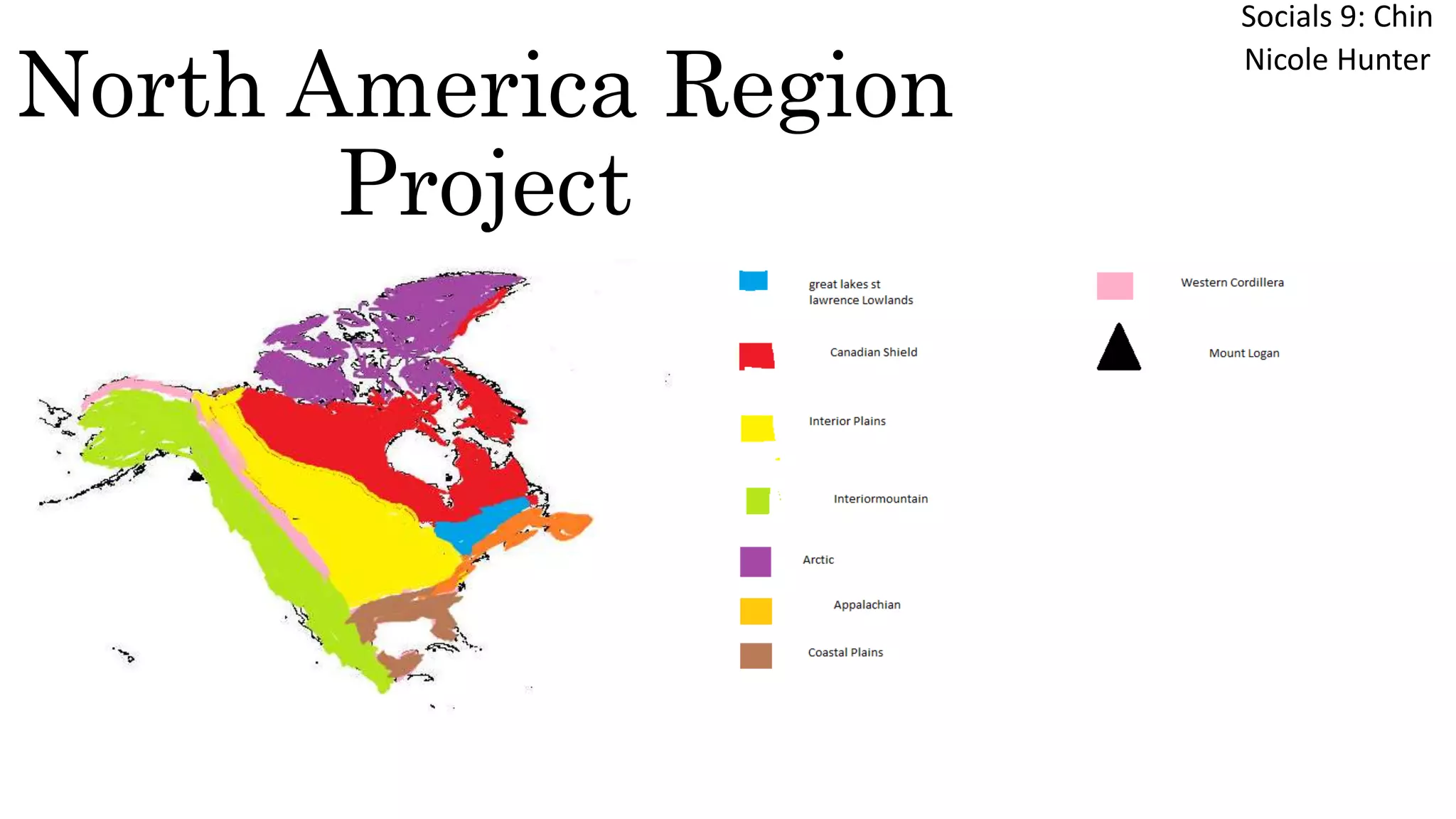
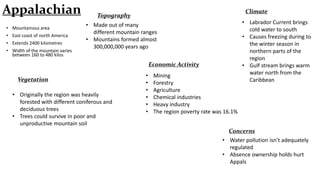
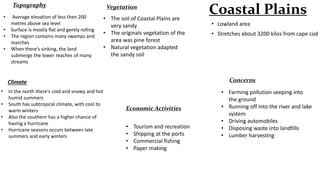
This document provides information on the major geographical regions of North America. It describes the key characteristics of each region such as location, topography, climate, vegetation, economic activities, and environmental concerns. The regions discussed include the Appalachian Mountains, Coastal Plains, Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowland, Interior Plains, Canadian Shield, Western Cordillera, Intermountain Region, Arctic, and Mount Logan. For each area, the summary highlights 2-3 defining features.