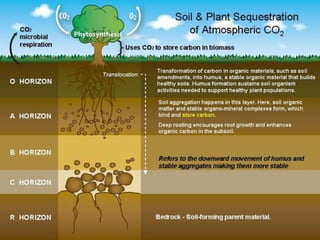
This document discusses land resources and soil types in India. It covers the different types of land under relief features like plains, mountains, and plateaus. The main land uses are agriculture, forests, and wastelands. The document also discusses the major soil types in India like alluvial, black, red and yellow soils. It provides details on the composition and characteristics of different soils. Land degradation and conservation measures are also summarized.