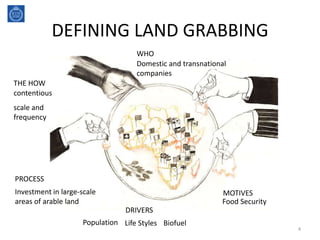
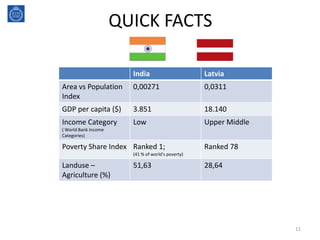
This document discusses land reforms, including guidelines for sustainable land reforms. It defines land grabbing and the problems it causes for smallholders, the landless, and indigenous people. It also examines the need for land reform and provides two approaches to land rights. The document then gives guidelines for sustainable land reform and provides quick facts and insights into land reforms that have occurred in India and Latvia, noting problems in both countries. It concludes by prioritizing the poor and emphasizing participation, awareness, regulation, and legislation in land reform frameworks.