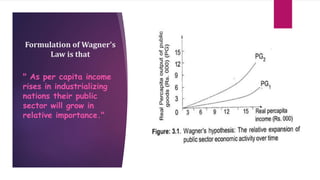
This document summarizes Wagner's hypothesis and the Peacock-Wiseman hypothesis about public expenditure. Wagner hypothesized that industrialization leads to increasing state activity and that public expenditure will rise faster than per capita income. The Peacock-Wiseman hypothesis emphasizes time patterns of spending rather than a theory of growth. It involves displacement effects as social disturbances expand the public sector, inspection effects as revenue lags required spending, and concentration effects as central government activity increases with economic growth. The document also lists criticisms of Wagner's hypothesis and defines intensive and extensive increases in state activity.