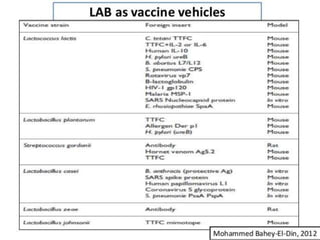
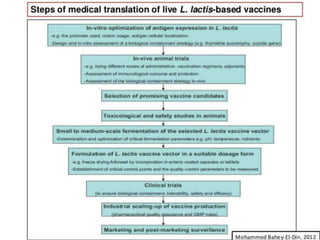
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are a group of beneficial microorganisms utilized in various food products and have potential biomedical applications, particularly as vaccine delivery vehicles. LAB can colonize human cavities and enhance the immune response due to their acid resistance and absence of lipopolysaccharides, minimizing risks associated with traditional vaccines. Current research is focused on developing genetically engineered LAB strains for vaccines against multiple pathogens, while addressing safety and environmental concerns.