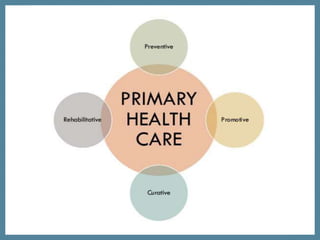
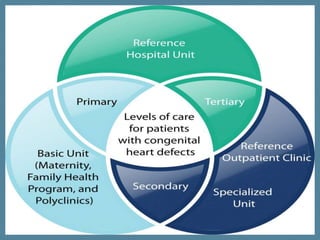
The document discusses the organization and various levels of healthcare, including primary, secondary, and tertiary care, highlighting their roles in maintaining health globally. It emphasizes that healthcare systems are influenced by social, economic conditions, and health policies, with a focus on the collaboration of healthcare providers in delivering patient care. The World Health Organization outlines requirements for effective healthcare systems, including well-trained professionals and the need for integration of health services based on patient needs.