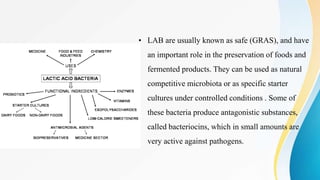
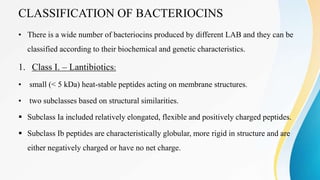
The document discusses the role of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) as biopreservatives in food, highlighting their antimicrobial properties and the production of bacteriocins, which help inhibit pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms. LAB are considered safe and play a significant role in extending food shelf life while also improving flavor and texture. Additionally, the document describes the classification, isolation, purification, and mode of action of various bacteriocins produced by LAB and their potential applications in food safety.