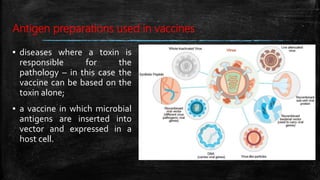
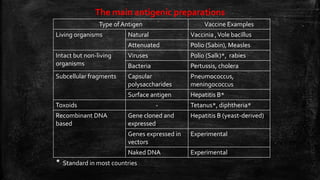
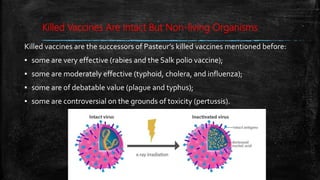
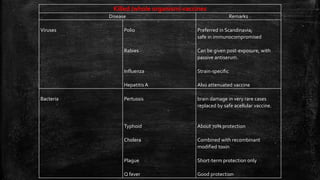
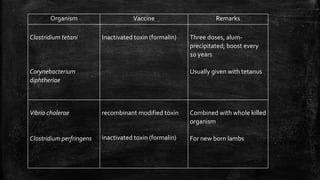
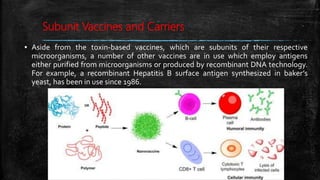
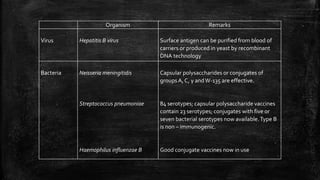
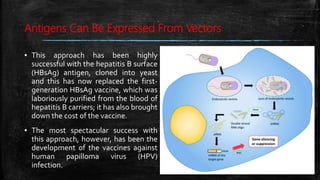
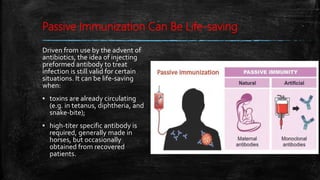
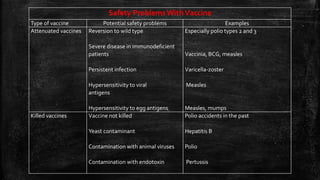
Vaccination is a successful application of immunological principles, utilizing immunological memory to protect against infectious diseases. Various types of vaccines include live attenuated, killed organisms, and toxins, each with specific mechanisms and examples of efficacy. The vaccine's effectiveness is dependent on the right immune response, stability, and appropriate use of adjuvants to enhance immunogenicity.