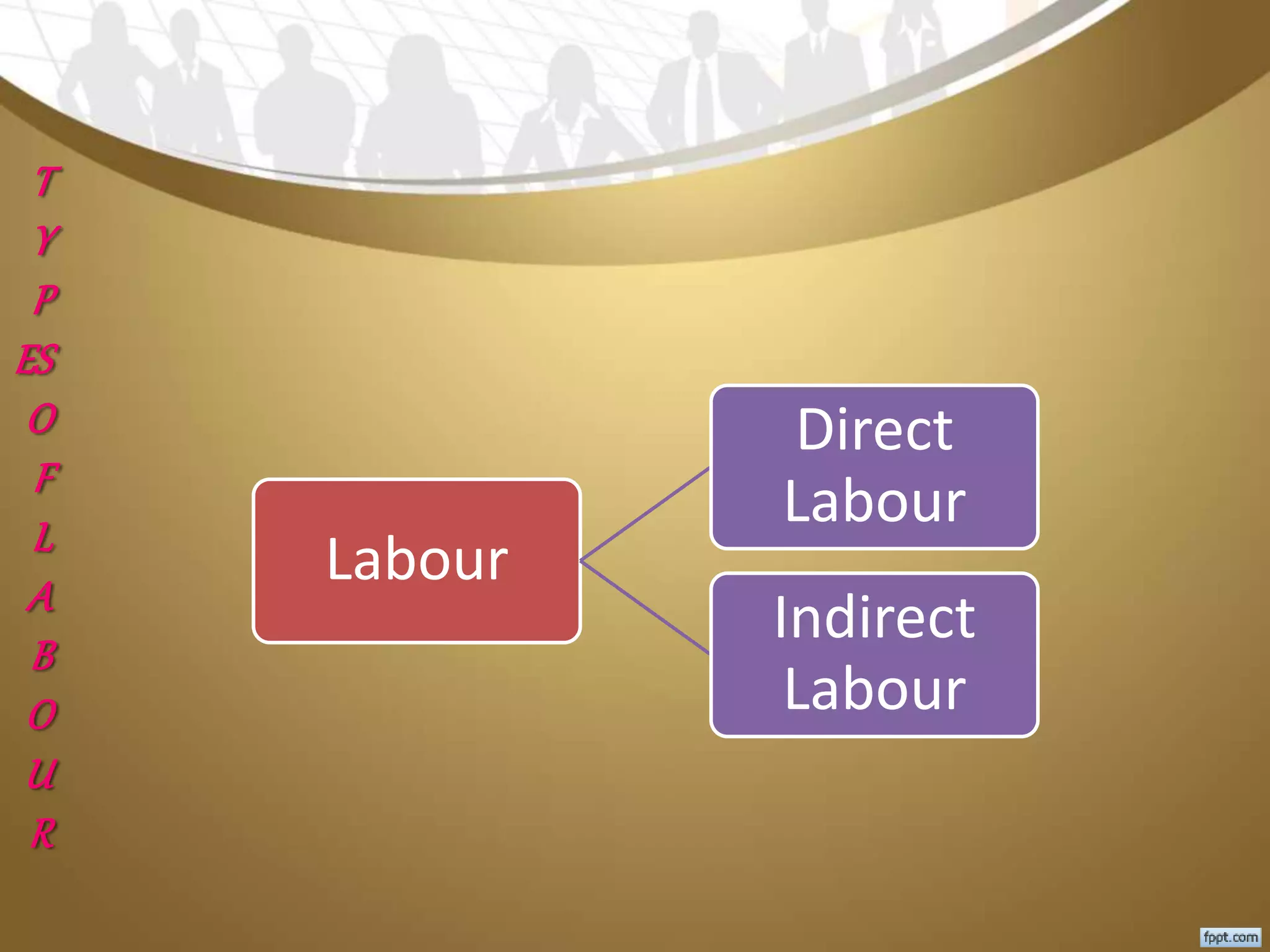
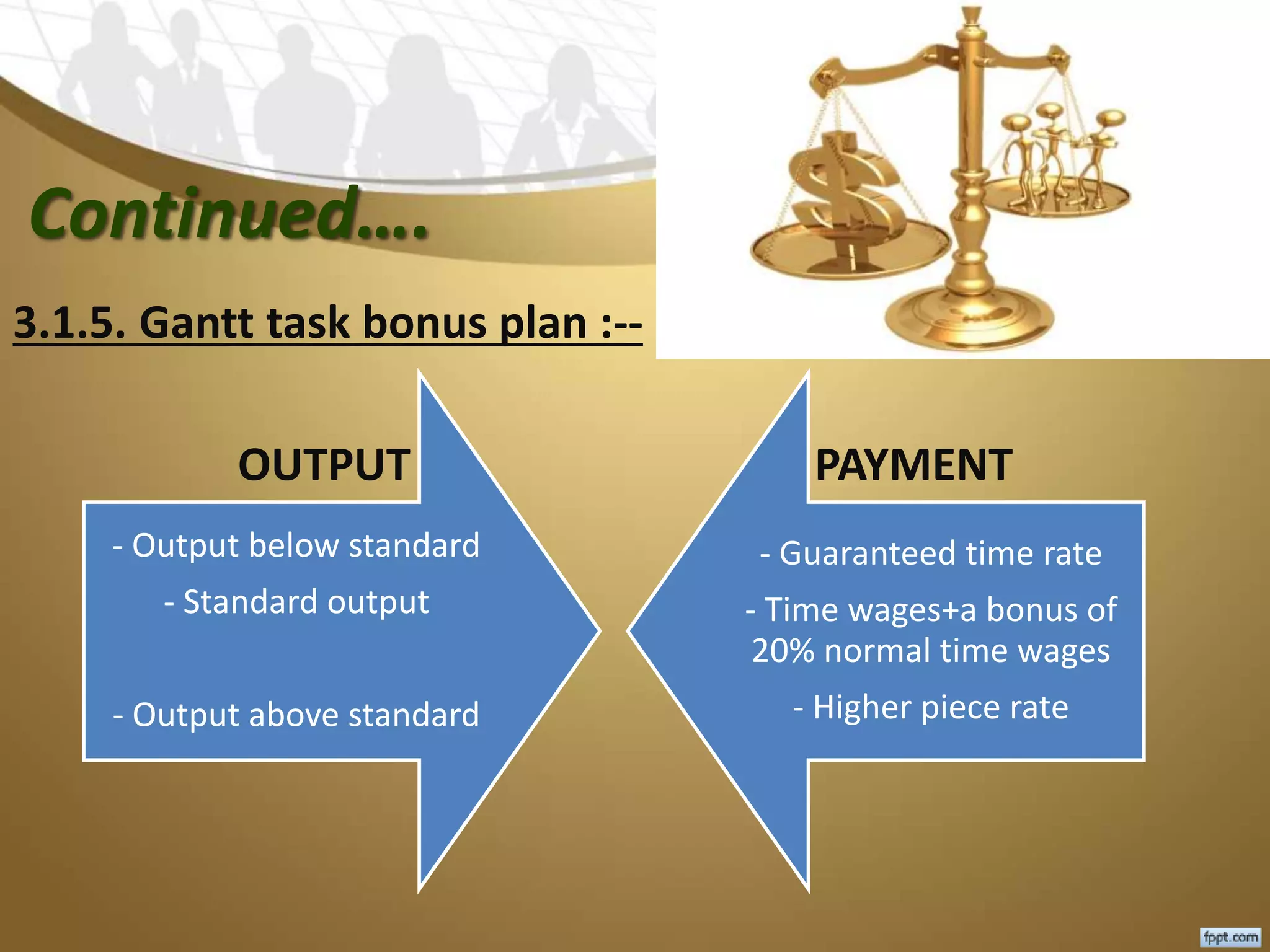
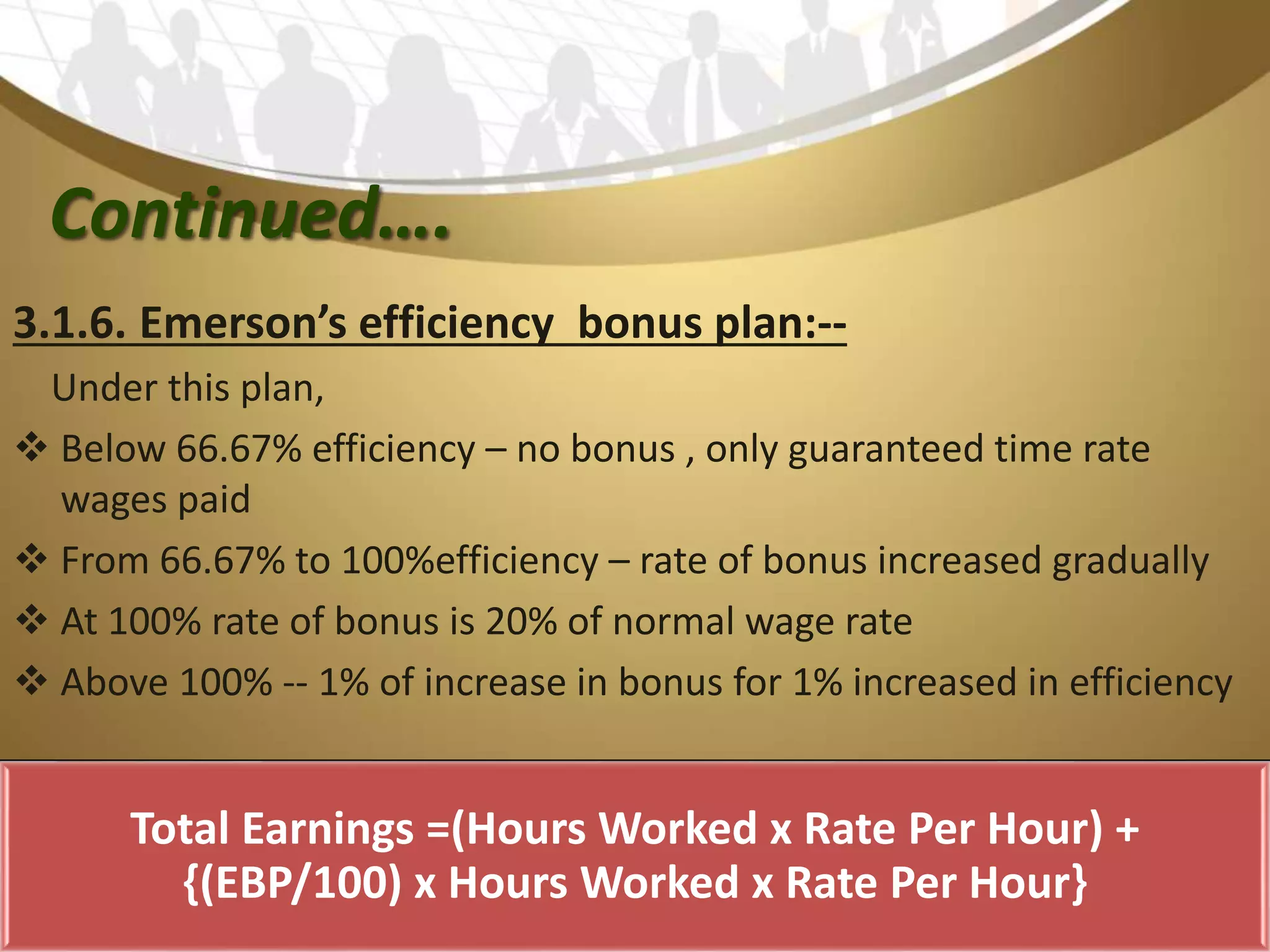
This document discusses labour cost control and labour cost management. It defines direct and indirect labour and explains different types of wages payment systems like time wage, piece wage and incentive wage systems. It also discusses factors for labour cost control like labour records, control of production methods and labour cost analysis. Methods to measure and control labour turnover are provided. The roles of different departments in labour cost management are outlined.