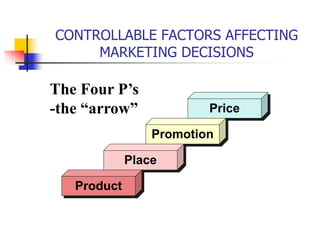
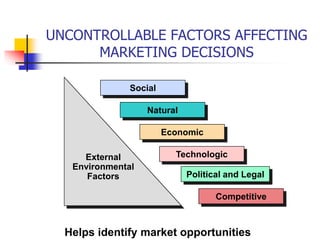
The document defines marketing as identifying and satisfying customer needs profitably. It discusses the evolution of marketing from a production orientation to a sales orientation to a modern marketing orientation focused on customer wants. Key aspects of marketing include identifying parties that can exchange value, communication between parties, and parties having the freedom to reject exchanges. The document also outlines external factors like the political, economic, social and technological environment that influence marketing decisions.