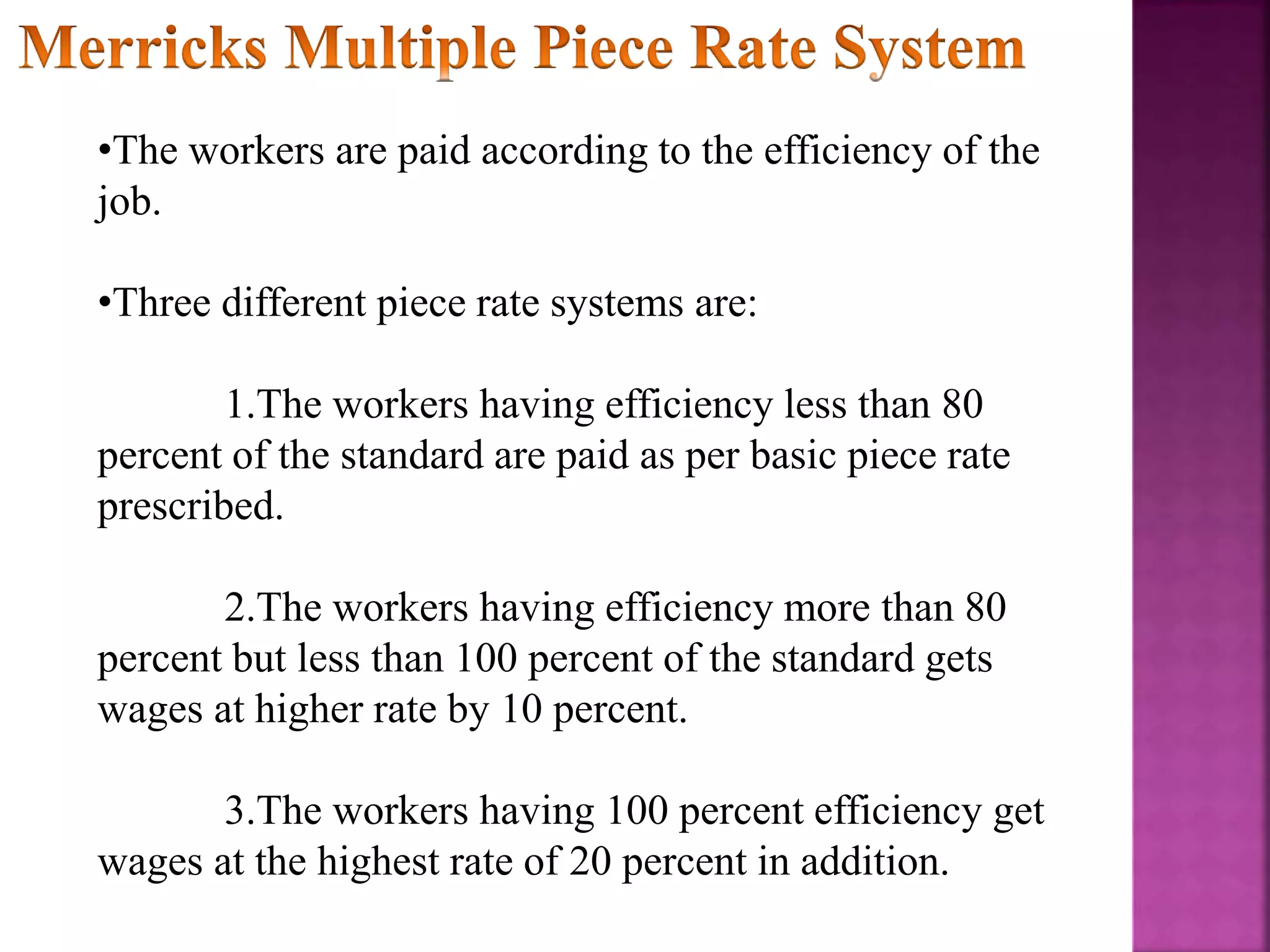
This document discusses various types of incentive plans used to motivate employees, including time-based plans like Halsey and Rowan plans, efficiency-based plans like Emerson plan, and sales-based commission plans. It provides details on how each plan calculates incentives and bonuses, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Key incentive plans covered are Halsey, Rowan, Emerson, Bedeaux, and various plans for white-collar workers involving bonuses, commissions, and profit sharing.