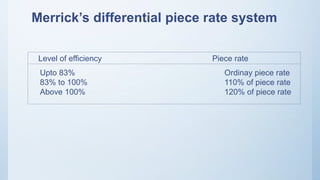
This document discusses various aspects of labour cost management including direct and indirect labour, labour turnover, time keeping, overtime, payroll, idle time, and remuneration. It describes different methods for tracking time and attendance as well as calculating wages. Various incentive plans are outlined, including Halsey, Rowan, and Merrick's differential piece rate systems. The document also examines causes and reduction of labour turnover through suitable wage policies and welfare measures.























![Halsey premiun plan & Halsey Weird
plan.
• Paid at a rate per hour.
• If worker takes standard time or more time he is paid for the actual time taken at
the time rate.
• If worker takes less than the standard time , then he is paid a bonus equal to 50%
of the time saved.
Eg:- std time = 50 hrs
Wage rate per hour = Rs 3
actual time taken =42 hrs
time saved = 50 -42 =8 hrs
Earnings = 3 X 42 + 50% 0f [8 hrs X 3]
=126+12 =Rs138](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labourcost-140827041117-phpapp01/85/Labour-cost-24-320.jpg)