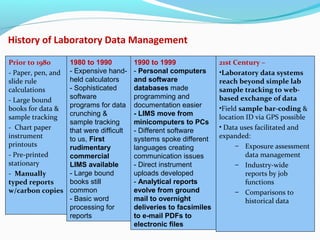
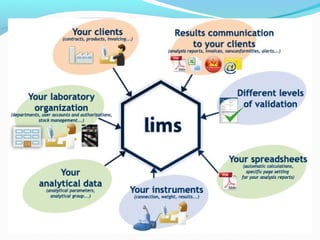
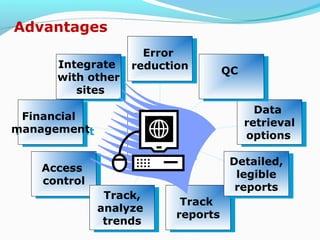
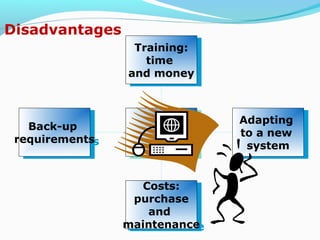
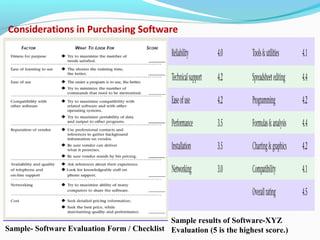
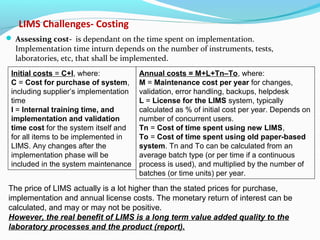
The document discusses the evolution and current requirements of Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), highlighting the transition from traditional methods to modern web-based solutions. It outlines the features necessary for a clinical LIMS to effectively manage patient information, regulatory compliance, and data integrity while addressing challenges like training, costs, and implementation risks. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of selecting the right system tailored to the unique needs of a laboratory to ensure efficient data management and improved workflow.