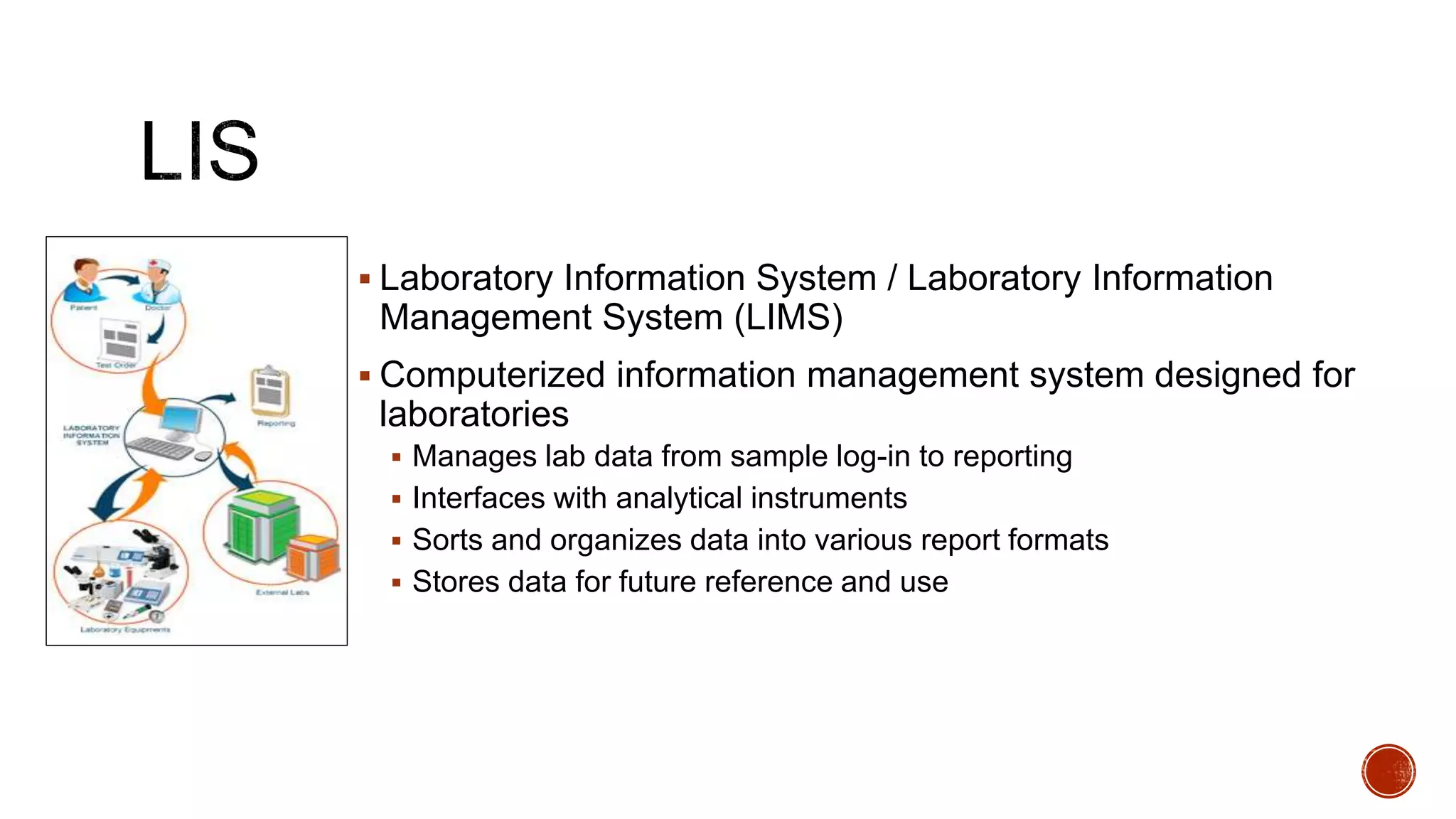
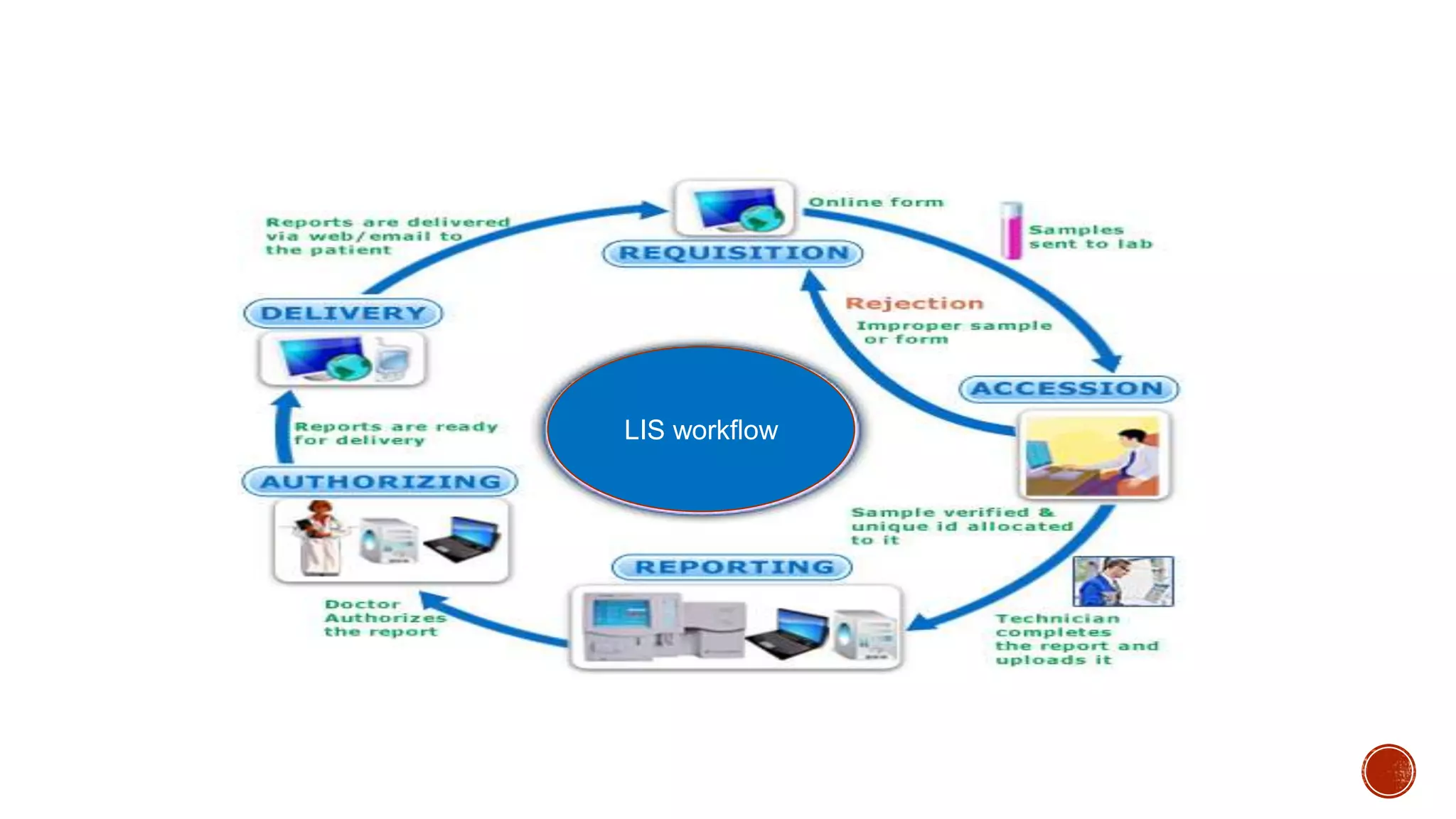
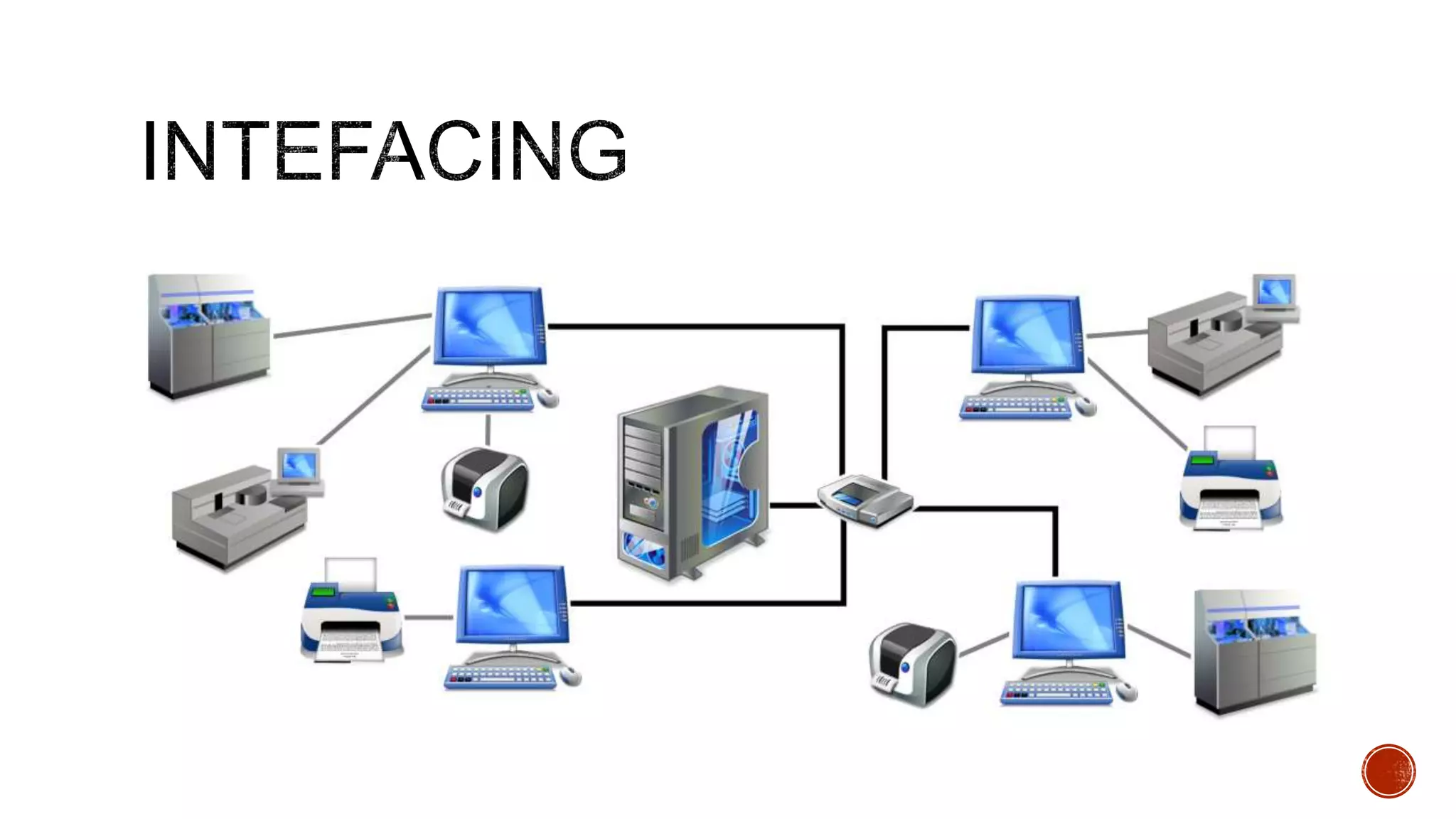
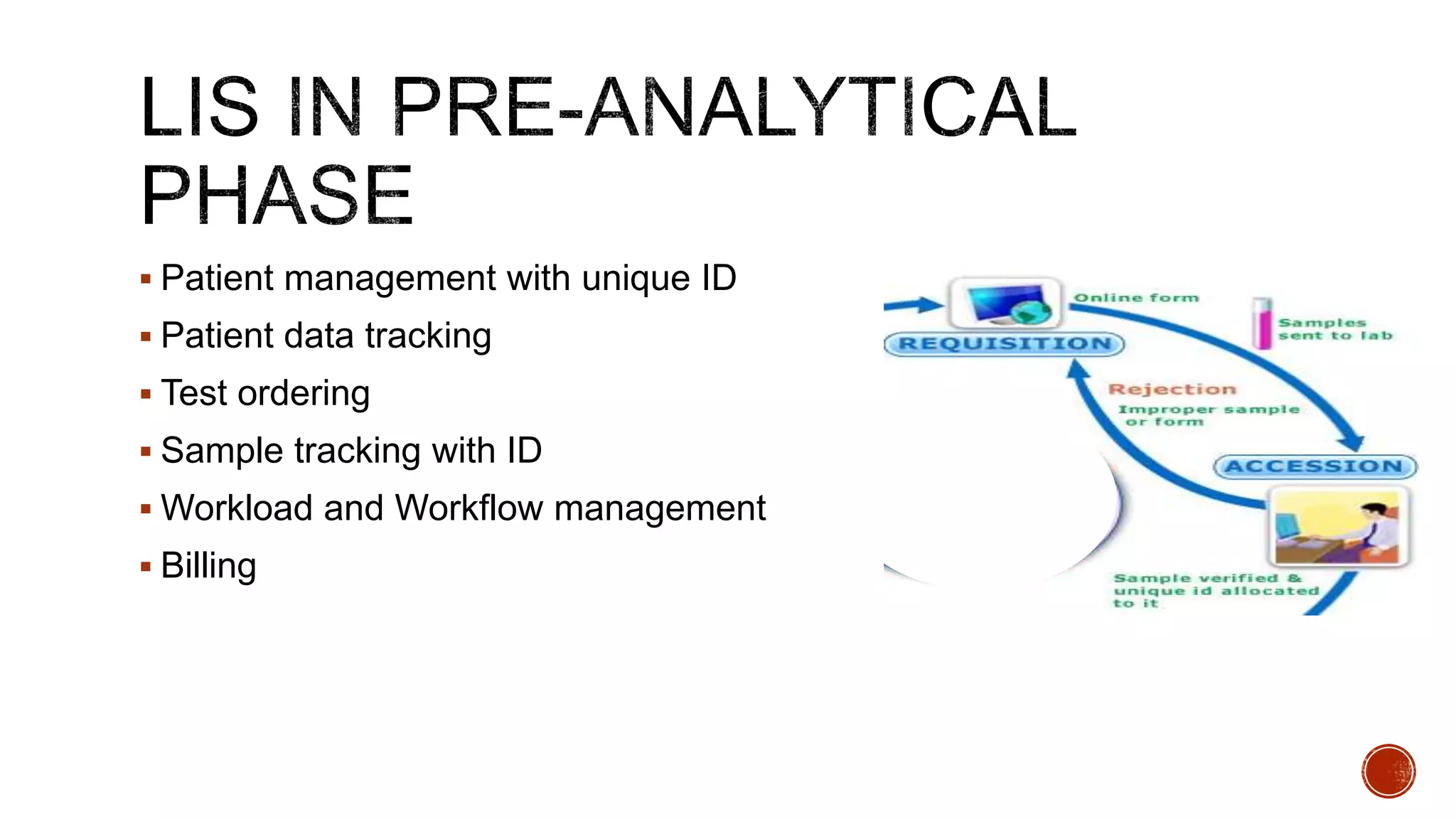
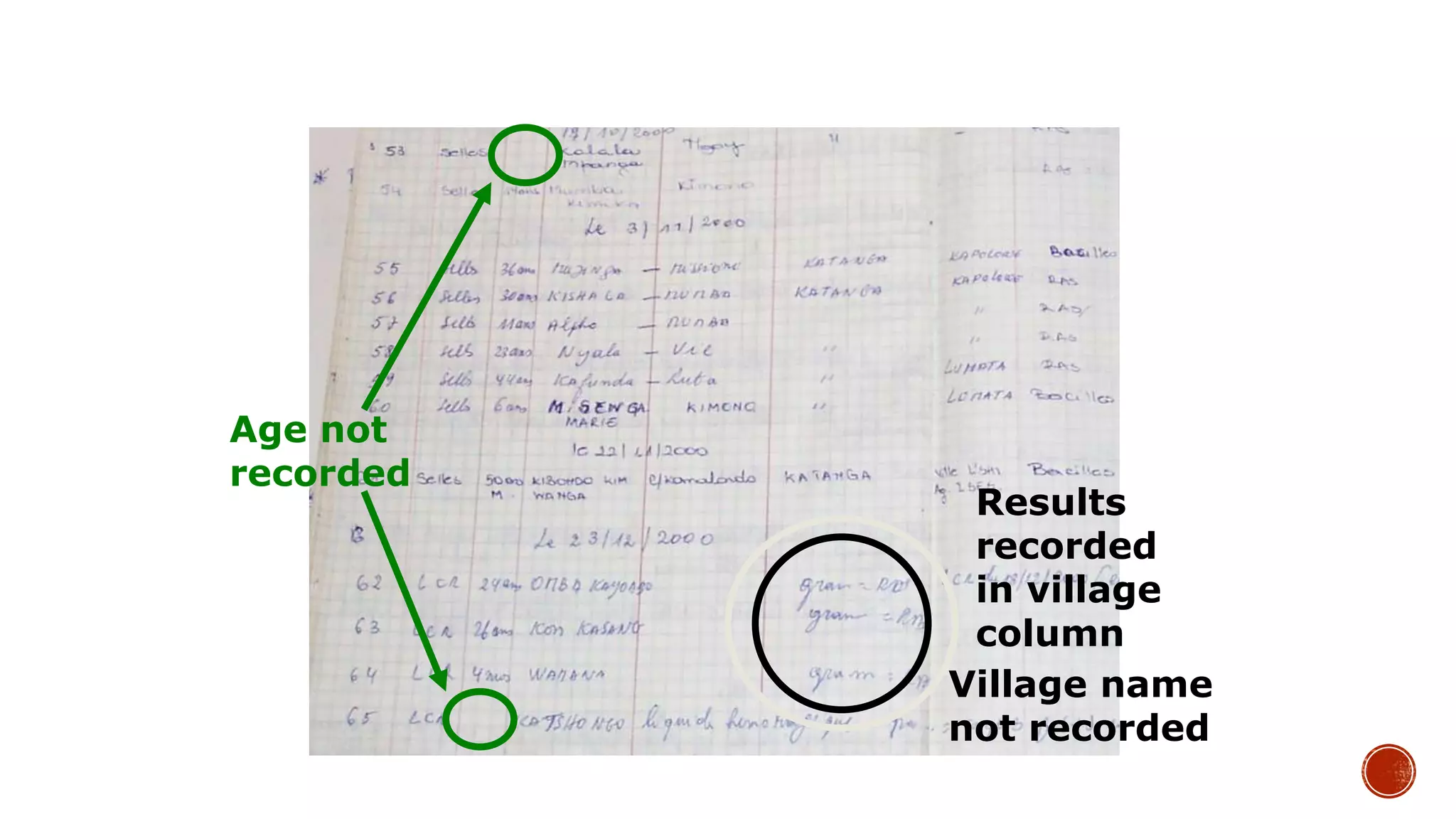
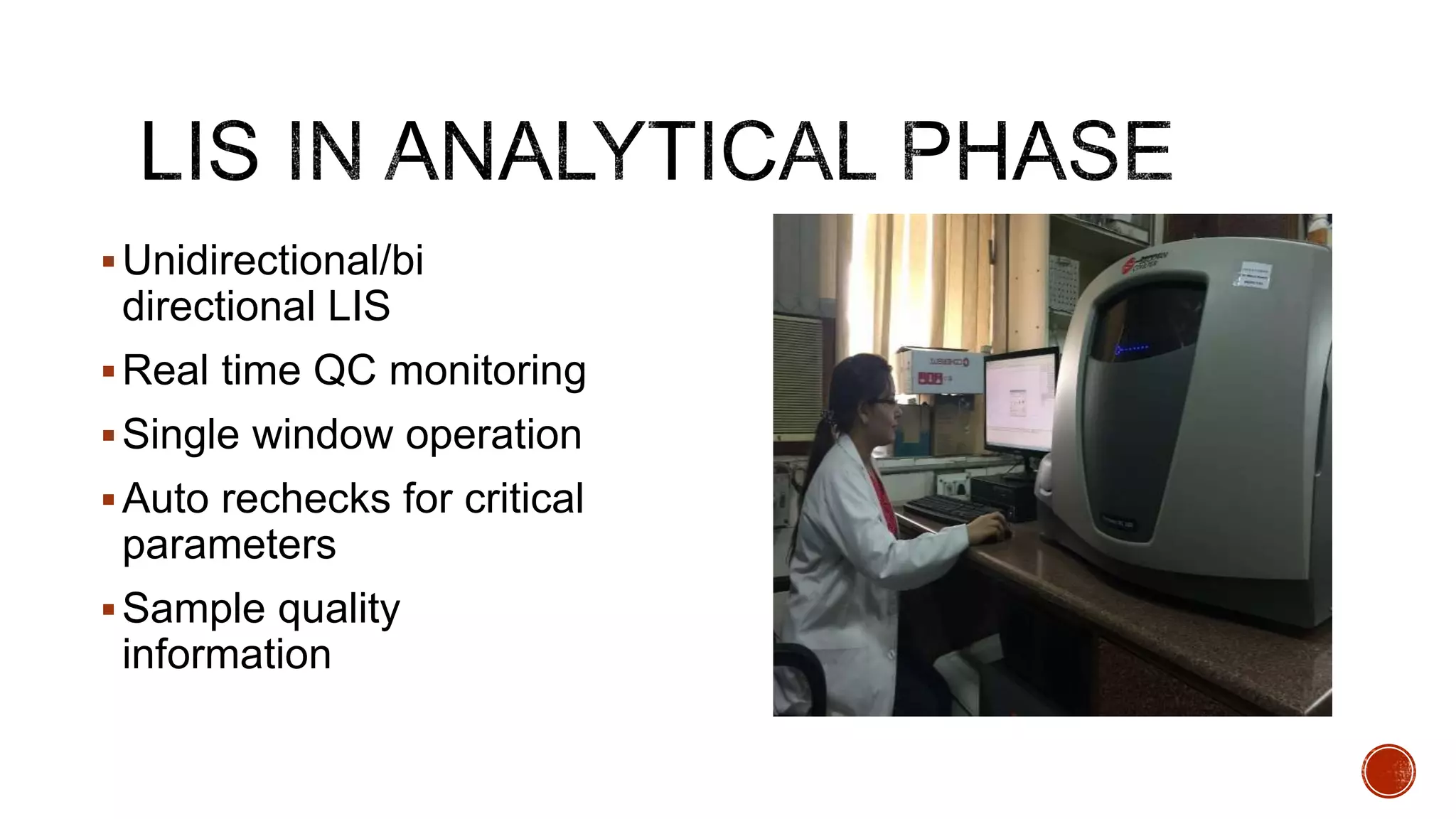
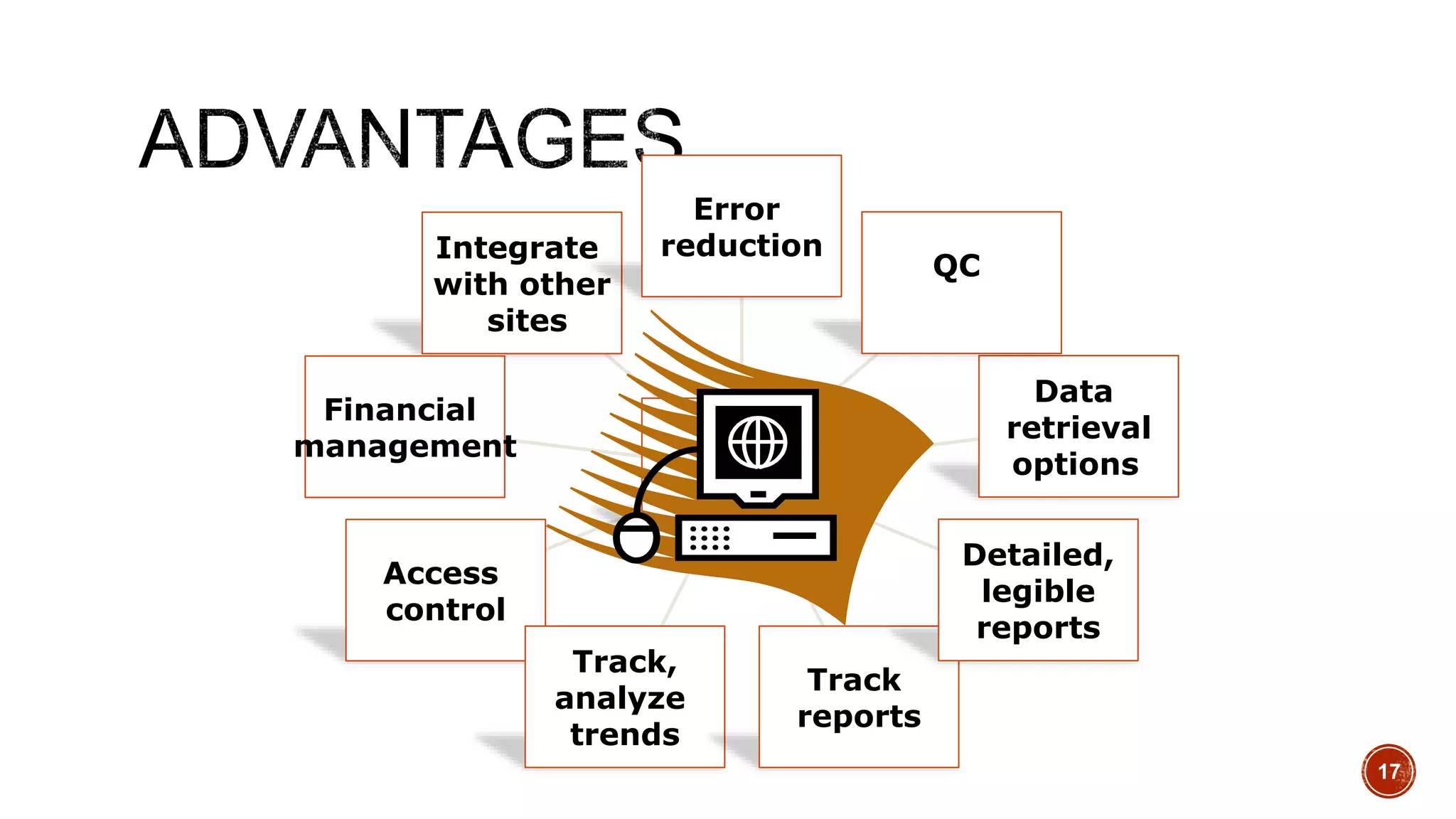
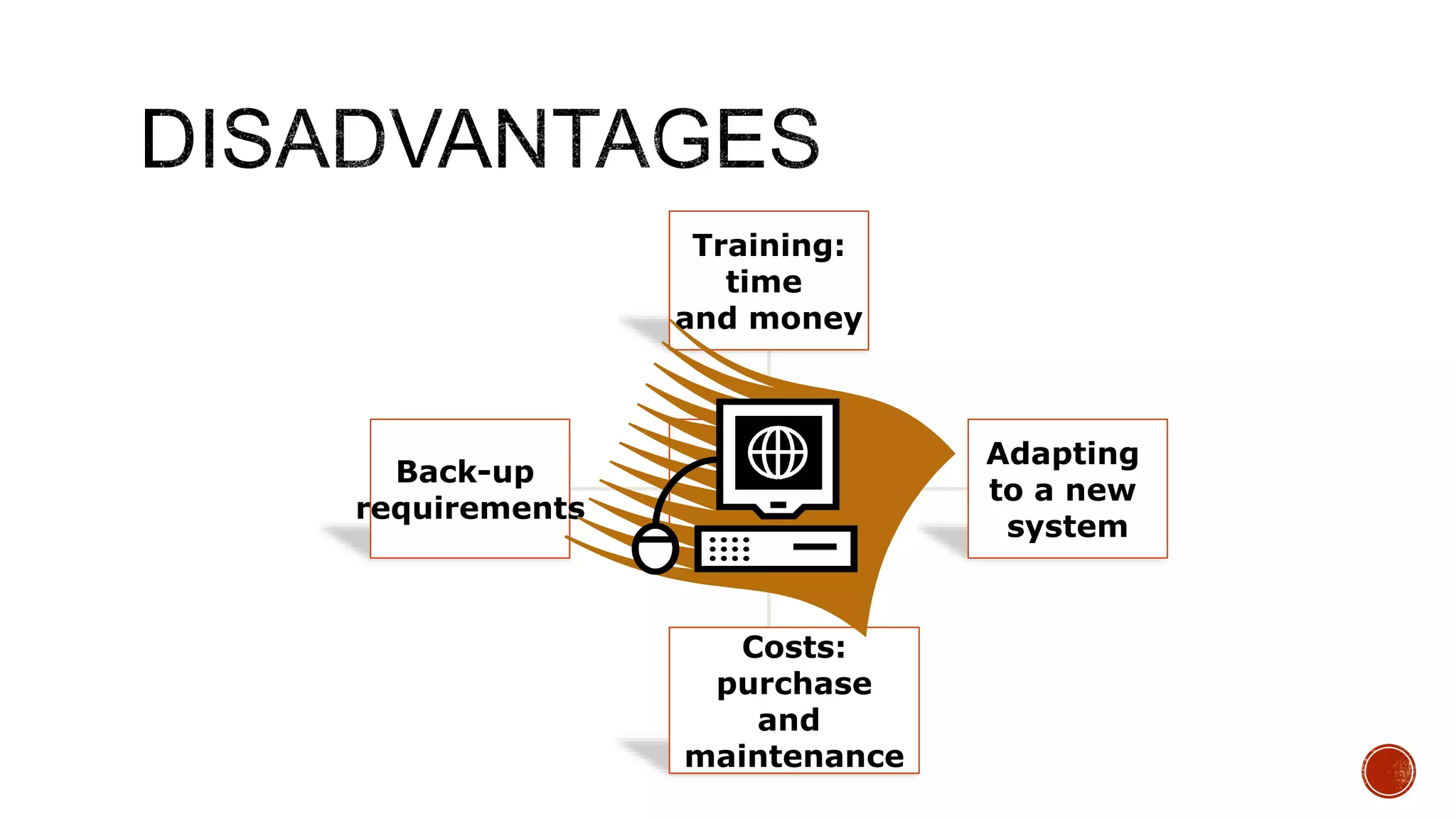
The document discusses the transition from paper-based to electronic laboratory reporting using a Laboratory Information System/Laboratory Information Management System (LIS/LIMS). It describes how LIS/LIMS interfaces with instruments, sorts data into reports, and stores data for future use. The document outlines the benefits of LIS/LIMS, including fewer errors, faster processing, multi-level checks, and easier access to reports. Finally, it discusses important considerations for LIS/LIMS implementation and validation.